Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student suffering from myopia is not able to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m. List two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen. With the help of ray diagrams, explain
(i) why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.
(ii) the type of the corrective lens used to restore proper vision and how this defect is corrected by the use of this lens.
(b) If, in this case, the numerical value of the focal length of the corrective lens is 5 m, find the power of the lens as per the new Cartesian sign convention
उत्तर
Two possible reasons due to which this defect of vision may have arisen are
(a) increase in curvature of the lens
(b) increase in length of the eyeball
(i) A myopic eye has its far point nearer than infinity. It forms the image of a distant object in front of its retina as shown in the figure given below. In the given case student's far point is 5 m. So, image of the object placed beyond 5 m from his eyes is formed in front of the retina and hence appears blurred. That is why the student is unable to see distinctly the objects placed beyond 5 m from his eyes.

(ii) Since a concave lens has an ability to diverge incoming rays, it is used to correct this defect of vision. The image is allowed to form at the retina by using a concave lens of suitable power as shown in the given figure.
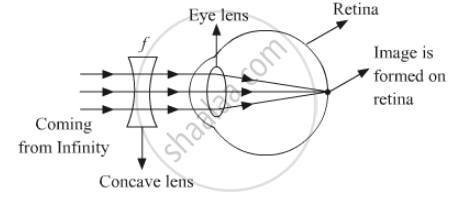
(b) Power of the required corrective lens (P) =`1/(f("in m"))`
`P =− 1/5 `
`P= −0.2 D`
Hence, the power of corrective lens is -0.2 D.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the far point of a person suffering from myopia (or short-sightedness)?
A man can read the number of a distant but clearly but he finds difficulty in reading a book.
From which defect of the eye is he suffering?
What is long-sightedness? State the two causes of long-sightedness (or hypermetropia). With the help of ray diagrams, show:
(i) the eye-defect long-sightedness.
(ii) correction of long-sightedness by using a lens.
An eye has a near point distance of 0.75 m. What sort of lens in spectacles would be needed to reduce the near point distance to 0.25 m? Also calculate the power of lens required. Is this eye long-sighted or short-sighted?
The near point of a long-sighted person is 50 cm from the eye.
(a) Can she see clearly an object at:
(i) a distance of 20 cm?
(ii) at infinity?
Enumerate the common defects of vision, their causes and the possible methods of correcting them.
A person cannot read newspaper placed nearer than 50 cm from his eyes. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this defect. List its two possible causes. Draw a ray diagram to show how this defect may be corrected using a lens of appropriate focal length.
What is Hypermetropia (far sightedness)?
Differentiate the eye defects: Myopia and Hypermetropia
When do we consider a person to be myopic or hypermetropic? Explain using diagrams how the defects associated with myopic and hypermetropic eye can be corrected?
