Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A hammer of mass 500 g, moving at 50 ms−1, strikes a nail. The nail stops the hammer in a very short time of 0.01 s. What is the force of the nail on the hammer?
उत्तर
The force of the nail on the hammer,
F = `"Change in momentum of hammer"/ "Time"`
F = `(m (v - u))/t`
F = `(0.50 kg (0 - 50 ms^-1))/(0.01 s)`
F = `(0.50 kg (0 - 50 ms^-1))/(0.01 s)`
F = -2500 N
The minus sign denotes the force that the nail applies to the hammer when it acts in the opposite direction of the hammer.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A 8000 kg engine pulls a train of 5 wagons, each of 2000 kg. along a horizontal track. If the engine exerts a force of 40000 N and the track offers a friction force of 5000 N, then calculate:
- the net accelerating force and
- the acceleration of the train.
An object of mass 100 kg is accelerated uniformly from a velocity of 5 ms−1 to 8 ms−1 in 6 s. Calculate the initial and final momentum of the object. Also, find the magnitude of the force exerted on the object.
A body of mass 5 kg is moving with a velocity of 10 m/s. A force is applied to it so that in 25 seconds, it attains a velocity of 35 m/s. Calculate the value of the force applied.
Name the law involved in the following situation:
a body of mass 5 kg can be accelerated more easily by a force than another body of mass 50 kg under similar conditions.
If a balloon filled with air and its mouth untied, is released with its mouth in the downward direction, it
moves upwards. Why ?
The acceleration produced by a force of 5 N acting on a mass of 20 kg in m/s2 is :
Newton’s III law is applicable
State Newton’s laws of motion?
Using the second law of motion, derive the relation between force and acceleration. A bullet of 10 g strikes a sand-bag at a speed of 103 m s-1 and gets embedded after travelling 5 cm. Calculate
(i) the resistive force exerted by the sand on the bullet
(ii) the time is taken by the bullet to come to rest.
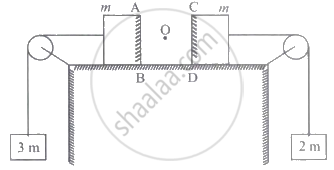
Two blocks each of mass m lie on a smooth table. They are attached to two other masses as shown in the figure. The pulleys and strings are light. An object O is kept at rest on the table. The sides AB and CD of the two blocks are plane and made reflecting. The acceleration of two images formed in those two reflecting surfaces with respect to each other is ______.