Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following.
Explain in detail free radical mechanism involved during preparation of addition polymer.
उत्तर
The free radical mechanism is most common in addition to polymerization. It is also called a chain reaction which involves three distinct steps. These are as follows:
i) Step 1: Chain initiation:
a. The chain reaction is initiated by a free radical which is formed from an initiator (catalyst) such as benzoyl peroxide, acetyl peroxide, tert-butyl peroxide, etc.
b. For example, acetyl peroxide generates methyl radical as shown below:
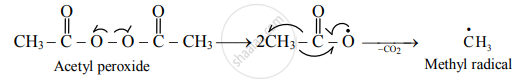
c. The free radical (say `"R"^•`) so formed attaches itself to the olefin (vinyl monomer) and produces a new radical, made up of two parts, namely, the attached radical and the monomer unit.
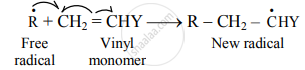
ii. Step 2: Chain propagation:
a. The new radical formed in the initiation step reacts with another molecule of vinyl monomer, forming another still bigger sized radical, which in turn reacts with another monomer molecule.
b. The repetition of this sequence takes place very rapidly. It is called chain propagation.
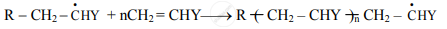
c. This step is very rapid and leads to high molecular mass radical.
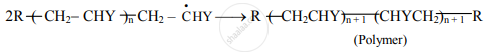
iii. Step 3: Chain termination:
a. At some stage, termination of the growing chain takes place. It may occur by several processes.
b. One mode of termination is by combination of two growing chain radicals.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are polymers classified on the basis of polymerisation process?
Answer the following in one sentence.
Give one example each of copolymer and homopolymer.
Answer the following.
Classify the following polymers as natural and synthetic polymers
- Cellulose
- Polystyrene
- Terylene
- Starch
- Protein
- Silicones
- Orlon (Polyacrylonitrle)
- Phenol-formedehyde resins
Answer the following.
Distinguish between thermosetting and thermoplastic resins. Write example of both the classes.
Attempt the following:
Classify the following polymer as straight-chain, branched-chain and cross-linked polymers.
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{- (CH2 - CH -)_\text{n}}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\\ce{\phantom{.......}CN}\end{array}\]
Attempt the following:
Classify the following polymer as straight-chain, branched-chain and cross-linked polymers.

Functional group present in terylene polymer is ______.
Explain homopolymers with examples.
Define fibres.
Which polymer from following is used as synthetic leather?
Which of the following properties is of the thermosetting polymers?
Identify the monomers used in the preparation of glyptal.
Which of the following is a natural polymer?
Which of the following pair represents natural polymers?
Which of the following compounds contain -CO-NH- linkage?
Which among the following polymers belongs to the class elastomers?
Which of the following properties is of thermoplastic polymer?
The polymer used in making handles of cookers and frying pans is ______.
The polymer used in making synthetic hair wigs is made up of ______.
Which of the following is a thermosetting polymer?
A synthetic polymer which is an ester is ______.
Define Polymers.
Write the classification of polymers on the basis of intermolecular forces.
What are homopolymers Give one example of homopolymers.
