Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An object of height 4.0 cm is placed at a distance of 30 cm from the optical centre 'O' of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw a ray diagram to find the position and size of the image formed. Mark optical centre 'O' and principal focus 'F' on the diagram. Also find the approximate ratio of size of the image to the size of the object.
उत्तर
Given that ,
u = -30 cm
f = 20 cm
v = ?
Using lens formula, we get
`1/f = 1/v - 1/u`
`=> 1/20 = 1/v - 1/(-30)`
`=> 1/v = (3-2)/60`
=> v = 60 cm
So the image will be formed at a distance of 60 cm from the lens as shown in the figure given below.

Now using magnification formula we can write,
`m = v/u = h_"image"/h_"object"`
`=> 60/(-30) = h_"image"/4`
`=> h_"image"` = -8 cm
The negative sign shows that the image formed will be inverted and real. The ratio of size of the image to the size of the object is `8/4 = 2`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If you focus the image of a distant object, whose shape is given below, on a screen using a convex lens, the shape of the image of this object on the screen would be:
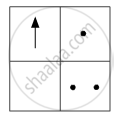
(a)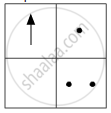
(b)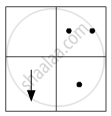
(c)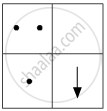
(d)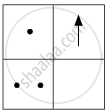
What type of lens would you use as a magnifying glass? How close must the object be to the lens?
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed in front of a convex lens between focus and optical centre. State three characteristics of the image formed.
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
Which part causes the greatest convergence?
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
What happens to the image formed by a convex lens if its lower part is blackened?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to form an inverted and enlarged image? Will the image be real or virtual? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate your answer.

A candle is placed between f and 2f a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram showing the position of the image.
