Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A ball falls to the ground as shown below :
What is the potential energy of ball at B?
उत्तर
Total energy of a free falling object remains conserved.
So,
Total energy at A = Total energy at B
So,
(K.E)A + (P.E)A = (K.E)B + (P.E)B
Thus
Total energy at A = (K.E)B + (P.E)B
Therefore,
(P.E)B = (80 – 48) J= 32 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A body falls freely under gravity from rest. Name the kind of energy it will possess while falling.
State whether the object possess kinetic energy, potential energy, or both :
A flying aeroplane _______________.
What kind of energy is possessed by the following?
A stone kept on roof-top _______________
What type of energy is possessed : by the piece of stone which is thrown away on releasing the stretched rubber strings of catapult?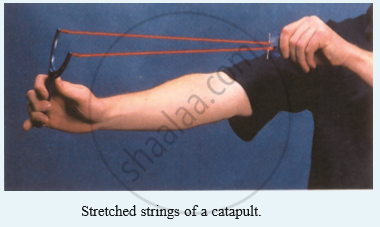
Give two examples where a body possesses both, kinetic energy as well as potential energy.
A ball of mass 0.5 kg slows down from a speed of 5 m/s so that of 3 m/s. Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the ball. State your answer giving proper units.
A stone is thrown upwards as shown in the diagram. When it reaches P, which of the following has the greatest value of the stone?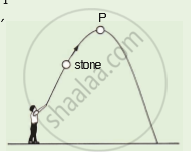
The hanging bob of a simple pendulum is displaced to one extreme position B and then released. It swings towards centre position A and then to the other extreme position C. In which position does the bob have :
(i) maximum potential energy?
(ii) maximum kinetic energy?
Which of the following energy change involves frictional force?
A girl with having a mass of 35 kg sits on a trolley of mass 5 kg. The trolley is given an initial velocity of 4 m s–1 by applying a force. The trolley comes to rest after traversing a distance of 16 m. (a) How much work is done on the trolley? (b) How much work is done by the girl?
