Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A homogeneous block floats on water (a) partly immersed (b) completely immersed. In each case state the position of centre of buoyancy B with respect to the centre of gravity G of the block.
उत्तर
When the body is partially immersed, its centre of buoyancy will be below the centre of gravity of the block.
When the body is completely immersed, its centre of buoyancy will coincide the centre of gravity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank with suitable word :
It is the................. force which makes objects appear lighter in water.
A body while floating sinks deeper in a liquid of low density than in a liquid of high density.
The density of a body which sinks in water is ......... than 1000 Kg m-3.
Name the S.I. unit of density. How is it related to g Cm-3?
How does the density of a body and that of a liquid determine whether the body will float or sink into that liquid?
State whether thrust is a scalar or vector?
The diagram below in Fig. 4.12 shows a device which makes the use of the principle of transmission of pressure.
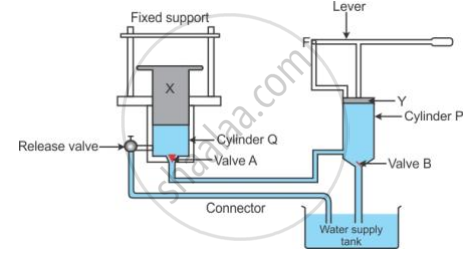
- Name the parts labelled by the letters X and Y.
- Describe what happens to valves A and B and to the quantity of water in the two cylinders when the lever arm is moved down.
- Give reasons for what happens to valves A and B in part (ii).
- What happens when the release valve is opened?
- What happens to valve B in cylinder P when the lever arm is moved up?
- Give a reason for your answer in part (v).
- State one use of the above device.
What is the cause of upthrust? At which point can it be considered to act?
Two spheres A and B, each of volume 100 cm3 is placed on water (density = 1.0 g cm-3). The sphere A is made of wood of density 0.3 g cm-3 and sphere B is made of iron of density 8.9 g cm-3.
- Find:
- The weight of each sphere, and
- The upthrust on each sphere.
- Which sphere will float? Give reason.
A beaker contains a liquid of density ‘ρ’ up to height ‘h’ such that ‘PA’ is atmospheric pressure and ‘g’ is the acceleration due to gravity. Answer the following questions:
- What is the pressure on the free surface of the liquid?
- What is the pressure on the base of the beaker?
- What is the lateral pressure at the base on the inner walls of the beaker?
