Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 - Matter Around Us Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 - Matter Around Us - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-term-1-english-class-7-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Matter Around Us
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board 3 Matter Around Us Evaluation [Pages 38 - 40]
Choose the appropriate answer.
Which one of the following is an example for a metal?
Iron
Oxygen
Helium
Water
Oxygen, hydrogen, and sulphur are examples for
metals
non-metals
metalloids
inert gases
Which of the following is a short and scientific way of representing one molecule of an element or compound?
Mathematical formula
Chemical formula
Mathematical symbol
Chemical symbol
The metal which is liquid at room temperature is ______.
chlorine
sulphur
mercury
silver
An element which is always lustrous, malleable and ductile is ______.
non-metal
metal
metalloid
gas
Fill in the blanks.
The smallest particle of matter that can exist by itself is ______.
A compound containing one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen is ______.
______ is the only non-metal which conducts electricity.
Elements are made up of______ kinds of atoms.
______ of some elements are derived from Latin or Greek names of the elements.
There are ______ number of known elements.
Elements are the______ form of pure substances.
The first letter of an element is always written in ______ letter.
Molecule containing more than three atoms are known as ______.
______ is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere.
Analogy
Mercury: Liquid at room temperature:: Oxygen: ______.
Non-metal conducting electricity :______ :: Metal conducting electricity : Copper
Elements : Combine to form compounds :: Compounds : ______.
Atoms: Fundamental particle of an element::______ : Fundamental particles of a compound.
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
Two different elements may have similar atoms.
True
False
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
Compounds and elements are pure substances.
True
False
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
Atoms cannot exist alone. They can only exist as groups called molecules.
True
False
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
NaCl represents one molecule of sodium chloride.
True
False
State true of false. If false, give the correct statement.
Argon is mono atomic gas.
True
False
Answer in brief.
Write the chemical formula and name the elements present in the following compounds.
- Sodium chloride
- Potassium hydroxide
- Carbon dioxide
- Calcium oxide
- Sulphur dioxide
Classify the following molecules as the molecules of element or compound
| 1. |  |
|
| 2. |  |
|
| 3. | 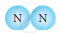 |
|
| 4. | 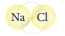 |
What do you understand by chemical formula of a compound? What is its significance?
Define the following term with an example.
Element
Define the following term with an example.
Compound
Define the following term with an example.
Metal
Define the following term with an example.
Non-metal
Define the following term with an example.
Metalloid
Write the symbols for the following elements and classify them as solid, liquid and gas. Aluminum, Carbon, Chlorine, Mercury, Hydrogen and Helium
Classify the following as metals, non-metals and metalloids.
Sodium, Bismuth, Silver, Nitrogen, Silicon, Carbon, Chlorine, Iron, Copper
Classify the following as elements and compounds.
Water, Common salt, Sugar, Carbon dioxide, Iodine and Lithium
Write the chemical formula for the following elements.
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Ozone
- Sulphur
What are elements? What are they made of?
Give two example of elements.
Define molecule.
What are compounds? Give two examples.
Give an example for the elements derived from their Latin names.
What is atomicity of elements?
Calculate the atomicity of H2SO4
Answer in detail.
Differentiate metals and non-metals.
Explain the characteristics of compounds
Describe the different ways in which we can write the symbols of elements. Give appropriate examples.
Differentiate between elements and compounds.
Explain the characteristics of compounds
Compare the properties of metals and nonmetals. Give three examples for each.
Write down the properties of metalloids.
Rewrite the given sentence in correct form.
Elements contain two or more kind of atoms and compounds contain only one kind of atom.
Higher Order Thinking Skills.
List out the metals, non-metals and metalloids which you use in your house, schools. Compare their properties.
Higher Order Thinking Skills.
What changes take place in the movement and arrangement of particles during heating process?
Higher Order Thinking Skills.
In the diagram given below, the circle, square and triangle represent the atoms of different elements.
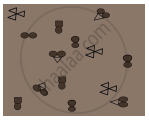
Identify all combinations that represent
- molecule of a compound
- molecule of an element consisting of two atoms
- molecule of an element consisting of three atoms
Higher Order Thinking Skills.
Aakash noticed that the metal latch on gate was difficult to open during hot sunny days. However, it was not difficult to open the same latch at night. Aakash observed that the latch and the gate are exposed to the sun during day time.
- Formulate a hypothesis based on the information provided.
- Briefly state how you would test the hypothesis.
Consider the following statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion: Oxygen is a compound.
Reason: Oxygen cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Assertion is true but reason is false
Assertion is false but reason is true.
Assertion: Hydrogen is an element.
Reason: Hydrogen cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is true but reason is
Assertion is false but reason is true.
Assertion: Air is a compound.
Reason: Air consists of carbon dioxide.
Assertion: Air is a mixture of elements only.
Reason: Only nitrogen, oxygen and neon gases exist in air.
Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Assertion is true but reason is false.
Assertion is false but reason is true.
Assertion: Mercury is solid in room temperature.
Reason: Mercury is a non-metal.
Solutions for 3: Matter Around Us
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 - Matter Around Us Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 - Matter Around Us - Shaalaa.com](/images/science-term-1-english-class-7-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 - Matter Around Us
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 3 (Matter Around Us) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board chapter 3 Matter Around Us are Atoms: Building Blocks of Matter, Molecules, Elements, Classification of Molecules, Types of Element: Metals, Types of Element: Non-metal, Type of Element: Metalloid, Symbols Used to Represent Atoms of Different Elements, Compound, Chemical Formula or Molecular Formula, Atomicity, Effect of Heat on Solid, Liquid and Gases.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board solutions Matter Around Us exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Matter Around Us Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Science - Term 1 [English] Class 7 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
