Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit.
उत्तर
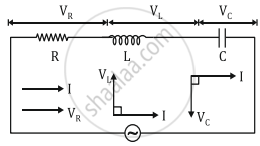 LCR Circuit |
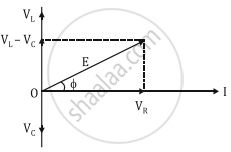 |
E = E0 sinωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Since all three of them are connected in series the current through them is the same. But the voltage across each element has a different phase relation with the current.
The potential difference VL, VC and VR across L, C and R at any instant is given by VL = IXL, VC = IXC and VR = IR, where I is the current at that instant.
VR is in phase with I. VL leads I by 90° and VC lags behind I by 90° so the phasor diagram will be as shown Assuming VL > VC, the applied emf E which is equal to the resultant of the potential drop across R, L & C is given as
`E^2 = I^2[R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2]`
Or I = `E/sqrt[[R^2 + (X_L - X_C)^2]` = `E/Z`, Where Z is Impedance.
Emf leads current by a phase angle φ as `tanφ = (V_L - V_C)/R = (X_L - X_C)/R`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(i) Find the value of the phase difference between the current and the voltage in the series LCR circuit shown below. Which one leads in phase : current or voltage ?
(ii) Without making any other change, find the value of the additional capacitor C1, to be connected in parallel with the capacitor C, in order to make the power factor of the circuit unity.
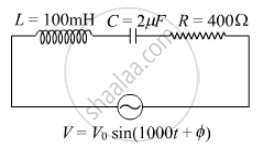
The time constant of an LR circuit is 40 ms. The circuit is connected at t = 0 and the steady-state current is found to be 2.0 A. Find the current at (a) t = 10 ms (b) t = 20 ms, (c) t = 100 ms and (d) t = 1 s.
An LR circuit with emf ε is connected at t = 0. (a) Find the charge Q which flows through the battery during 0 to t. (b) Calculate the work done by the battery during this period. (c) Find the heat developed during this period. (d) Find the magnetic field energy stored in the circuit at time t. (e) Verify that the results in the three parts above are consistent with energy conservation.
Answer the following question.
What is the phase difference between the voltages across the inductor and the capacitor at resonance in the LCR circuit?
Answer the following question.
Draw the diagram of a device that is used to decrease high ac voltage into a low ac voltage and state its working principle. Write four sources of energy loss in this device.
A series LCR circuit with L = 0.12 H, C = 480 nF, R = 23 Ω is connected to a 230 V variable frequency supply.
(a) What is the source frequency for which current amplitude is maximum. Obtain this maximum value.
(b) What is the source frequency for which average power absorbed by the circuit is maximum. Obtain the value of this maximum power.
(c) For which frequencies of the source is the power transferred to the circuit half the power at resonant frequency? What is the current amplitude at these frequencies?
(d) What is the Q-factor of the given circuit?
In series LCR circuit, the phase angle between supply voltage and current is ______.
In an LCR circuit having L = 8 henery. C = 0.5 µF and R = 100 ohm in series, the resonance frequency in radian/sec is
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator ______.
When an alternating voltage of 220V is applied across device X, a current of 0.25A flows which lags behind the applied voltage in phase by π/2 radian. If the same voltage is applied across another device Y, the same current flows but now it is in phase with the applied voltage.
- Name the devices X and Y.
- Calculate the current flowing in the circuit when the same voltage is applied across the series combination of X and Y.
