Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
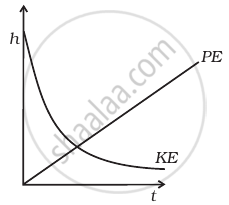
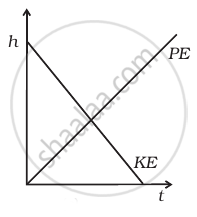
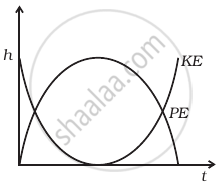
A raindrop falling from a height h above ground, attains a near terminal velocity when it has fallen through a height (3/4)h. Which of the diagrams shown in figure correctly shows the change in kinetic and potential energy of the drop during its fall up to the ground?
पर्याय
उत्तर
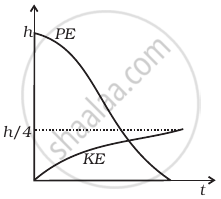
Explanation:
At height h from the ground, raindrops have maximum potential energy. And kinetic velocity will be zero (at the instant when it dropped its velocity will be zero), then as the raindrop falls its PE starts decreasing and kinetic energy starts increasing.
The total mechanical energy will remain conserved if we neglect the air resistance. If there is some air resistance, there is some force called upthrust (in fluids) which opposes its motion. It depends upon the velocity of object as the velocity increases, upthrust also increases. Hence during the fall of raindrops first its velocity increases and then becomes constant after some time.
This constant velocity is called terminal velocity, hence KE also becomes constant. PE decreases continuously as the drop is falling continuously.