Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A market for a good is in equilibrium. The demand for the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change.
A market for a good is in equilibrium. There is 'increase' in demand for the good. Explain the chain of effects of this change
उत्तर
Consider DD to be the initial demand curve and SS to be the supply curve of the market. Market equilibrium is achieved at Point E, where the demand and supply curves intersect each other. Therefore, the equilibrium price is OP, and the equilibrium quantity demanded is OQ.
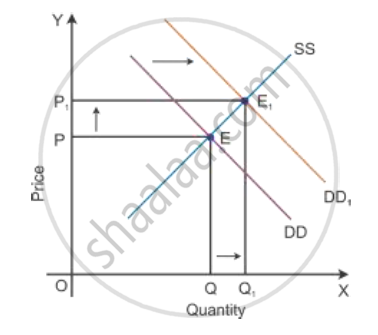
When there is an increase in income of consumers, consumers would tend to spend more on normal goods than the inferior goods where the prices of all goods, tastes and preferences remain constant. There will be a shift in the demand curve towards the right to DD1 with an increase in the demand, and the supply curve SS will remain the same. This implies that at the initial price OP1, there is an excess demand of OQ to OQ1 units at the initial price OP.
Because of an increase in the demand, there will be an increase in competition among buyers. So, they would be willing to pay more prices to obtain more units of a good in the market. Hence, there will be an increase in the market price to OP2. Now, the new market equilibrium will be at Point E1, where the new demand curve DD1 intersects the supply curve SS.
This clearly states that if the demand curve shifts towards the right, the price of the good tends to increase with an increase in the demand for a good. Thus, the direction of change in equilibrium price and quantity is the same whenever there is a shift in the demand curve.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "increase" both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on the market price
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "decrease" both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on market price
A market for a good is in equilibrium. The supply of good "decreases". Explain the chain of effects of this change
A market for a product is in equilibrium. Demand for the product "decreases." Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram
Explain its chain of effects on the market of that good. Use diagram
Draw average revenue and marginal revenue curves in a single diagram of a firm which can sell more units of a good only by lowering the price of that good. Explain.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an ‘increase’ in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
Explain market equilibrium.
What will happen if the price prevailing in the market is
(i) above the equilibrium price?
(ii) below the equilibrium price?
How are equilibrium price and quantity affected when income of the consumers increase.
Using supply and demand curves, show how an increase in the price of shoes affects the price of a pair of socks and the number of pairs of socks bought and sold.
How will a change in price of coffee affect the equilibrium price of tea? Explain the effect on equilibrium quantity also through a diagram.
Compare the effect of shift in the demand curve on the equilibrium when the number of firms in the market is fixed with the situation when entry-exit is permitted.
Considering the same demand curve as in exercise 22, now let us allow for free entry and exit of the firms producing commodity X. Also assume the market consists of identical firms producing commodity X. Let the supply curve of a single firm be explained as
qSf = 8 + 3p for p ≥ 20
= 0 for 0 ≤ p < 20
(a) What is the significance of p = 20?
(b) At what price will the market for X be in equilibrium? State the reason for your answer.
(c) Calculate the equilibrium quantity and number of firms.
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a fall in the price of substitute goods.
