Advertisements
Advertisements
Refer to the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow.
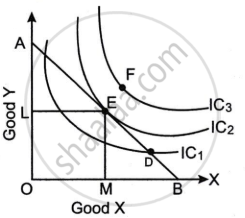
- What does the line AB represent? Why is the line AB negatively sloped? (2)
- At which one of the given points, D, E and F, will the consumer attain equilibrium? Explain. (2)
- Briefly explain why the consumer is not in equilibrium at the other two points. (2)
Concept: Consumer's Equilibrium
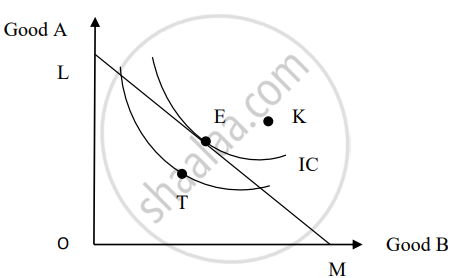
Points K and T will NOT be attained by the consumer. Select the reason from the options given below.
Concept: Indifference Curve
Utility maximising consumers would like to decrease the consumption when ______.
Concept: Total Utility and Marginal Utility
A firm under perfect competition is a price taker but the industry is the price maker. Defend or refute this statement by giving a reason.
Concept: Market Demand
Will you defend or refute the case depicted in the following diagram? Provide a rationale in support of your view.
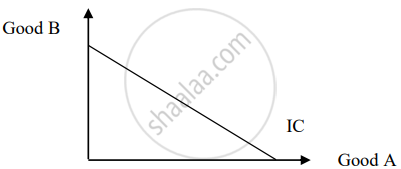
Concept: Indifference Curve
Name the law which deals with the behaviour of marginal utility when the consumer consumes a commodity continuously at a given time. Explain this law with the help of a diagram.
Concept: Diminishing Marginal Utility
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
|
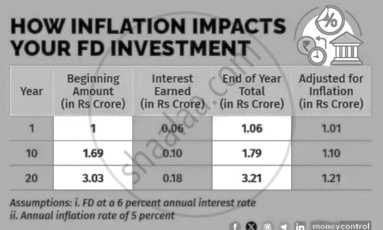
In India, Fixed deposits have long been a favourite investment choice of people, especially senior citizens, as it promise steady returns. It attracts those who are seeking a stable income. But it’s an illusion in the period of inflation. Inflation is the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding the purchasing power of money. In simple terms, what money could buy today might not a few years down the line. Fixed deposits are financial instruments offered by banks where you deposit a lump sum amount for a fixed period at a predetermined rate of interest. Consider an investment of Rs 1 crore in a fixed deposit at a 6% annual interest rate and the annual rate of inflation is 5%. By the 10th year your pre inflation return is 1.79 crore, but post inflation it’s just 1.10 crore. The nominal value of investment in fixed deposits may appear to grow, inflation significantly diminishes their real value and purchasing power over time.
|
- What is the theme of the extract? (2)
- Differentiate between Demand pull and Cost push inflation. (2)
- What are the demand deposits and time deposits? (2)
- Since 1998 RBI has been using new measures of money supply, M0, M1, M2 and M3. Which one of these measures incorporates fixed deposit as one of its components? Mention the other components of that measure. (2)
Concept: Demand
Answer the following question.
Draw diagrams to show the elasticity of demand when it is:
(i) Greater than one
(ii) Less than one
(iii) Unity
Concept: Elasticity of Demand
Answer the following question.
Explain the geometric method of calculating the elasticity of supply.
Concept: Degrees of Elasticity of Demand
If the price of a commodity and total expenditure on that commodity change in the same direction, the price elasticity of demand will be ______.
Concept: Type of Elasticity of Demand
The price of a good decreases from ₹100 to 80 per unit. If the price elasticity of demand for the good is 2 and the original quantity demanded is 30 units, calculate the new quantity demanded.
Concept: Elasticity of Demand
When can the income elasticity of demand be negative?
Concept: Type of Elasticity of Demand
If the price elasticity of demand for a commodity is 2 and the percentage change in price is 5, the percentage change in quantity demanded will be ______.
Concept: Type of Elasticity of Demand
If the price hike in the market is about 10% and this leads to the fall in the quantity demanded by 12%, calculate the price elasticity of demand. Mention the degree of price elasticity of demand.
Concept: Type of Elasticity of Demand
Which one of the following will cause a rise in the equilibrium price of rice when the demand for rice remains the same?
Concept: Movements Along and Shifts in Supply Curve
The price of a mobile handset has risen in the market. But the dealers have not been able to increase the supply proportionately.
What will be the price elasticity of supply for the mobile handset? Draw the supply curve to indicate the type of elasticity.
Concept: Measurement of Price Elasticity of Supply - Percentage-change Method
An increase in the number of firms in the market causes a rightward shift in the market supply curve, but the individual supply curve may shift leftward. Justify the statement.
Concept: Movements Along and Shifts in Supply Curve
Give two differences between intended supply and actual supply.
Concept: Determinants of Supply
Prices of air conditioners and refrigerators have shot up in the new year as consumer durables makers pass on the impact of rising raw material costs and higher freight charges to customers, while home appliances like washing machines may witness a 5–10 per cent price hike later this month or by March.
(Source: The Economic Times)
Explain the behaviour of supply of this consumer durable. Illustrate the same in a diagram.
Concept: Determinants of Supply
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a fall in the price of substitute goods.
Concept: Market Equilibrium