Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An alternating current I = 14 sin (100 πt) A passes through a series combination of a resistor of 30 Ω and an inductor of `(2/(5pi))` H. Taking `sqrt2` = 1.4 calculate the rms value of the voltage drops across the resistor and the inductor.
उत्तर
Given: I = 14 sin (100 πt) A, R = 30 Ω, L = `2/(5pi)`H
From here
ω = 100π
`X_L = omegaL` (inductive reactance)
= `100pi xx 2/(5pi) = 40Omega`
Impedance, Z = `sqrt(R^2 + X_L^2) = sqrt((30)^2 + (40)^2)`
Z = `sqrt(900 + 1600) = 50Omega`
`V_{rms} = I_{rms} xx Z`
We know `I_{rms} = I_0/sqrt2 = 14/1.4 = 10A`
So, `V_{rms} = 10 xx 50`
`V_{rms} = 10 xx 50`
`V_{rms}` = 500V
The voltage drop across the resistor,
`V_R = I_{rms} xx R`
= `10 xx 30`
= 300V
The voltage drop across the inductor,
`V_L = I_{rms} xx X_2`
= `10 xx 40`
= 400V
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a series RL circuit, the resistance and inductive reactance are the same. Then the phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is
How will you define RMS value of an alternating current?
What do you mean by resonant frequency?
Predict the polarity of the capacitor in a closed circular loop when two bar magnets are moved as shown in the figure.

Which of the following graphs represent the variation of current(I) with frequency (f) in an AC circuit containing a pure capacitor?
In an a.c circuit, peak value of voltage is 423 volts, its effective voltage is ______.
For a series LCR circuit, I vs ω curve is shown:
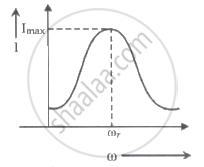
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly capacitive.
- To the left of ωr, the circuit is mainly inductive.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is equal to the resistance of the circuit.
- At ωr, impedance of the circuit is 0.
An inductor of 0.5 mH, a capacitor of 200 µF, and a resistor of 2Ω are connected in series with a 220V ac source. If the current is in phase with the emf, the frequency of ac source will be ______ × 102 Hz.
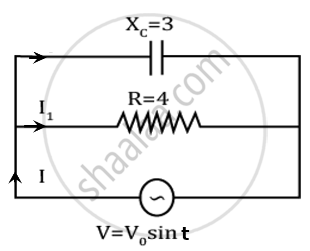
A capacitor and resistor are connected with an AC source as shown in figure. Reactance of capacitor is XC = 3 Ω and resistance of resistor is 4 Ω. Phase difference between current I and I1 is approx ______.
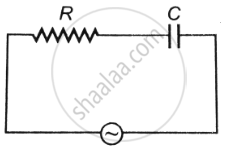
A 50 Hz AC source of 20 volts is connected across R and C as shown in figure. The voltage across R is 12 volt. The voltage across c is ______.