ISC (Commerce)
ISC (Science)
Academic Year: 2023-2024
Date & Time: 18th March 2024, 2:00 pm
Duration: 3h
Advertisements
- Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper.
- They must NOT start writing during this time.
- Answer all questions in Part I (compulsory) and six questions from Part-II, choosing two questions from Section-A, two from Section-B and two from Section-C.
- All working, including rough work, should be done on the same sheet as the rest of the answer.
- The intended marks for questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ]
According to the Principle of duality, the Boolean equation
(A+ B') • (A+ 1) =A+ B' will be equivalent to ______.
(A' + B) • (A'+ 1) = A' + B
(A • B') +(A • 0) = A • B'
(A' • B) +(A' • 1) =A' • B
(A' • B) +(A' • 0) =A' • B
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
When a sequence of OR, NOT, NOR are connected in series, the logic gate obtained is ______.
AND
NOT
OR
XOR
Chapter: [0.02] Computer Hardware
Idempotence Law states that ______.
X + X = X
X + X' = 0
X + X = 1
X + X' = X
Chapter: [0.02] Computer Hardware
Assertion: For proposition ∼A=> B, its contrapositive is B =>∼A
Reason: Contrapositive is the converse of inverse for any proposition.
Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for the Assertion.
Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for the Assertion.
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
The complement of the Boolean expression (P' • Q) (R • S') is ______.
(P' + Q) • (R' + S)
(P + Q') • (R' + S)
(P' + Q) • (R + S')
(P + Q') • (R + S')
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Assertion: Recursive data structure follows the LIFO principle.
Reason: Execution of recursive code follows the concepts of data structure Queue.
Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation for the Assertion.
Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation for the Assertion.
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Chapter: [0.11] Recursion
State any one use of interfaces in Java.
Chapter: [0.1] Arrays, Strings
Write the cardinal form of the maxterm X + Y' + Z.
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Write the canonical SOP expression for F (A, B) = A <=> B.
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
State any one difference between instance variable and class variable.
Chapter: [0.05] Objects
Advertisements
Convert the following infix notation to postfix form.
(P + Q * R - S)/T * U
Chapter: [0.13] Data Structures
An array ARR [ -5 .....15, 10.....20] stores elements in Row Major Wise with each element requiring 2 bytes of storage. Find the address of ARR [10] [15] when the base address is 2500.
Chapter: [0.1] Arrays, Strings
The following function is a part of some class:
int jolly(int[] x, int n, int m)
{
if (n<0)
return m;
else if(n<x.length)
m=(x[n]>m)?x[n]:m;
return jolly(x, --n, m);
}
- What will be the output of jolly() when the value of x[ ]={6,3,4,7,1}, n=4 and m=0?
- What function does jolly() perform, apart from recursion?
Chapter: [0.11] Recursion
The following function is a part of some class which is used to find the smallest digit present in a number. There are some places in the code marked by ?1?, ?2?, ?3? which must be replaced by an expression/a statement so that the function works correctly.
int small_dig(int n)
{ int min=?1?;
while(n!=0)
{
int q=n/10;
int r=?2?*10;
min=r>min ? ?3? : r;
n=q;
}
return min;
}
- What is the expression or statement at ?1?
- What is the expression or statement at ?2?
- What is the expression or statement at ?3?
Chapter: [0.08] Statements, Scope
To be recruited as the Principal in a renowned College, a candidate must satisfy any one of the following criteria:
- The candidate must be a Postgraduate and should either possess a B.Ed. degree or a teaching experience of more than 15 years?
OR - The candidate must be an employee of the same college with a teaching experience of more than 15 years.
OR - The candidate must be a Postgraduate but not an employee of the same college and should have a teaching experience of more than 15 years.
The inputs are:
| INPUTS | |
| P | Candidate is a Postgraduate |
| S | Candidate is an employee of the same College |
| E | Candidate has a teaching experience of more than 15 years |
| B | Candidate possesses a B.Ed. degree |
(In all the above cases, 1 indicates yes and 0 indicates no)
Output: X - Denotes eligibility of a candidate [1 indicates eligibility and 0 indicates ineligibility in all cases]
Draw the truth table for the inputs and outputs given above and write the SOP expression for X (P, S, E, B).
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Reduce the above expression X (P, S, E, B) by tiifig 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e., octal, quads and pairs).
Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Reduce the Boolean function F (A,B,C,D) = π (0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14) by using 4-variable Karnaugh map, showing the various groups (i.e., octal, quads and pairs).
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Draw the logic gate diagram for the reduced expression. Assume that the variables and their complements are available as inputs.
Chapter: [0.02] Computer Hardware
Verify if the following proposition is a Tautology, Contradiction or Contingency using a truth table.
((A=>B)∧(B=>C))=>(A=>C)
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Advertisements
Find the complement of the following expression and reduce it by using Boolean laws.
P•( 13 ± Q)•Q•(Q+R')
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
How is a decoder different from a multiplexer?
Chapter: [0.01] Boolean Algebra
Draw the logic circuit for 3:8 decoder (Octal decoder). Which multiplexer can be derived from the Octal decoder?
Chapter: [0.02] Computer Hardware
Draw the logic gate diagram for 2-input OR gate using NAND gates only. Show the expression at each Step.
Chapter: [0.02] Computer Hardware
Write the canonical form of the cardinal terms, m3 and M5 for F (A, B, C, D).
Chapter: [0.04] Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
Design a class DeciHex to accept a positive integer in decimal number system from the user and display its hexadecimal equivalent.
Example 1:
Decimal number= 25
Hexadecimal equivalent= 19
Example 2:
Decimal number =28
Hexadecimal equivalent = 1C
Some of the members of the class are given below.
| Class name | DeciHex |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| num | stores the positive integer |
| hexa | string to store the hexadecimal equivalent of num |
| Methods / Member functions: | |
| DeciHex() | constructor to initialise the data members with legal initial values |
| void getNum() | to accept a positive integer |
| void convert(int n) | to find the hexadecimal equivalent of the formal parameter 'n' using the recursive technique |
| void display() | to display the decimal number and its hexadecimal equivalent by invoking the function convert() |
Specify the class DeciHex giving details of the constructor( ), void getNum( ), void convert(int) and void display(). Define a main() function to create an object and call all the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Chapter: [0.11] Recursion
A class Ins Sort contains an array of integers which sorts the elements in a particular order.
Some of the members of the class are given below.
| Class name | InsSort |
| arr[ ] | stores the array elements |
| size | stores the number of elements in the array |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| InsSort(int s) | constructor to initialise size= s |
| void getArray( ) | accepts the array elements |
| void insertionSornt( ) | sorts the elements of the array in descending order using the in descending order using the Insertion Sort technique |
| double find( ) | calculates and returns the average of all the odd numbers in the array |
| void display( ) | displays the elements of the array in a sorted order along with the average of all the odd numbers in the array by invoking the function find( ) with an appropriate message |
Specify the class InsSort giving details of the constructor(), void getArray( ), void insertionSort( ), double find() and void display(). Define a main( ) function to create an object and call all the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Chapter: [0.04] Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
Design a class Coding to perform some string related operations on a word containing alphabets only.
Example: Input: "Java"
Output: Original word: Java
J=74
a=97
v= 118
a=97
Lowest ASCII code: 74
Highest ASCII code: 118
Some of the members of the class are given below:
| Class name | Coding |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| wrd | stores the word |
| len | stores the length of the word |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Coding() | constructor to initialise the data members with legal initial values |
| void accept( ) | to accept a word |
| void find() | to display all the characters of 'wrd' along with their ASCII codes. Also display the lowest ASCII code and the highest ASCII code, in 'wrd' |
| void show() | to display the original word and all the characters of 'wrd' along with their ASCII codes. Also display the lowest ASCII code and the highest ASCII code in 'wrd', by invoking the function find() |
Specify the class Coding giving details of the constructor( ), void accept( ), void find( ) and void show(). Define a main() function to create an object and call all the functions accordingly to enable the task.
Chapter: [0.04] Programming in Java (Review of Class Xi Sections B and C)
CardGame is a game of mental skill, built on the simple premise of adding and removing the cards from the top of the card pile.
The details of the class CardGame are given below.
| Class name | CardGame |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| cards[] | array to store integers as cards |
| cap | to store the maximum capacity of array |
| top | to store the index of the topmost element of the array |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| CardGame(int cc) | constructor to initialise cap=cc and top= -1 |
| void addCard(int v) | to add the card at the top index if possible, otherwise display the message “CARD PILE IS FULL” |
| int drawCard( ) | to remove and return the card from the top index of the card pile, if any, else return the value -9999 |
| void display( ) | to display all the cards of card pile |
- Specify the class CardGame giving details of the functions void addCard(int) and int drawCard( ). Assume that the other functions have been defined.
The main() function and algorithm need NOT be written. - Name the entity described above and state its principle.
Chapter: [0.13] Data Structures
A super class EmpSal has been defined to store the details of an employee. Defie a subclass (overtime to compute the total salary of the employee, after adding the overtime amount based on the following criteria.
- If hours are more than 40, then 5000 are added to salary as an overtime amount
- If hours are between 30 and 40 (both inclusive), then 3000 are added to salary as an overtime amount
- If hours are less than 30, then the salary remains unchanged The details of the members of both the classes are given below:
| Class name | EmpSal |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| empnum | to store the name of the employee |
| empcode | integer to store the employee code |
| salary | to store the salary of the employee in decimal |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| EmpSal(...) | parameterised constructor to assign values to data members |
| void show() | to display the details of the employee |
| Class name | Overtime |
| Data members/instance variables: | |
| hours | integer to store overtime in hours |
| totsal | to store the total salary in decimal |
| Methods/Member functions: | |
| Overtime(....) | parameterised constructor to assign values to data members of both the classes |
| void calSal() | calculates the total salary by adding the overtime amount to salary as per the criteria given above |
| void show() | to display the employee details along with the total salary (salary +overtime amount) |
Assume that the super class EmpSal has been defined. Using the concept of inheritance, specify the class Overtime giving the details of the constructer (...), void calSal() and void show().
The super class, main function and algorithm need NOT be written.
Chapter: [0.12] Inheritance and Polymorphism
With the help of an example, briefly explain the dominant term in complexity.
Chapter: [0.14] Complexity and Big O Notation
Answer the following questions based on the diagram of a Binary Tree given below:
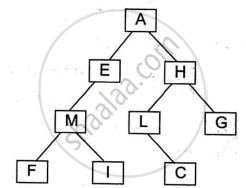
- Name the external nodes of the tree.
- State the degree of node M and node L.
- Write the post-order traversal of the above tree structure.
Chapter: [0.13] Data Structures
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CISCE previous year question papers Class 12 Computer Science (Theory) with solutions 2023 - 2024
Previous year Question paper for CISCE Class 12 -2024 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Computer Science (Theory), you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CISCE Class 12.
How CISCE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Computer Science (Theory) will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
