Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A space craft flying in a straight course with velocity of 75 km s-1 fires its rocket motors for 6.0 s. At the end of this time its speed is 120 km s-1 in the same direction.
Find
(i) The space craft's average acceleration while the motors were firing
(ii) The distance travelled by the space craft in the first 10 s after the rocket motors were started, the motors being in action for only 6 s.
उत्तर
Given, the initial velocity u = 75 km/s
Final velocity v = 120 km/s
Time taken = 6 s
(i) Acceleration = (Final velocity - Initial velocity)/time taken
= [(120 - 75)/6] kms-2
= (45/6) kms-2
= 7.5 kms-2
(ii) Distance travelled by the aircraft in the first 10 s = Distance travelled in the first 6 s + Distance travelled in the next 4 s.
Distance travelled in the first 6s (S1) = ut + (1/2) at2
(S1) = ut + (1/2) at2
(S1) = (75)(6) + (1/2) (7.5)(6)2
(S1) = 450 + 135
(S1) = 585 km
Distance travelled in the next 4 s (S2) = Speed × time
Speed at the end of 6 s is 120 km/s.
(S2) = (120) (4)
(S2) = 480 km
Thus, the distance travelled by the aircraft in the first 10 s = (S1) + (S2) = 585 + 480 = 1065 km.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give one example of the following motion:
Uniform retardation
Draw a graph for acceleration against time for a uniformly accelerated motion. How can it be used to find the change in speed in a certain interval of time?
Figure given below shows a velocity-time graph for a car starting from rest. The graph has three parts AB, BC and CD.
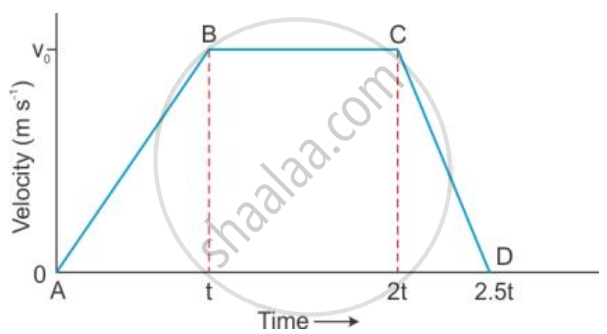
(a) Is the magnitude of acceleration higher or lower than that of retardation ? Give a reason .
(b) Compare the magnitude of acceleration and retardation .
A ball is rolling from A to D on a flat and smooth surface. Its speed is 2 cm/s. On reaching B, it was pushed continuously up to C. On reaching D from C, its speed had become 4 cm/s. It took 2 seconds for it to go from B to C. What is the acceleration of the ball as it goes from B to C?
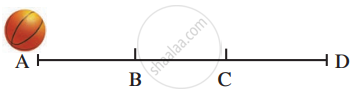
From the diagram given below, calculate acceleration.

A cyclist driving at 5 ms−1, picks a velocity of 10 ms−1, over a distance of 50 m. Calculate
- acceleration
- time in which the cyclist picks up above velocity.
What is the SI unit of acceleration?
Figure represents graphically the velocity of a car moving along a straight road over a period of 100 hours.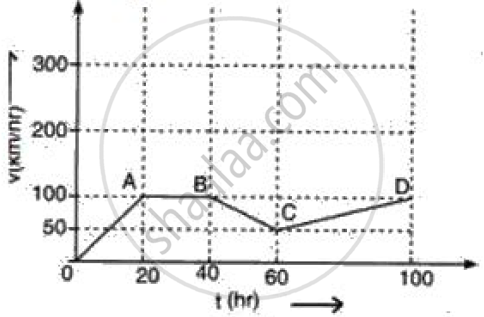
Calculate the acceleration along AB and the retardation along BC.
The speed of a particle is constant. Will it have acceleration? Justify with an example.
What is the difference between uniform acceleration and non–uniform acceleration?
