Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
According to the third law of motion, when we push on an object, the object pushes back on us with an equal and opposite force. If the object is a massive truck parked along the roadside, it will probably not move. A student justifies this by answering that the two opposite and equal forces cancel each other. Comment on this logic and explain why the truck does not move.
उत्तर
- The truck has a large mass. Therefore, the static friction between the truck and the road is also very high.
- To move the car, one has to apply more force more than the static friction. Therefore, when someone pushes the truck and the truck does not move, then it can be said that the applied force in one direction is cancelled out by the frictional force of equal amount acting in the opposite direction.
- Therefore, a large, unbalanced force is required to move the truck.
- Therefore, the student is right in justifying that the two opposite and equal cancel each other.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If action is always equal to the reaction, explain how a horse can pull a cart.
A stone of 1 kg is thrown with a velocity of 20 m s−1 across the frozen surface of a lake and comes to rest after travelling a distance of 50 m. What is the force of friction between the stone and the ice?
What is the force which produces an acceleration of 1 m /s2 in a body of mass 1 kg ?
A girl weighing 25 kg stands on the tloor. She exerts a downward force of 250 N on the floor. What force does the floor exert on her ?
If action is always equal to reaction, explain why a cart pulled by a horse can be moved.
Do action and reaction act on the same body or different bodies ? How are they related in magnitude and direction ? Are they simultaneous or not ?
Explain why, a runner presses the ground with his feet before he starts his run.
According to the third law of motion, action and reaction :
Give a scientific reason.
Even though the magnitudes of action force and reaction forces are equal and their directions are opposite, their effects do not get cancelled.
Consider a frame that is made up of two thin massless rods AB and AC as shown in the figure. A vertical force `vec"P"` of magnitude 100 N is applied at point A of the frame.
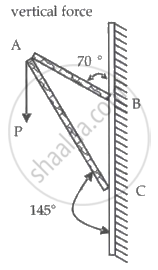
Suppose the force is `vec"P"` resolved parallel to the arms AB and AC of the frame.
The magnitude of the resolved component along the arm AC is xN.
The value of x, to the nearest integer, is ______.
[Given: sin(35°) = 0.573, cos(35°) = 0.819, sin(110°) = 0.939, cos(110°) = –0.342]
