Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An extended object is placed at a distance of 5.0 cm from a convex lens of focal length 8.0 cm. (a) Draw the ray diagram (to the scale) to locate the image and from this, measure the distance of the image from the lens. (b) Find the position of the image from the lens formula and see how close the drawing is to the correct result.
उत्तर
Given,
Object distance, (u) = 5.0 cm
Focal length (f) of convex lens = 8.0 cm
(a)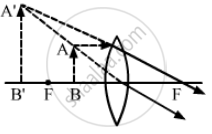
(b)
Using lens formula: \[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{u} = \frac{1}{f}\]
Where v is the image distance,
on putting the given values we get:
\[\frac{1}{v} - \frac{1}{\left( - 5 \right)} = \frac{1}{8}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = \frac{1}{8} - \frac{1}{5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{v} = \frac{- 3}{40}\]
\[ \therefore v = - 13 . 3 \text{ cm }\]
Hence, the position of the image from the lens is 13.3 cm.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What type of wavefront will emerge from a (i) point source, and (ii) distance light source?
The equation of refraction at a spherical surface is \[\frac{\mu_2}{\nu} - \frac{\mu_1}{\mu} = \frac{\mu_2 - \mu_1}{R}\]
Taking \[R = \infty\] show that this equation leads to the equation
\[\frac{\text{ Real depth }}{\text{ Apparent depth }} = \frac{\mu_2}{\mu_1}\]
for refraction at a plane surface.
A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. Find the location and nature of the image if a point object is placed on the principal axis at a distance of (a) 9.8 cm, (b) 10.2 cm from the lens.
A slide projector has to project a 35 mm slide (35 mm × 23 mm) on a 2 m × 2 m screen at a distance of 10 m from the lens. What should be the focal length of the lens in the projector?
A converging lens of focal length 15 cm and a converging mirror of focal length 10 cm are placed 50 cm apart with common principal axis. A point source is placed in between the lens and the mirror at a distance of 40 cm from the lens. Find the locations of the two images formed.
A 5 mm high pin is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. A second lens of focal length 5 cm is placed 40 cm from the first lens and 55 cm from the pin. Find (a) the position of the final image, (b) its nature and (c) its size.
A point object is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a convex lens. The image is formed on the other side at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. When a concave lens is placed in contact with the convex lens, the image shifts away further by 30 cm. Calculate the focal lengths of the two lenses.
A ball is kept at a height h above the surface of a heavy transparent sphere made of a material of refractive index μ. The radius of the sphere is R. At t = 0, the ball is dropped to fall normally on the sphere. Find the speed of the image formed as a function of time for \[t < \sqrt{\frac{2h}{g}}\] . Consider only the image by a single refraction.
Define the term 'focal length of a mirror'.
According to new Cartesian sign conventions, all the distances are measured from the ______.
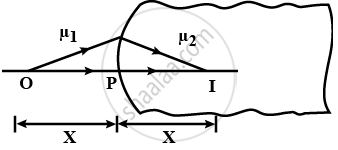
A spherical surface of radius R separates two medium of refractive indices µ1 and µ2, as shown in figure. Where should an object be placed in the medium 1 so that a real image is formed in medium 2 at the same distance?
Define the critical angle for a given pair of media and total internal reflection. Obtain the relation between the critical angle and refractive index of the medium.
A point object in the air is placed symmetrically at a distance of 60 cm in front of a concave spherical surface with a refractive index of 1.5. If the radius of curvature of the surface is 20 cm, find the position of the image formed.
Obtain an expression for refraction at a single convex spherical surface, i.e., the relation between μ1 (rarer medium), μ2 (denser medium), object distance u, image distance v and the radius of curvature R.
Assertion: If critical angle of glass-air pair `("μg" = 3/2)` is θ1 and that of water-air pair `("μw" = 4/3)` is θ2, then the critical angle for the water-glass pair will lie between θ1 and θ2.
Reason: A medium is optically denser if its refractive index is greater.
