Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between conservative and nonconservative forces.
उत्तर
| Conservative force | Non-conservative force | |
| 1. | If work done by or against a force is independent of the actual path, the force is said to be a conservative force. | If work done by or against a force is dependent of the actual path, the force is said to be a non- conservative force. |
| 2. | During work done by a conservative force, the mechanical energy is conserved. | During work done by a nonconservative force, the mechanical energy may not be conserved. |
| 3. | Work done is completely recoverable. | Work done is not recoverable. |
| 4. | Example: gravitational force, magnetic force etc. | Example: Frictional force, air drag etc. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
In the following table, every entry on the left column can match with any number of entries on the right side. Pick up all those and write respectively against A, B, C and D.
| Name of the force | Type of the force | ||
| A | Force due to tension in a string | P | EM force |
| B | Normal force | Q | Reaction force |
| C | Frictional force | R | Conservative force |
| D | Resistive force offered by air or water for objects moving through it. | S | Non-conservative force |
Find the odd man out:
Answer the following question.
You are sitting next to your friend on ground. Is there any gravitational force of attraction between you two? If so, why are you not coming together naturally? Is any force other than the gravitational force of the earth coming in the picture?
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between real and pseudo force.
Answer the following question.
Distinguish between contact and non-contact forces
Answer the following question.
State the formula for calculating work done by a force. Are there any conditions or limitations in using it directly? If so, state those clearly. Is there any mathematical way out for it? Explain.
40000 litre of oil of density 0.9 g/cc is pumped from an oil tanker ship into a storage tank at 10 m higher level than the ship in half an hour. What should be the power of the pump?
Solve the following problem.
Power is the rate of doing work or the rate at which energy is supplied to the system. A constant force F is applied to a body of mass m. Power delivered by the force at time t from the start is proportional to ______.
Derive the expression for power in terms of F, m, and t.
Solve the following problem.
Derive the expression for power in terms of F, m, and t.
Variation of a force in a certain region is given by F = 6x2 – 4x – 8. It displaces an object from x = 1 m to x = 2 m in this region. Calculate the amount of work done.
Solve the following problem.
In the following table, every item on the left side can match with any number of items on the right-hand side. Select all those.
| Types of collision | Illustrations | ||
| a. | Elastic collision | i. | A ball hit by a bat. |
| b. | Inelastic collision | ii. | Molecular collisions responsible for pressure exerted by a gas. |
| c. | Perfectly inelastic collision | iii. | A stationary marble A is hit by marble B and the marble B comes to rest. |
| d. | Head-on collision | iv. | A blob of clay dropped on the ground sticks to the ground. |
| v. | Out of anger, giving a kick to a wall. | ||
| vi. | A striker hits the boundary of a carrom board in a direction perpendicular to the boundary and rebounds. | ||
Two spheres of masses m and M are situated in air and the gravitational force between them is F. The space around the masses is now filled with a liquid of specific gravity 3. The gravitational force will now be ______
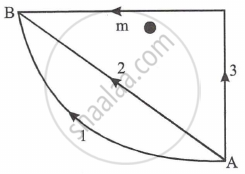
If W1, W2 and W3 represent the work done in moving a particle from A to B along three different paths 1, 2 and 3 (as shown in fig) in the gravitational field of the point mass 'm'. Find the correct relation between W1, W2 and W3.
Two particles of mass m1 and m2, approach each other due to their mutual gravitational attraction only. Then ______.
What is the amount of work done by a person when
- he holds a mass of 2 kg for 5 second and
- he lifts the same mass through 1 meter to keep it on the top of a table? g = 9.8 m/s2
A force of F = `("x"/2 + 15) "N"` acts on a particle. If x 2 is in metre, calculate the work done by the force during the displacement of the particle from x = 0 to x = 4 m
Work done in sliding a 1 kg block up a rough inclined plane of height 5 m is 100 J. Work done against the friction is ______.
(g = 10 m/s2)
'n' number of balls each having mass 'm' and velocity 'u' hit a wall elastically and normally in 2 seconds. The force exerted by them on the wall is ______.
Out of the fundamental forces in nature, maximum and minimum range is respectively for ______.
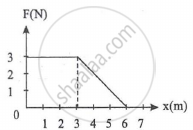
A force F acting on an object varies with distance x as shown here. The force is in N and x in m. The work done by the force in moving the object from x = 0 to x = 6 m is ______.
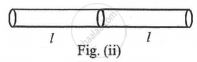
Two rods of same length and transfer a given amount of heat 12 second, when they are joined as shown in figure (i), But when they are joined as shown in figure (ii), then they will transfer same heat in same conditions in ______.