Advertisements
Advertisements
Discuss any four factors affecting price elasticity of demand.
Concept: Elasticity of Demand
Explain any four exceptions to the law of supply
Concept: Concept of Supply - Supply Schedule and Supply Curve
Give any two differences between returns to a factor and returns to scale.
Concept: Returns to a Factor
Explain the implication of ‘freedom of entry and exit to the firms’ under perfect competition.
Concept: Features of Perfect Competition
Show with the help of a diagram, how a perfectly competitive firm earns a normal profit in short-run equilibrium.
Concept: Features of Perfect Competition
Answer the following question.
With the help of a diagram, show the circular flow of income in a two-sector model with Savings and Investment.
Concept: Circular Flow of Income (Two Sector Model)
State whether the following items will be included in the estimation of National Income or not? Give a reason for your answer.
Fresh tomatoes used by a food processing company.
Concept: Aggregates Related to National Income - Gross National Product (GNP)
Answer the following question.
Define marginal utility. When can it be negative?
Concept: Total Utility and Marginal Utility
Answer the following question.
Discuss the relationship between the income of the consumer and demand for a commodity with respect to normal goods, inferior goods, and necessities.
Concept: Demand
Answer the following question.
Differentiate between the extension of demand and an increase in demand, using diagrams.
Concept: Movement Along and Shifts in the Demand Curve
Answer the following question.
Explain with the help of a diagram the consumer’s equilibrium through utility approach.
Concept: Conditions of Consumer's Equilibrium Using Marginal Utility Analysis
Answer the following question.
Discuss any two properties of the indifference curve.
Concept: Properties of Indifference Curve
The aggregate utility obtained from the consumption of a specific unit of a commodity is called ______.
Concept: Cardinal Approach (Utility Analysis)
The figure given below shows the relation between the quantity demanded for the good X and the price of the good Z. What type of goods are X and Z?
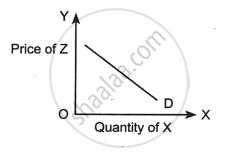
Concept: Demand
With the help of a diagram, explain how the consumer will attain equilibrium on the consumption of a single commodity at a given price.
Concept: Consumer's Equilibrium
Milk is used for making curd, sweets and chocolates.
What type of demand does milk have? Give a reason.
Concept: Demand
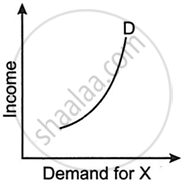
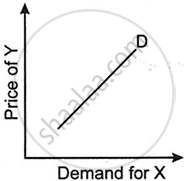
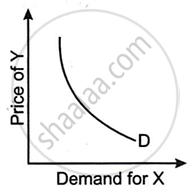
Figures (A), (B) and (C) given below represent different types of Demand curves.
 |
 |
 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) |
What kind of goods do each of these Demand curves represent? Give a reason for each of the curves.
Concept: Demand Curve and Its Slope
Draw a straight-line demand curve joining both the axes. Indicate the following on the demand curve.
Elasticity of demand is equal to zero
Concept: Demand Curve and Its Slope
Draw a straight-line demand curve joining both the axes. Indicate the following on the demand curve.
Elasticity of demand is greater than one
Concept: Derivation of Demand Curve
Observe the graph given below and answer the question that follow.
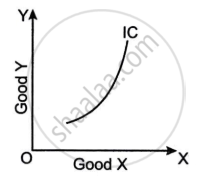
- Give a reason to explain if the graph shown above can be a common phenomenon or not. [2]
- What is an indifference map? Draw its diagram. [2]
- State any two differences between cardinal utility and ordinal utility. [2]
Concept: Indifference Curve
