Topics
Basics of Information Technology
- An Introduction to IT (Information Technology)
- Data and Information
- Computer
- Components of a Computer
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Types of Computer Memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory Unit (Secondary Storage Devices)
- Computer Hardware and Software
- Categories of a Software
- Introduction to Operating System (OS)
- LINUX
- Basics of Graphical User Interface (GUI)
- Command Line Interface (CLI)
- LINUX
- Types of Networks
- Network Configurations
- Internet
- Network Protocol
- IT Enabled Services
- Careers in IT
- Recent Trends in IT
Introduction to DBMS
- Database
- Database Management System Software (DBMS)
- Applications of DBMS
- Advantages of DBMS
- Data Types in the DBMS
- Introduction to Data Model
- Relational Model of DBMS
- Properties of Transactions (ACID)
- Introduction of RDBMS
- Basic Database Concepts
- Relationships in a Database
- Introduction to SQL
- Categories of SQL Commands
Impressive Web Designing
- Introduction to Web Designing
- Components of web
- Introduction to HTML
- Different Tags in HTML
- Tags
- HTML Table
- HTML Hyperlinks
- Form and Form Controls in HTML
- Tags Used to Create Form in HTML
- Javascript in HTML
- Decision Making Statement in Javascript
- JavaScript Functions
- JavaScript Event Handling
Cyber Law
- Introduction to Cyberlaw
- Cyber Crime
- Cyber Crime Examples
- Cyber Safety and Security
- Do’s and Don’ts for Students in Cyber World
- Security Procedures
- Security Procedures
- Indian Information Technology Act (IT Act)
- Introduction
- Architecture of Computer
Introduction:
The word "computer" is derived from the Latin word "computare," which means "to calculate," "to count," "to sum up," or "to think together." An electronic device that accepts input from the user, processes it according to the instructions given to it, and gives the required result in the form of output is a computer.
- The computer has evolved through five generations since its creation.
- The first-generation computers were used between 1946 and 1959.
- The ENIAC computer was a prominent example of this generation.
- Valves (vacuum tubes) were used in their construction, which was large in size and consumed a lot of electricity.
- Excessive electricity usage generated heat, causing frequent shutdowns.
- Modern computers are 5th-generation computers, which are far more advanced, efficient, and compact compared to earlier generations.
Architecture of Computer:
Computer architecture defines the structure and functionality of a computer system. It specifies how hardware components (like CPU, memory, and input/output devices) interact with software to perform tasks. It includes the design, organisation, and operation of the computer.
- Hardware components such as the system unit, monitor, keyboard, and storage devices work together.
- Input devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse, microphone) feed data into the computer, while output devices (e.g., monitor, speakers, printer) display or produce results.
- Storage devices like hard drives, CD/DVD drives, and flash memory store data and programs.
- The architecture determines how efficiently a computer processes data and executes instructions.
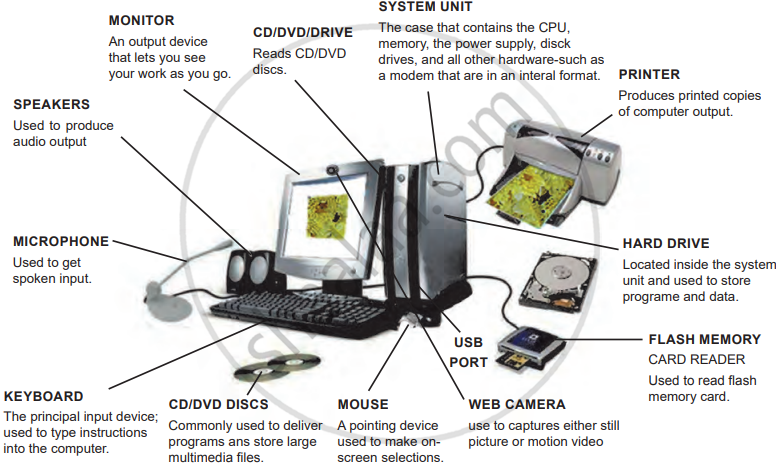
Computer System and Peripherals
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
