Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A number of theories have been used to understand 'personality'. Discuss how efforts have been inade to categorise people into personality types since ancient times.
उत्तर
Type theory presumes that people can be categorised into a series of categories or types based on no overlapping characteristics.
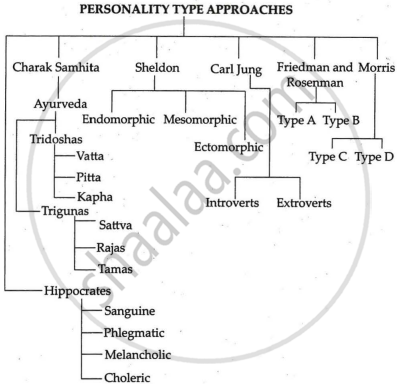
- Greek physician Hippocrates, regarded as the “father of modern medicine,” held that a person’s physical and mental health were interconnected. To extend his idea, he suggested four personality types based on the temperament’s major humour and fluids.
- Sanguine: cheerful, active and optimistic.
- Phlegmatic: touchy, sluggish, calm and apathetic.
- Melancholic: sad, broocling and morose.
- Choleric: irritable, hot-tempered and excitable.
- The three “Dashas”—Vata, Pitta, and Kapha—that make up the Indian discipline of medicine, known as Ayurveda, or Charak Samhita, are used to categorise persons.
- Based on qualities (gunas), there are three different types of personalities.
- Sattva: The qualities of sincerity, detachment, discipline, keen intelligence, self-control, and spirituality are included in the Sattva Guna.
- Rajas: Rajas Guna consists of some worldly characteristics, such as the need for instant gratification and a materialistic mindset. They are both inventive and envious.
- Tamas: The Tamas Guna is made up of all the vices in the world, including mental instability, rage, arrogance, laziness, etc.
Based on the physical constitution, Sheldon has categorised personalities.- Endomorphic: They are big, soft, and round, and they are relaxed and social, like eating and enjoying themselves.
- Mesomorphic: They have a rectangular, well-built body shape with a strong muscular structure. They are bold, energetic, assertive, and dominating.
- Ectomorphic: They have a body shape that is long, thin, and fragile. They are brainy, artistic, introvert and are fond of solitude and inward-looking.
- Carl Jung grouped all people into:
- Introverts: They are socially withdrawn, passive, quiet, cautious and reserved.
- Extroverts: Socially outgoing, talkative, impulsive and thrill-seeking.
- Meyer Friedman and Ray Rosenman (1974) identified psychological variables and suggested that individuals can be grouped into two personality types:
- Type-A: Type-A, coronary-prone behaviour pattern. They are never content, constantly pressed for time, overworked, and competitive.
- Type-B: The neutral behaviour pattern, often known as type B, is marked by an easygoing, relaxed way of life.
-
More recent research by Morris has suggested Type-C and Type-D personalities.
-
Type-C personalities are cancer-prone and are defined by their lack of aggressiveness, suppression of anger, and submission to external authorities to avoid disputes.
-
Type-D personalities are generally pessimistic and prone to depression.
-
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is trait approach to personality?
How would Horney’s explanation of depression be different from that of Alfred Adler?
What is the main proposition of humanistic approach to personality? What did Maslow mean by self-actualisation?
Which of the following lists presents Freud’s psychosexual stages in the order in which they occur?
Two statements are given in the question below as Assertion (A) and Reasoning (R).
Assertion (A): A person who has strong aggressive tendencies may see other people as being excessively aggressive towards him/her.
Reason (R): People adopt an ego defense mechanism called projection in which they attribute their own traits to others.
An individual’s sole concern with the satisfaction of __________ needs would reduce him/her to the level of animals.
The ____________ focuses on the specific psychological attributes along which individuals tend to differ in consistent and stable ways.
Sixteen Personality Factor (16 PF) Questionnaire was developed by ____________.
Which is the correct sequence of the stages involved in creative thinking?
The b coefficient obtained in multiple regression is
Which of the following is considered to be the most promising empirical approach to the study of personality?
______ is a state of preparedness or alertness.
Self is conceptualized in Western and Eastern perspectives on personality, respectively, as:
______ is the ability to adjust satisfactorily to the various strains of the environment we meet in life and mental hygiene is the means we take to assure this adjustment.
Who first attempted to describe personality traits in terms of Lexi can descriptors?
The view that "adjustment differs from maladjustment in degree rather than in kind" is psychologically
According to Freud, children pass through all the following psychosexual stages of development except
Who said that two major components of "person's" psychology were the twin notions of basic anxiety and basic hostility?
Spranger's typology is based on man's ______
WAT was devised by ______
Dr. Maki questioned a group of 9th graders about their career aspirations. This is an example of an ______
The ______ focuses on the specific psychological attributes along which individuals tend to differ in consistent and stable ways.
The ______ are stable and are considered the building blocks of personality.
Amit throws temper tantrums every time he goes to the market with his parents. He insists that they buy him a new toy every time. Identify the most suitable behavioural technique to modify this unwanted behaviour.
How does trait differ from type approach?
