Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A shift in demand curve has a larger effect on price and smaller effect on quantity when the number of firms is fixed compared to the situation when free entry and exist is permitted. Explain.
उत्तर
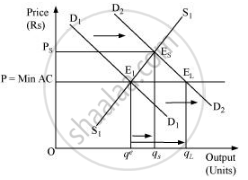
The above figure depicts both the cases when the number of firms is fixed (in short run) and when the number of firms is not fixed (in long run). P = min AC represents the long run price line; D1D1 and D2D2 represents the demand in the short run and the long run respectively. The point E1 represents the initial equilibrium, where the demand and the supply intersect each other.
Let us suppose that the demand curve shifts, assuming that the number of firms is fixed. Now, the new equilibrium will be at ES (as it is short run equilibrium), where the supply curve and the demand curve D2D2 intersect each other. The equilibrium price is Ps and equilibrium quantity is qs.
On the other hand, under the assumption of free entry and exit, an increase in demand will shift the demand curve rightwards to D2D2. The new equilibrium will be at E2 (as it is a long run equilibrium) with the equilibrium price P = min AC and equilibrium quantity qL.
Therefore, on comparing both the cases, we find that when the firms are given the freedom of entry and exit, the equilibrium price remains the same. The price is lower than that of the short run equilibrium price (Ps); whereas, the long run equilibrium quantity (qL) is more than that of the short run equilibrium quantity (qs).
Similarly, for the leftward demand shift, it can be found that the short run equilibrium price (Ps) is lower than the long run equilibrium price and the short run equilibrium quantity (qs) in less than the long run equilibrium quantity (qL).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain how changes in prices of other products influence the supply of a given product.
Explain the effect of Change in own price
Explain the effect of change in price of substitute on demand of a good.
Assuming that 'increase' in investment is Rs 900 crore and marginal propensity to consume
is 0.6. explain the working of the multiplier.
How is the demand for a good affected by a rise in the prices of other goods? Explain.
Why is the demand curve of a firm under monopolistic competition more elastic than under monopoly? Explain.
When do we say that there is an excess demand for a commodity in the market?
When do we say that there is an excess supply for a commodity in the market?
Suppose the demand and supply curve of commodity X in a perfectly competitive market are given by:
qD = 700 − p
qS = 500 + 3p for p ≥ 15
= 0 or 0 ≤ p 15
Assume that the market consists of identical firms. Identify the reason behind the market supply of commodity X being zero at any price less than Rs 15. What will be the equilibrium price for this commodity? At equilibrium, what quantity of X will be produced?
Fill up the blank.
The shape of the average revenue curve under perfect competition would be ____________.
