Topics
Electric Charges and Fields
- Electric Charges
- Conductors and Insulators
- Basic Properties of Electric Charge
- Coulomb’s Law - Force Between Two Point Charges
- Superposition Principle - Forces Between Multiple Charges
- Introduction of Electric Field
- Electric Field Due to a System of Charges
- Physical Significance of Electric Field
- Electric Field Lines
- Electric Flux
- Electric Dipole
- Dipole in a Uniform External Field
- Continuous Distribution of Charges
- Gauss’s Law
- Applications of Gauss’s Law
- Charging by Induction
- Electric Field Due to a Point Charge
- Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet and Uniformly Charged Thin Spherical Shell (Field Inside and Outside)
- Superposition Principle of Forces
- Force Between Two Point Charges
Electrostatics
Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- Electric Potential
- Potential Due to a Point Charge
- Potential Due to an Electric Dipole
- Potential Due to a System of Charges
- Equipotential Surfaces
- Relation Between Electric Field and Electrostatic Potential
- Potential Energy of a System of Charges
- Potential Energy of a Single Charge
- Potential Energy of a System of Two Charges in an External Field
- Potential Energy of a Dipole in an External Field
- Electrostatics of Conductors
- Dielectrics and Polarisation
- Capacitors and Capacitance
- The Parallel Plate Capacitor
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacity
- Combination of Capacitors
- Energy Stored in a Capacitor
- Van De Graaff Generator
- Capacitance of a Parallel Plate Capacitor with and Without Dielectric Medium Between the Plates
- Free Charges and Bound Charges Inside a Conductor
- Conductors and Insulators Related to Electric Field
- Electrical Potential Energy of a System of Two Point Charges and of Electric Dipole in an Electrostatic Field
- Electric Potential Difference
Current Electricity
Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
Current Electricity
- Electric Current
- Electric Currents in Conductors
- Ohm's Law (V = IR)
- Current Density
- Drift of Electrons and the Origin of Resistivity
- Limitations of Ohm’s Law
- Resistivity of Various Materials
- Temperature Dependence of Resistance
- Electrical Power
- Cells, Emf, Internal Resistance
- Combination of Cells in Series and in Parallel
- Kirchhoff’s Rules
- Wheatstone Bridge
- Conductivity and Conductance;
- Delta Star Transformation
- Potential Difference and Emf of a Cell
- Measurement of Internal Resistance of a Cell
- Potentiometer
- Metre Bridge
- Combination of Resistors - Series and Parallel
- Electrical Resistivity and Conductivity
- V-I Characteristics (Linear and Non-linear)
- Flow of Electric Charges in a Metallic Conductor
Moving Charges and Magnetism
- Magnetic Force
- Sources and Fields of Magnetic Force
- Magnetic Field, Lorentz Force
- Magnetic Force on a Current-carrying Conductor
- Motion in a Magnetic Field
- Magnetic Field Due to a Current Element, Biot-Savart Law
- Magnetic Field on the Axis of a Circular Current Loop
- Ampere’s Circuital Law
- Solenoid and the Toroid - the Solenoid
- Force Between Two Parallel Currents, the Ampere
- Circular Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole
- Torque on a Rectangular Current Loop in a Uniform Magnetic Field
- Moving Coil Galvanometer
- Oersted’s Experiment
- Solenoid and the Toroid - the Toroid
- Magnetic Diapole
- Torque on a Current Loop in Magnetic Field
- Force on a Current - Carrying Conductor in a Uniform Magnetic Field
- Force on a Moving Charge in Uniform Magnetic and Electric Fields
- Straight and Toroidal Solenoids (Only Qualitative Treatment)
- The Magnetic Dipole Moment of a Revolving Electron
- Velocity Selector
- Cyclotron
Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
Magnetism and Matter
- Introduction of Magnetism
- The Bar Magnet
- Magnetism and Gauss’s Law
- Magnetisation and Magnetic Intensity
- Magnetic Properties of Materials
- Permanent Magnet and Electromagnet
- Curie Law of Magnetism
- Hysteresis Loop
- The Earth’s Magnetism
- Torque on a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet) in a Uniform Magnetic Field
- Dipole in a Uniform External Field
- Magnetic Field Intensity Due to a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet) Perpendicular to Its Axis
- Magnetic Field Intensity Due to a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet) Along Its Axis
- Magnetic Dipole Moment of a Revolving Electron
- Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole and Its Magnetic Dipole Moment
- Magnetic Substances
Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Electromagnetic Induction
- Electromagnetic Induction
- The Experiments of Faraday and Henry
- Magnetic Flux
- Faraday’s Law of Induction
- Lenz’s Law and Conservation of Energy
- Motional Electromotive Force (e.m.f.)
- Mutual Inductance
- Self Inductance
- A.C. Generator
- Energy Consideration: a Quantitative Study
- Eddy Currents
- Induced e.m.f. and Induced Current
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Alternating Current
- Alternating Currents and Direct Currents
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Resistor
- Representation of AC Current and Voltage by Rotating Vectors - Phasors
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to an Inductor
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Capacitor
- Different Types of AC Circuits: AC Voltage Applied to a Series LCR Circuit
- Power in AC Circuit: the Power Factor
- Forced Oscillations and Resonance
- Transformers
- LC Oscillations
- Reactance and Impedance
- Peak and Rms Value of Alternating Current Or Voltage
- Alternating Currents
Atoms and Nuclei
Electromagnetic Waves
- Elementary Facts About Electromagnetic Wave Uses
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Transverse Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Displacement Current
Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- Reflection of Light by Spherical Mirrors
- Refraction
- Refraction at Spherical Surfaces and Lenses
- Refraction by a Lens
- Combination of Thin Lenses in Contact
- Refraction at Spherical Surfaces
- Power of a Lens
- Refraction Through a Prism
- Optical Instruments
- Optical Instruments: Simple Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Compound Microscope
- Optical Instruments: Telescope
- Optical Instruments: the Eye
- Snell’s Law
- Concave Mirror
- Rarer and Denser Medium
- Lens Maker's Formula
- Thin Lens Formula
- Concept of Lenses
- Some Natural Phenomena Due to Sunlight
- Dispersion by a Prism
- Magnification
- Total Internal Reflection
- Ray Optics - Mirror Formula
- Light Process and Photometry
Electronic Devices
Communication Systems
Wave Optics
- Introduction of Wave Optics
- Huygens' Principle
- Refraction of a Plane Wave
- Refraction at a Rarer Medium
- Reflection of a Plane Wave by a Plane Surface
- Coherent and Incoherent Addition of Waves
- Interference of Light Waves and Young’s Experiment
- Diffraction of Light
- The Single Slit
- Seeing the Single Slit Diffraction Pattern
- Refraction of Monochromatic Light
- Polarisation
- Law of Malus
- Principle of Superposition of Waves
- Corpuscular Theory
- Plane Polarised Light
- The Validity of Ray Optics
- The Doppler Effect
- Width of Central Maximum
- Resolving Power of Microscope and Astronomical Telescope
- Interference
- Proof of Laws of Reflection and Refraction Using Huygens' Principle
- Brewster's Law
- Fraunhofer Diffraction Due to a Single Slit
- Coherent and Incoherent Sources and Sustained Interference of Light
- Speed of Light
- Reflection and Refraction of Plane Wave at a Plane Surface Using Wave Fronts
Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Dual Nature of Radiation
- Electron Emission
- Photoelectric Effect - Hertz’s Observations
- Photoelectric Effect - Hallwachs’ and Lenard’s Observations
- Experimental Study of Photoelectric Effect
- Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light
- Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation: Energy Quantum of Radiation
- Particle Nature of Light: The Photon
- Einstein’s Equation - Particle Nature of Light
- Davisson and Germer Experiment
- de-Broglie Relation
- Wave Nature of Matter
The Special Theory of Relativity
Atoms
- Introduction of Atoms
- Alpha-particle Scattering and Rutherford’s Nuclear Model of Atom
- Atomic Spectra
- Bohr’s Model for Hydrogen Atom
- Energy Levels
- The Line Spectra of the Hydrogen Atom
- De Broglie’s Explanation of Bohr’s Second Postulate of Quantisation
- Heisenberg and De Broglie Hypothesis
- Thompson Model
- Dalton's Atomic Theory
- Hydrogen Spectrum
Nuclei
- Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus
- Size of the Nucleus
- Mass - Energy
- Nuclear Binding Energy
- Nuclear Force
- Introduction of Radioactivity
- Alpha Decay
- Beta Decay
- Gamma Decay
- Introduction of Nuclear Energy
- Nuclear Fission
- Nuclear Fusion – Energy Generation in Stars
- Controlled Thermonuclear Fusion
- Nuclear Reactor
- Mass Defect and Binding Energy
- Atomic Mass, Mass - Energy Relation and Mass Defect
- Law of Radioactive Decay
Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
- Concept of Semiconductor Electronics: Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
- Classification of Metals, Conductors and Semiconductors
- Energy Bands in Conductors, Semiconductors and Insulators
- Intrinsic Semiconductor
- Extrinsic Semiconductor
- p-n Junction
- Semiconductor Diode
- Application of Junction Diode as a Rectifier
- Integrated Circuits
- Feedback Amplifier and Transistor Oscillator
- Transistor as a Device
- Basic Transistor Circuit Configurations and Transistor Characteristics
- Transistor Action
- Transistor: Structure and Action
- Digital Electronics and Logic Gates
- Transistor as an Amplifier (Ce-configuration)
- Transistor and Characteristics of a Transistor
- Zener Diode as a Voltage Regulator
- Special Purpose P-n Junction Diodes
- Diode as a Rectifier
- Triode
Communication Systems
- Detection of Amplitude Modulated Wave
- Production of Amplitude Modulated Wave
- Basic Terminology Used in Electronic Communication Systems
- Sinusoidal Waves
- Modulation and Its Necessity
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
- Need for Modulation and Demodulation
- Satellite Communication
- Propagation of Electromagnetic Waves
- Bandwidth of Transmission Medium
- Bandwidth of Signals
- Elements of a Communication System
The Special Theory of Relativity
- The Special Theory of Relativity
- The Principle of Relativity
- Maxwell'S Laws
- Kinematical Consequences
- Dynamics at Large Velocity
- Energy and Momentum
- The Ultimate Speed
- Twin Paradox
- Lens and its Types
- Cross-Sections of Convex and Concave Lenses
Lens and its Types:
A lens is a transparent medium bounded by two surfaces that refracts light. Lenses are widely used in spectacles, telescopes, cameras, and magnifying devices. They help in focusing, magnifying, or dispersing light rays to form clear images.
- Convex Lens (Converging Lens) → Thicker at the center, bends light inward, forming a real or virtual image.
- Concave Lens (Diverging Lens) → Thinner at the centre, it bends light outward, always forming a virtual image.
| Lens Type | Description | Image Formation | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biconvex | Both surfaces are convex, thicker at the center | Forms real or virtual images | Magnifying glasses, cameras, telescopes |
| Plano-Convex | One surface is flat; the other is convex | Converges light to a focal point | Laser systems, projectors |
| Positive Meniscus | Curved outward but thinner at the edges | Reduces spherical aberration | High-quality camera lenses |
| Biconcave | Both surfaces are concave, thinner at the center | Forms only virtual images | Used in eyeglasses for myopia (nearsightedness) |
| Plano-Concave | One surface is flat; the other is concave | Diverges light rays | Beam expanders, optical instruments |
| Negative Meniscus | Curved inward but thicker at the edges | Minimizes distortion | Specialized optical systems |
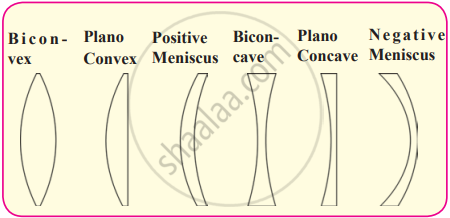
Types of lenses
Cross-Sections of Convex and Concave Lenses
1. Convex Lens (Diagram a)
A convex lens is formed by two spherical surfaces bulging outward.
- The surfaces S₁ and S₂ represent parts of two spheres.
- C₁ and C₂ are the centres of curvature of these spheres.
- The surface labelled 1 is part of sphere S₁, and surface 2 is part of sphere S₂.
- The lens is thicker at the centre and thinner at the edges.
- It converges light rays, making it useful in magnifying glasses, cameras, and telescopes.
2. Concave Lens (Diagram b)
A concave lens is formed by two spherical surfaces curving inward.
- The surfaces S₁ and S₂ represent sections of two spheres.
- C₁ and C₂ are the centres of curvature of these spheres.
- The surface labelled 1 is part of sphere S₁, and its surface 2 is part of sphere S₂.
- The lens is thinner at the centre and thicker at the edges.
- It diverges light rays, making it useful for correcting myopia (nearsightedness) and in laser applications.
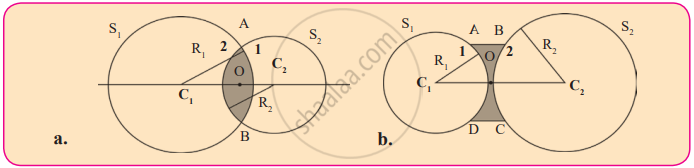
Cross-sections of convex and concave lenses
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
Video Tutorials
Shaalaa.com | Ray Optics part 28 (Refraction by lens)
to track your progress
Series: 2
0%
Ray Optics part 28 (Refraction by lens)
00:12:40 undefined
00:12:40 undefined
Ray Optics part 29 (Sign convention in lens)
00:08:00 undefined
00:08:00 undefined
Ray Optics part 30 (Image formation by lens)
00:03:05 undefined
00:03:05 undefined
Ray Optics part 31 (Refraction by lens)
00:13:48 undefined
00:13:48 undefined
Ray Optics part 32 (Refraction by lens: comparison)
00:01:39 undefined
00:01:39 undefined
Ray Optics part 42 (Human Eye)
00:11:31 undefined
00:11:31 undefined
Ray Optics part 43 (Image formation at eye)
00:13:09 undefined
00:13:09 undefined
Ray Optics part 44 (Defect of vision)
00:09:08 undefined
00:09:08 undefined
Ray Optics part 45 (Numerical Eye)
00:09:40 undefined
00:09:40 undefined
