Advertisements
Advertisements
The price of a mobile handset has risen in the market. But the dealers have not been able to increase the supply proportionately.
What will be the price elasticity of supply for the mobile handset? Draw the supply curve to indicate the type of elasticity.
Concept: Measurement of Price Elasticity of Supply - Percentage-change Method
An increase in the number of firms in the market causes a rightward shift in the market supply curve, but the individual supply curve may shift leftward. Justify the statement.
Concept: Movements Along and Shifts in Supply Curve
Give two differences between intended supply and actual supply.
Concept: Determinants of Supply
Prices of air conditioners and refrigerators have shot up in the new year as consumer durables makers pass on the impact of rising raw material costs and higher freight charges to customers, while home appliances like washing machines may witness a 5–10 per cent price hike later this month or by March.
(Source: The Economic Times)
Explain the behaviour of supply of this consumer durable. Illustrate the same in a diagram.
Concept: Determinants of Supply
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a fall in the price of substitute goods.
Concept: Market Equilibrium
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a rise in the prices of inputs.
Concept: Market Equilibrium
Rate of interest on savings account is more than that on recurring account.
Concept: Market Equilibrium
Explain Price Ceiling with the help of a diagram:
Concept: Price Ceiling
The diagram given below shows the change in price of cotton shirts. Which one of the following causes the equilibrium price to move from P1 to P2?
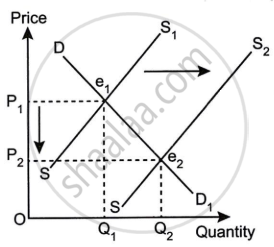
Concept: Equilibrium Price
A huge production of onions and lack of storage facilities have caused a continuous fall in its price. This may adversely affect the production of onions in the subsequent year. With the help of a diagram, briefly explain the measures that the government should adopt to combat this situation.
Concept: Price Floor
Naseer is planning to buy a car for his family. Observe the image shown below and select the MOST rational reaction of Naseer.
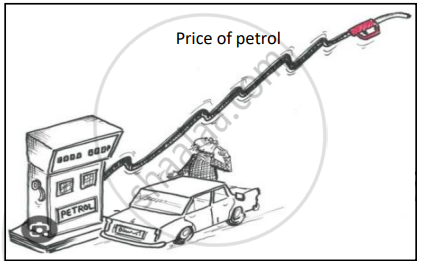
Concept: Price Floor
Answer the following question.
Name the market where average revenue is equal to marginal revenue. Give a reason for your answer.
Concept: Total, Average and Marginal Revenue
Answer the following question.
Give one difference between accounting cost and opportunity cost.
Concept: Concept of Opportunity Cost
Answer the following question.
The cost function of a firm is given below
| Output | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total cost | 100 | 250 | 370 | 550 | 740 |
Calculate:
(i) AFC
(ii) AVC
(iii) MC
Concept: Relationship Between Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost and Marginal Cost
Answer the following question.
Explain how a producer can maximize profit by using MR and MC curves.
Concept: Concept of Opportunity Cost
What is meant by accounting cost?
Concept: Concept of Producer's Equilibrium
Calculate Total variable cost and Marginal cost from the data given below.
| Output (units) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Total cost | 40 | 60 | 78 | 97 |
Concept: Cost - Marginal Cost
What is meant by the break-even point?
Concept: Relationship Between Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost and Marginal Cost
Draw a well-labelled diagram to show the break-even point.
Concept: Relationship Between Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost and Marginal Cost
State whether the following is True or False. Give a reason for your answer.
TVC is an avoidable cost.
Concept: Cost -variable Cost
