Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A marriage between a colourblind man and a normal woman produces ____________.
पर्याय
All carrier daughters and normal sons
50% carrier daughters and 50% normal daughters
50% colourblind sons and 50% normal sons
All carrier offsprings
उत्तर
A marriage between a colourblind man and a normal woman produces All carrier daughters and normal sons.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give scientific reasons : Colour blindness is more common in men than in women.
Choose the correct answer:
A colour blind woman marries a normal man, in the progeny _________
A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart shown below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness in them.
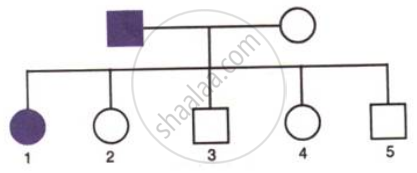
How many daughters and how many sons have been born in the family?
A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart shown below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness in them.
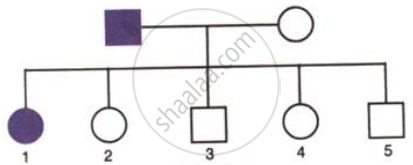
Name one other trait in humans which follows a similar pattern of inheritance.
Why do men suffer from hemophilia and colour blindness? Under what conditions do women suffer from these disorders?
Explain the Term Linkage.
Long answer type question.
Explain cris-cross inheritance with suitable example.
Explain the inheritance of sex-linked characters in human being.
If a woman has an allele for an X-Linked condition i.e. haemophilia, on one of her X chromosomes then this chromosome can be inherited by ______
Girl of normal vision whose father was colour blind marries a man of normal vision whose father was also colour blind. The sons of this marriage would be ______.
What would be the progeny obtained if a haemophilic male marries a female with normal blood clotting?
Identify the progeny produced if a colour blind male marries a normal vision female.
If a carrier woman marries a normal visioned man, what is the percentage possibility of sons being colourblind?
If a colour blind man marries a normal visioned woman, what is the percentage of offsprings showing colour blindness phenotypically?
Types of sex- linked genes:
(Haemophilia, Ichthyosis, nephritis, Myopia, Hypertrichosis, Retinitis pigmentosa)
| Column 'A' | Column 'B' | |
| (1) | Completely X- linked genes | ______ |
| (2) | Completely Y- linked | ______ |
| (3) | Incompletely sex-linked genes | ______ |
