Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
Explain the relation between the Average Variable Cost (AVC) curve and the Marginal Cost (MC) curve. Use diagram
उत्तर
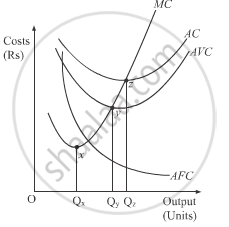
- When AVC is falling up to point y, MC falls at a faster rate up to point x and stays below the AVC curve.
- When AVC is rising after point y, MC rises at a faster rate after point x and remains above the AVC curve.
- When AVC is at minimum point (i.e at point y), MC is equal to AVC.
- MC curve cuts the AVC curve at its minimum point at y.
- The minimum point of the MC curve (x) will always lie left to the minimum point of AVC curve (y).
- AVC and MC both are derived from TVC.
`"AVC" = "TVC"/"Q"`
`"MC" = (Δ"TC")/(Δ"Q") = (Δ"TVC")/(Δ"Q")`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the relation between marginal cost and average variable cost when marginal cost is rising and average variable cost is falling?
Draw Average Variable Cost, Average Total Cost ad Marginal Cost curves in a single diagram.
What is the relation between Average Variable Cost and Average Total Cost, if Total Fixed Cost is zero?
What happens to the difference between Average Total Cost and Average Variable Cost as production is increased?
State the relation between MC curve and AVC and ATC curves.
Answer the following question.
The cost function of a firm is given below
| Output | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Total cost | 100 | 250 | 370 | 550 | 740 |
Calculate:
(i) AFC
(ii) AVC
(iii) MC
Explain whether the statement is true or false with reasons.
Total cost curve and Total variable cost curve are parallel to each other.
What is meant by the break-even point?
Draw a well-labelled diagram to show the break-even point.
