Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A unicellular animal P having no fixed shape ingests a food particle by forming temporary finger-like projections Q. The food particle is engulfed with a little surrounding water to form a temporary stomach R inside it. The chemicals S from surrounding cytoplasm enter into R and break down food into small and soluble molecules by chemical reactions. The digested food is absorbed directly into cytoplasm by the process T. The undigested food is thrown out of the body by the rupture of a cell organelle U in a process called V.
(a) Name the unicellular animal P.
(b) What are (i) Q, and (ii) R?
(c) Name (i) chemical S, and (ii) process T.
(d) Name (i) organelle U, and (ii) process V.
उत्तर
(a) The unicellular animal P isAmoeba.
(b) (i) Q is pseudopodia and (ii) R is the food vacuole.
(c) (i) Chemical S is the digestive enzyme and (ii) process T is diffusion.
(d) (i) Organelle U is cell membrane and (ii) process V is egestion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
All the animals can be divided into three groups on the basis of their eating habits. Name the three groups.
What is the scientific name of the animals which is only meat eaters?
What is the scientific name of the animals which is only plant eaters?
How does Amoeba engulf the food particle?
What is common for Cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Classify the following into herbivores, carnivores and omnivores:
Lion, Man, dog, Goat, Crow, Elephant, Snake, Hawk, Rabbit, Deer
X is a wild animal which eats only the flesh of other animals whereas Y is a domestic animal which feeds mainly on green grass.
(a) What are animals like X known as?
(b) What are animals Y known as?
(c) Which animal, X or Y, has a longer small intestine? Why?
(d) Name one animal which is like X.
(e) Name one animal which is like Y.
What type of arrangement exists in the bodies of large animals to meet their oxygen requirements adequately?
In the expriment of preparing a temporary mount of a leaf peel to observe stomata, we use two liquids other than water. Name these two liquids and state when and why these liquids are used.
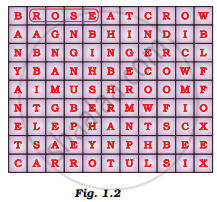
Spot as many organisms as possible in the puzzle given in Figure 1.2 by encircling them as shown. Write the names on a sheet of paper and categorise them into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Classify the heterotrophs into herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and saprophytes.