Advertisements
Chapters
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 - Air and Atmosphere Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 - Air and Atmosphere - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-6-icse_6:86f10377132e4627bf38e72d54ea19e4.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 6: Air and Atmosphere
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CISCE Selina for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Exercise 1
What is atmosphere?
Why can’t we see air?
What is wind?
What would have happened if there would have been no atmosphere around the earth?
When water is heated, we see bubbles rising up. Why?
Why is air called a mixture? Give five facts in support of your answer.
What are the main components of air?
Write down the composition of three main gases present in air by volume.
What do you observe when Ice cold water is filled in a glass tumbler.
What do you observe when a burning candle is covered with an inverted jar.
What do you observe when Carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water.
What do you observe when a beam of light is allowed to enter in a closed dark room through a small hole.
Write the chemical name of Lime water
Write the chemical name of The white insoluble solid formed on the reaction of carbon dioxide with lime water.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Exercise 2
Name two important processes supported by oxygen present in air.
Give two uses of the following component present in air:
oxygen
Give two uses of the following component present in air:
nitrogen
Give two uses of the following component present in air:
carbon dioxide
Give two uses of the following component present in air:
water vapour
Define the following:
Respiration
Define the following:
Photosynthesis
Define the following:
Combustion.
What are fuels?
Give two examples of modern fuels.
Give reason:
Aquatic animals and plants are able to survive in the matter.
Give reason:
A burning candle stops burning if covered with a glass tumbler
Give reason:
Mountaineers and divers carry oxygen cylinders with them.
Give reason:
When water is heated, we see bubbles rising up.
Name the processes which maintain the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the air. How is it done?
State two similarities and two differences between respiration and burning.
Define rusting?
What are the two necessary conditions for rusting of iron?
Give the chemical name of rust.
How is air useful to water boats?
How is air useful to agriculture?
How is air useful to windmills?
How is air useful to scooters and cars.?
State the full form of LPG and CNG? How are the two different in their composition?
Why is nitrogen important to all living beings?
What is nitrogen fixation?
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Exercise 3
What is air pollution?
Mention five causes of air pollution.
Name two air pollutants which affect our health.
Name two air pollutants which cause acid rain.
Name two air pollutants which cause global warming.
What is meant by ozone depletion?
State four steps to be taken to control air pollution.
Name three greenhouse gases.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Objective Type Questions 1
Fill in the blank
The layer of air around the earth is called the ________.
Fill in the blank
Although we cannot see air, we can ___it.
Fill in the blank
Air is a ______ of gases
Fill in the blanks
Plants and animals maintain the balance of carbon ___________and _________ in the air.
Fill in the blank
Polluted air is harmful to ____.
Fill in the blank
The supporter of combustion in air is _____.
Fill in the blank
Green plants need ________________to prepare food.
Fill in the blanks
Oxygen is used in ___________the food to get _______.
Fill in the blank
Aquatic plants and animals use _________ in water.
Fill in the blank
The reddish-brown powder on the surface of iron nails exposed to air and moisture is called _____.
Write ‘true’ or ‘false for the following;
Air is a compound.
True
False
Write ‘true’ or ‘false for the following;
Carbon dioxide is given out during photosynthesis
True
False
Write ‘true’ or ‘false for the following;
The composition of air was discovered by Lavoisier.
True
False
Write ‘true’ or ‘false for the following;
The major component of air is oxygen.
True
False
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Multiple Choice Questions
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Air consists of
only oxygen
only nitrogen
only carbon dioxide
all of these
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Air pollution is due to the
cutting of green plants
gases like carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, etc.
smoke given out by factories
all of the above
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
The gases which cause acid rain are
sulphur dioxide and oxygen
nitrogen and oxygen
carbon dioxide and water vapour
nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Rust is
hydrated iron oxide
hydrated copper sulphate
anhydrous iron oxide
none of the above
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Photosynthesis is a process in which plants
take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide
take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen
take in nitrogen and give out oxygen
none of the above
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Fuels which do not leave any residue on burning are
coal and wood
coal and LPG
wood and CNG
LPG and CNG
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Respiration
is a slow process
is a natural and continuous process
takes place at body temperature
all of the above
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
Which of the following is not a greenhouse gas?
carbon dioxide
sulphur dioxide
methane
nitrogen
Tick (√) the correct alternative from the choice given for the following statement.
The substance which accelerates the speed of a reaction without itself undergoing any change is called
catalyst
pollutant
fuel
none of the above
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Additional Questions For Practice
State what do you understand by the term ‘air’. Explain its importance to mankind.
Give a brief account of the discovery of air and the scientists involved.
What is meant by the term ‘atmosphere’? State the role played by the atmosphere for the survival of mankind.
Explain in brief the different layers of the atmosphere and the basic functions of the main layers.
Describe a simple experiment with the help of a diagram to show that Air occupies space
Describe a simple experiment with the help of a diagram to show that Air has mass
Describe a simple experiment with the help of a diagram to show that Air exerts pressure
Describe a simple experiment with the help of a diagram to show that Air is highly compressible
Name the components of air with their approximate percentage by volume in air. Does the percentage by volume of each component remain the same, in the atmosphere of different parts of the world? Explain with reasons.
With the help of a labeled diagram, describe a simple experiment to show the presence of oxygen and nitrogen in air using a piece of white phosphorus.
You are given a test tube with two outlets and a bottle of lime water. Using same, how would you demonstrate experimentally the presence of carbon dioxide in air.
Give a reason why water droplets appear on the outer surface of a tumbler containing ice.
Explain the importance of nitrogen of the air for plant growth.
Give a reason why nitrogen is filled in food packets and not oxygen.
State what would happen, if the air above the earth contained mainly oxygen and no nitrogen
State the utility of oxygen for respiration in living organisms
State the utility of oxygen for respiration in plants
Explain the importance of carbon dioxide for (a) photosynthesis (b) warming the earth’s environment. State what would happen if excess carbon dioxide as a pollutant is released into the atmosphere.
State in brief how water vapour in the atmosphere determines the climatic conditions
Give a reason why two different rare (inert) gases find application in advertisement signs and fluorescent bulbs.
A mixture has a variable composition. Give three other reasons why air is considered a mixture and not a compound.
State a reason why there is a balance in the amount of carbon dioxide in the air, even though carbon dioxide is released into the atmopshere by various processes.
Name three different appliances where air is utilized.
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE 6 Air and Atmosphere Objective Type Questions 2
Match the statements in List 1 with the correct answers in List 2
| List 1 | List 2 | ||
| 1 | An impurity in air | A | Water vapour |
| 2 | The component of air which supports combustion | B | Respiration |
| 3 | The inert component in the air slightly soluble in water | C | Rare gases |
| 4 | The component of air which minimizes the rate of evaporation | D | Sulphur dioxide |
| 5 | The process which involves oxidation of food substance in living organisms | E | Helium |
| 6 | The component of air which finds application in observation balloons | F | Carbon dioxide |
| 7 | The process which involves oxidation of substances, liberating heat and light energy | G | Combustion |
| 8 | The component of air which is heavier than air and fairly soluble in water | H | Nitrogen |
| 9 | The process by which atmospheric carbon dioxide is absorbed by plants resulting in the formation of carbohydrates | I | Photosynthesis |
| 10 | The component of air which is lighter than air and less than 1% in air | J | Oxygen |
The diagrams below represents an experiment to show the presence of a component of air.
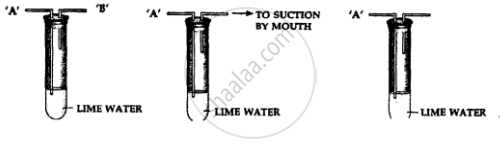
- State why air is sucked from – outlet ‘B’ and not from outlet “A”
- State why the air is sucked ‘slowly’ from the outlet “B”
- State the observation seen after completion of the experiment.
- State the reason for the above observation seen.
- Name another component which if present in air as a pollutant would have given a similar observation
Complete the statement given below by filling in the blank with the correct word from the words given below
The ______ is a layer which extends up to about 10-50 km. above the earth.
atmosphere
troposphere
stratosphere
Complete the statement given below by filling in the blank with the correct word from the words given
___________is an example of a pollutant present in the air.
carbon dioxide
stratosphere
nitrogen dioxide
water vapour
hydrogen sulphide
Complete the statement given below by filling in the blank with the correct word from the words given:
The component of air used in photosynthesis is ______ and the products of photosynthesis is oxygen.
oxygen
carbon dioxide
nitrogen
Complete the statement given below by filling in the blank with the correct word from the words given:
The product formed which is common to both combustion and respiration is ______.
oxygen
carbon dioxide
nitrogen dioxide
Complete the statement given below by filling in the blank with the correct word from the words given:
The component of air which is variable in air above sea level and in air in general ______.
oxygen
nitrogen
water vapour
Name the following:
The product formed when phosphorus burns in oxygen.
Name the following:
The layer of atmosphere which contains the ozone layer.
Name the following:
The active component of air which supports combustion and is used up in burning
Name the following:
The main, rare (inert) gas present in air.
Name the following:
The component of air which is present more in industrial areas.
Name the following:
The type of bacteria which directly absorb nitrogen from the air and converted soluble nitrates in the soil.
Name the following:
The product of respiration released in exhaled air, other than carbon dioxide.
Name the following:
An inert gas which has a low boiling point and is used for producing very low temperatures
Name the following:
A process which removes carbon dioxide from the air.
Name the following:
The component of air which does not support combustion.
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’. If false write the correct statement.
The mesosphere in the atmosphere, contains most of the air, fit for respiration
True
False
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’. If false write the correct statement.
The percentage of carbon dioxide in the air is between 0.2 to 0.4%.
True
False
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’. If false write the correct statement.
Carbon dioxide, water vapour and energy in the form of heat are evolved during respiration.
True
False
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’. If false write the correct statement.
Photosynthesis is a process by which green plants prepare their own food in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
True
False
State whether the following statement is ‘true’ or ‘false’. If false write the correct statement.
Air is a mixture and not a compound since the components of air cannot be separated by physical methods.
True
False
Give word equation for the following conversion:
Nitrogen of the air to nitric oxide
Give word equation for the following conversion:
Nitric oxide to nitrogen dioxide
Give word equation for the following conversion:
Nitrogen dioxide to nitric acid
Give word equation for the following conversion:
Nitric acid to soluble nitrates in the soil
Give word equation for the following conversion:
Carbon dioxide in the air to carbohydrates in plants.
Solutions for 6: Air and Atmosphere
![Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 - Air and Atmosphere Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 - Air and Atmosphere - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-chemistry-english-class-6-icse_6:86f10377132e4627bf38e72d54ea19e4.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 - Air and Atmosphere
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE 6 (Air and Atmosphere) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE chapter 6 Air and Atmosphere are Importance of Oxygen, Importance of Nitrogen, Atmosphere and Its Layers, Composition and Components of Air, Importance of Air, Process of Photosynthesis, Rusting, Air Pollution and Its Causes, Effects of Air Pollution, Prevention of Air Pollution, Photosynthesis: Food-Making Process in Plants, Air Around Us, Importance of Carbon Dioxide, Air is a Mixture.
Using Selina Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE solutions Air and Atmosphere exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Air and Atmosphere Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Chemistry [English] Class 6 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
