Topics
Electronic Components/ Study of Components and Circuits
- Introduction to Electronic Components
- Classification Of Components
- Resistors
- Types of Resistors
- Capacitors
- Types of Capacitors
- Inductors
- Basics of Transformers
- Basics of Semiconductor Devices
- PN Junction Diode
- Half Wave Rectifier
- Types of diodes
- Transistors
- Transistor Amplifier
- Basic of Transistor as a Switch
- Switch Mode power Supply (SMPS)
- Classification of IC’S
Logic Gates and Sequential Circuit
- Introduction of Logic gates and sequential circuits
- Basics of Logic Gates
- Types of gates
- Odd/Even Parity
- DE-MORGAN'S Theorem
- NAND Gate is an Universal Building Block
- HALF ADDER AND FULL ADDER
- Multiplexers
- Demultiplexer
- Encoder
- Decoder
- FLIP-FLOPS
- Counters
- Shift Registers
Functional Hardware of Pc
Peripheral Devices
- Introduction
- RC time constant
Capacitors
A capacitor, also known as a condenser, is a key passive component in electrical and electronic circuits, used to store and release electrical energy. Capacitors have a specific charge storage capacity, measured in farads, and come in fixed and variable types, ranging from picofarads to microfarads. They consist of two parallel conducting surfaces separated by a dielectric material.
Charging & Discharging
When a battery connects to a capacitor, current flows, indicated by a meter. Initially, plates A and B have equal electrons. Upon connection, electrons accumulate on plate A, creating electrostatic induction. This forces plate B to pass electrons to the battery, resulting in a negative charge on plate A and a positive charge on plate B. Electrons flow until the capacitor voltage matches the battery voltage.
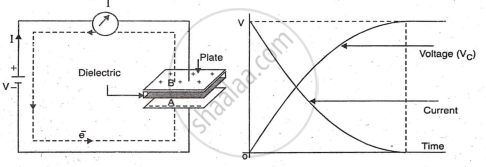
RC Time Constant
The time constant in timer circuits is the time for a capacitor to charge to 63.28% of the applied voltage or discharge to 36.72% of its initial voltage. It is calculated using the formula:
T = R x C.
Remember: In 5 time constant, capacitor gets charged to applied voltage or in 5 time constant it will get completely discharged.
Paper Capacitors (Fixed Capacitors)
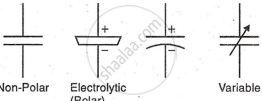
All fixed non-polar capacitors have a similar construction: two conducting surfaces separated by a dielectric material. A paper capacitor is made by rolling two thin metal foils with dielectric-impregnated Kraft paper. These non-polar capacitors can be connected in any direction, as polarity is not marked.
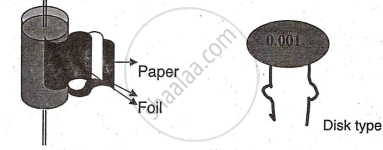
Specialty: Medium capacitance, small size, non-polar.
Range: 500pF to 1µF, voltage rating 100V to 1000V.
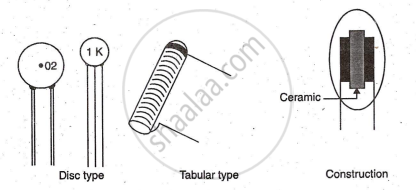
Mica & Ceramic Capacitor (Fixed Capacitors)
Mica: The construction is like paper capacitor, only the dielectric material used is mica foil or mica sheet as shown.
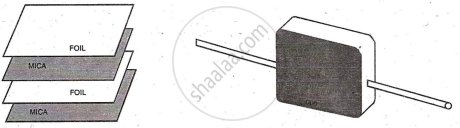
Specialty: High temperature range -55°C to 150°C, non-polar.
Range: 5pF to 10,000pF, voltage rating around 500V.
Ceramic: These capacitors are commonly observed in many circuits. The construction of ceramic capacitors is different than paper and mica capacitors. It is built by depositing silver plates on each side of a thin ceramic material disc. During the process tinned wire leads are attached to each plate.
Speciality: Economical at 1 Rs. per piece.
Range: 3pF to 2µF, voltage range 3V to 6000V, non-polar.
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor (Fixed Capacitors)
This polar capacitor has marked positive and negative terminals, with polarity being crucial to prevent damage. Unlike non-polar capacitors, they offer higher capacitance due to electrolyte.
Construction:
It consists of an aluminum foil electrode with an aluminum oxide film (dielectric) and an electrolyte (second plate). A plain aluminum foil layer provides electrical contact between one terminal and the electrolyte. Typically used in DC circuits, such as rectifier filters, rather than AC circuits.
Specialty: High values, high cost, polar capacitors
Range: 1µF to 3000µF, voltage rating 1V to 500V.
Air Gang Capacitor (Variable Capacitors)
An air gang condenser is a variable capacitor with two sets of parallel plates: a fixed stator and a movable rotor on a shaft. Rotating the shaft changes the plate area overlap, thus varying capacitance. Used in valve radios with two gang capacitors and miniature types in transistor receivers. Other adjustable variable capacitors are trimmers and padders.
Specialty : Used for tuning the radio, large size, high cost but high operating voltage~
Typical Range: 1 pF to 500 pF. Maximum operating voltage 1 KV
