Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Acids, Bases and Salts
3: Metals and Non-metals
4: Carbon and its Compounds
5: Periodic Classification of Elements
6: Life Processes
7: Control and Coordination
8: How do Organisms Reproduce
9: Heredity and Evolution
10: Light - Reflection and Refraction
11: Human Eye and Colourful World
12: Electricity
▶ 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
14: Sources of Energy
15: Our Environment
16: Management of Natural Resources
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 13 of CBSE, Karnataka Board NCERT for Science [English] Class 10.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 1 [Page 224]
Why does a compass needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 2 [Page 228]
Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Write any three properties of magnetic lines of force.
Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 3 [Pages 229 - 230]
Consider a circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current ______.
is zero
decreases as we move towards its end
increases as we move towards its end
is the same at all points
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 4 [Pages 231 - 232]
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
mass
speed
velocity
momentum
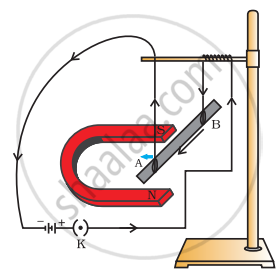
In the Activity shown below, how do we think the displacement of rod AB will be affected if
- current in rod AB is increased
- a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used
- length of the rod AB is increased?
|
A positively-charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is ______.
towards south
towards east
downward
upward
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 5 [Page 233]
State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
What is the principle of an electric motor?
What is the role of the split ring in an electric motor?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 6 [Page 236]
Explain different ways to induce current in a coil.
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 7 [Page 237]
State the principle of an electric generator.
Name some sources of direct current.
Which sources produce alternating current?
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each______.
two revolutions
one revolution
half revolution
one-fourth revolution
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Intext Questions 8 [Page 238]
Name safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
An electric oven of 2 kW is operated in a domestic electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you expect? Explain.
What precaution should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Exercises [Pages 240 - 241]
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
The field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire
The field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire
The field consists of radial lines originating from the wire
The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire
The phenomenon of electromagnetic induction is
the process of charging a body
the process of generating magnetic field due to a current passing through a coil
producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil
the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor
The device used for producing electric current is called a ______.
generator
galvanometer
ammeter
motor
The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit ______.
reduces substantially
does not change
increases heavily
vary continuously
State whether the following statement is true or false.
An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false.
An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false
The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false.
A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
True
False
List two methods of producing magnetic fields.
How does a solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the help of a bar magnet? Explain.
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field?
Draw figure ‘Electric motor’ and working
What is the Principle of an Electric motor?
What is the function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Name some devices in which electric motors are used
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is pushed into the coil?
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is withdrawn from inside the coil?
A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil?
Two circular coils A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Give reason.
State the rule to determine the direction of a magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current.
State the rule to determine the direction of a force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
State the rule to determine the direction of a current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Explain the underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labelled diagram. What is the function of brushes?
What happens to the flow of electric current during a short circuit?
What is the function of an earth wire?
Solutions for 13: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE, Karnataka Board Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board 13 (Magnetic Effects of Electric Current) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current are Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Properties of magnetic lines of force, Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Electric Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Household Electrical Circuits, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Electric Generator, Direct Current Motor, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current, Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Properties of magnetic lines of force, Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Electric Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Household Electrical Circuits, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Electric Generator, Direct Current Motor, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current, Magnetic Effect of Electric Current, Properties of magnetic lines of force, Right-hand Thumb Rule, Magnetic Field Due to Current in a Loop (Or Circular Coil), Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carving Cylindrical Coil (or Solenoid), Force on a Current Carrying Conductor in a Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field, Magnetic Field Due to a Current Carrying Straight Conductor, Electric Motor, Electromagnetic Induction, Alternating Current (A.C.) Generator, Household Electrical Circuits, Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, Electric Generator, Direct Current Motor, Distinction Between an A.C. Generator and D.C. Motor, Types of Current.
Using NCERT Science [English] Class 10 solutions Magnetic Effects of Electric Current exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE, Karnataka Board Science [English] Class 10 students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 13, Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Science [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Science [English] Class 10 CBSE, Karnataka Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
![NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current NCERT solutions for Science [English] Class 10 chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Shaalaa.com](/images/9788174506368-science-english-class-10_6:a32f9ca51afc49958d7ed07fd814f6f6.jpg)