Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define progressive wave.
उत्तर
Waves in which a disturbance created at one place travels to distant points and keeps travelling unless stopped by an external force are known as travelling or progressive waves.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer briefly.
Draw a wave and indicate points which are
- in phase
- out of phase
- have a phase difference of `pi/2`
Answer briefly.
Define the relation between velocity, wavelength and frequency of the wave.
Answer briefly.
Explain what is meant by phase of a wave.
Solve the following problem.
A certain sound wave in air has a speed 340 m/s and wavelength 1.7 m for this wave, calculate
- the frequency
- the period
Solve the following problem.
A tuning fork of frequency 170 Hz produces sound waves of wavelength 2 m. Calculate the speed of sound.
Sound wave A has period 0.015 s, sound wave B has a period of 0.025 s. Which sound has greater frequency?
Two sinusoidal plane waves of the same frequency having intensities I0 and 4I0 are travelling in the same direction. The resultant intensity at a point at which waves meet with a phase difference of zero radians is ______
Two waves of the same amplitude superimpose to produce two beats per second. What is the ratio of minimum loudness to that of one of the waves?
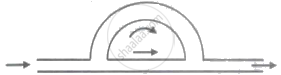
Sound waves are passing through two routes one in straight path and the other along a semicircular path of radius r and are again combined into one pipe and superposed as shown in the figure. If the velocity of sound waves in the pipe is v, then frequencies of resultant waves of maximum amplitude will be integral multiples of ______.
In frequency modulated wave ______.
The wave of the wavelength 30 cm and frequency 100 Hz will be ______.
When the kinetic energy of an electron is increased, the wavelength of the associated wave will ______.
A progressive wave of frequency 50 Hz is travelling with velocity 350 m/s through a medium. The change in phase at a given time interval of 0.01 s is ______.
When the observer moves towards a stationary source with velocity V1, the apparent frequency of emitted note is F1. When observer moves away from the source with velocity V1, the apparent frequency is F2. If V is the velocity of sound in air and `"F"_1/"F"_2=2` then `"V"/"V"_1` is equal to ______.
The displacement-time graphs of two particles A and B are straight lines making angles of 30° and 60° respectively with the time axis. If the velocity of A is vA and that of B is vB, the value of vA/vB is ______.
The wavelength of two waves are 50 and 51 cm respectively. If the temperature of the room is 20°C then what will be the number of beats produced per second by these waves, when the speed of sound at 0°C is 332 m/s?
In communication system, the process of superimposing a low frequency signal on a high frequency wave is known as ______.
A source of 300 Hz frequency, an observer and a wind are moving as shown in the figure with respect to the ground. The frequency heard by observation is ______.
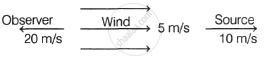
(Take, the speed of sound in air = 340 m/s)
An astronaut is approaching the moon. He sends out a radio signal of frequency 5000 MHz and the frequency of echo is different from that of the original frequency by 100 kHz. His velocity of approach wrt, to the moon, is ______.
A progressive wave of frequency 500 Hz is travelling with a velocity of 360 m/s. How far apart are two points 60° out of phase?
Wave of frequency 500 Hz has a phase velocity 360 ms-1. The phase difference between two displacement at a certain point at time 10-3 s apart will be ______.
