- Sunlight is the primary energy source, captured by plants (producers) and passed through consumers and decomposers.
- Energy diminishes as it moves up the food chain due to heat loss.
- Decomposers recycle organic matter into inorganic nutrients, supporting plant growth.
- Nutrient cycling ensures the availability of essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Living organisms rely on abiotic elements like air, water, and soil for survival.
- Biological activities, like respiration and decomposition, impact abiotic factors.
- Plants absorb nutrients from the soil, supporting primary productivity.
- Animals depend on plants for food and oxygen derived from photosynthesis.
- Decomposers maintain ecosystem balance by breaking down waste and dead matter.
- A constant interplay exists between biotic and abiotic components for ecosystem stability.
Topics
Overview of Environmental Aspects
- Definition, Scope and Importance of Environmental Study
- Need for Public Awareness of Environmental Education
- Introduction to Depletion of Natural Resources
- Global Crisis Related to – Population, Water, Sanitation and Land
- Ecosystem
- Study of Ecosystems
- Energy Flow in Ecosystem
- Overview of Food Chain
- Food Web
- Ecological Pyramid
- Concept of Ecological Succession and Its Impact on Human Beings
Aspects of Sustainable Development
- Concept and Definition of Sustainable Development
- Social, Economical and Environmental Aspects of Sustainable Development
- Control measures: 3R (Reuse, Recovery, Recycle)
- Resource utilization as per the carrying capacity (in brief)
Environmental Pollution
E‐Pollution
- Definition, Sources and Effects of E-Pollution
Noise Pollution
- Sources, Effects of Noise Pollution
- Threshold Limit for Different Areas and Control Methods
Nuclear Pollution
- Sources and Effects of Nuclear Pollution
Water Pollution
- Sources of Water Pollution
- Treatment of Domestic and Industrial Waste Water
Land Pollution
- Solid Wastes
- Solid Waste Management by Land Filling
- Composting and Incineration
Air Pollution
- Sources of Air Pollution
- Consequences of Air Pollution
- Greenhouse Effect
- Photochemical Smog
- Cleaning of gaseous effluents to reduce air contaminants namely dust particle or particulate matters
Pollution Control Legislation
- Functions and Powers of Central and State Pollution Control Board
- Environmental Clearance, Consent and Authorization Mechanism
Renewable Sources of Energy
- Importance of Renewable Sources of Energy
- Principle and working with schematic diagram of Solar Energy
- Principle and Working with Wind Energy
- Principle and working with schematic diagram of Hydropower
- Renewable Sources of Energy Geothermal Energy
Technological Advances to Overcome Environmental Problems
- Concept of Green Buildings
- Various Indoor Air Pollutants and Their Effects on Health
- Carbon Credit: Introduction and General Concept
- Disaster Management
- Ecosystem
- Basic categories of ecosystem
1) Terrestrial
2) Aquatic
Introduction to Ecosystem:
The word “ecosystem” was coined in the 1930s when scientist Ray Claffam was asked to describe the relationship between physical and biological factors. His answer was “ecosystem,” and his colleague A.G. Tansley first used the term in 1935. It is also sometimes called a biotic community.
An ecosystem is a natural system formed by the interaction between living organisms (biotic factors) and non-living components (abiotic factors) of the environment. It represents a community of organisms and their physical surroundings, functioning as a single, self-sustaining unit.
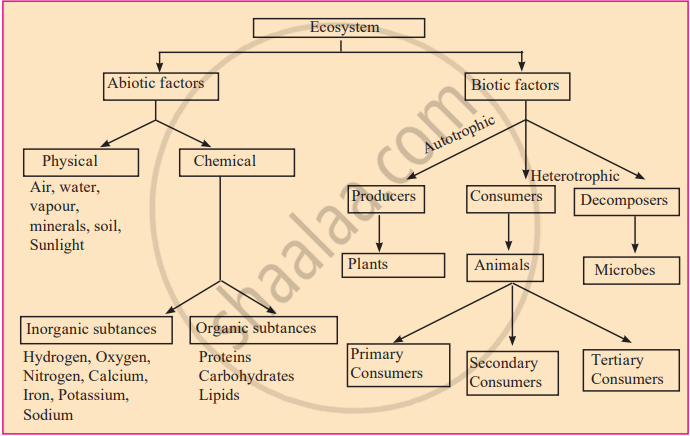
Components of Ecosystem
Interactions in the Ecosystem:
If you would like to contribute notes or other learning material, please submit them using the button below.
