Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A(1, 6) and B(3, 5), find the equation of the locus of point P such that segment AB subtends right angle at P. (∠APB = 90°)
उत्तर
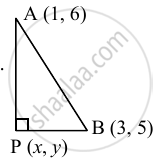
Let P(x, y) be any point on the required locus.
Given, A(1, 6) and B(3, 5),
∠APB = 90°
∴ ΔAPB is a right angled triangle.
By Pythagoras theorem,
AP2 + PB2 = AB2
∴ [(x – 1)2 + (y – 6)2] + [(x – 3)2 + (y – 5)2] = (1 – 3)2 + (6 – 5)2
∴ x2 – 2x + 1 + y2 – 12y + 36 + x2 – 6x + 9 + y2 – 10y + 25 = 4 + 1
∴ 2x2 + 2y2 – 8x – 22y + 66 = 0
∴ x2 + y2 – 4x – 11y + 33 = 0
∴ The required equation of locus is
x2 + y2 – 4x – 11y + 33 = 0.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If A(1, 3) and B(2, 1) are points, find the equation of the locus of point P such that PA = PB.
A(– 5, 2) and B(4, 1). Find the equation of the locus of point P, which is equidistant from A and B.
A(2, 4) and B(5, 8), find the equation of the locus of point P such that PA2 – PB2 = 13.
If the origin is shifted to the point O'(2, 3), the axes remaining parallel to the original axes, find the new co-ordinates of the points A(1, 3)
If the origin is shifted to the point O'(1, 3), the axes remaining parallel to the original axes, find the old co-ordinates of the points C(5, 4)
If the origin is shifted to the point O'(1, 3), the axes remaining parallel to the original axes, find the old co-ordinates of the points D(3, 3)
Obtain the new equations of the following loci if the origin is shifted to the point O'(2, 2), the direction of axes remaining the same: 3x – y + 2 = 0
Obtain the new equations of the following loci if the origin is shifted to the point O'(2, 2), the direction of axes remaining the same: x2 + y2 – 3x = 7
Obtain the new equations of the following loci if the origin is shifted to the point O'(2, 2), the direction of axes remaining the same: xy – 2x – 2y + 4 = 0
Let A (2, 3), B (3, -6), C (5, - 7) be three points. If P is a point satisfying the condition PA2 + PB2 = 2 PC2, then a point that lies on the locus of P is ______.
Equation of locus of a point, such that its distance from the origin is one-third of the sum of its distance from co-ordinate axes, is ______
In a triangle ABC, A ≡ (0, 2), B ≡ (4, 0). If the centroid of the triangle lies on the locus y = x, then the equation of locus of the third vertex C is ______
If the origin is shifted to the point (-4, 7), axes remaining parallel, (-5, q) lies on the new X-axis and (p, 4) lies on the new Y-axis, then the values of p and q are ______
Equation of locus of a point which is equidistant from (1, 2) and (– 5, 4) is ______.
The locus of a point that is equidistant from the lines `x + y - 2sqrt(2)` = 0 and `x + y - sqrt(2)` = 0 is ______.
