Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A pea plant with blue colour flower denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flower denoted by ww.
(a) What is the expected colour of the flowers in their F1 progeny?
(b) What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flower in F2 generation, when the flowers of F1 plants were selfed?
(c) State the expected ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
उत्तर
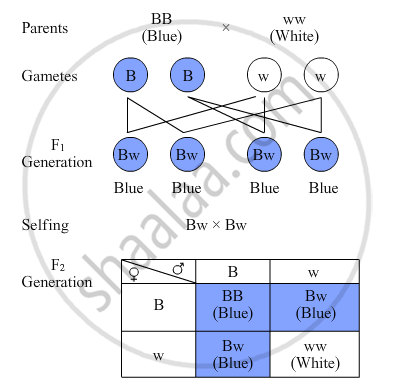
(a) The expected colour of flowers in their F1 progeny is blue.
(b) 1/4 of the F2 generation have white flowers. So, we can calculate the percentage as follows:-
1/4 × 100 = 25%
Hence, the percentage of plants bearing white flowers in F2 progeny is 25.
(c) The ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny is 1 (BB) : 2 (Bw).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Mendel crossed tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants in his experiment. Write his observations giving reason on the F1 and F2 generations.
With the help of two suitable examples, explain why certain experiences and traits earned by people during their lifetime are not passed on to their next generations. When can such traits be passed on?
Name the scientist who gave the laws of inheritance.
It it an example of monohybrid cross or dihybrid cross?
How do Mendel's experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
For his experiments on heredity, Mendel used :
papaya plants
potato plants
pea plants
pear plants
A red-haired woman marries a brown-haired man, and all the children are brown haired. Explain this genetically.
Define Heredity. Give two examples.
If a round, green seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY) the seeds produced in F1 generation are
A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (VV) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (vv) flowers will be ______.
