Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following.
What is a Class I lever?
उत्तर
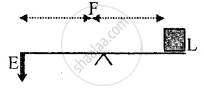
In Class I levers (also called levers of first order), the fulcrum lies between the load and the effort, i.e., the load and the effort are on the opposite sides of the fulcrum.
Examples: See-saw, pairs of scissors, pliers, beam balance, etc.
The mechanical advantage of a Class I lever is always greater than one. These levers act as force multipliers.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you mean by the mechanical advantage of a lever?
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
A pair of scissors
Name the class to which the following lever belong:
a beam balance
Draw diagram to illustrate the position of fulcrum, load, and effort, of the following:
a see-saw.
Answer the following.
Name the simplest of all types of machines.
Name the three classes of levers and state how are they distinguished. Give two examples of each class.
What is the use of the lever if its mechanical advantage is
- more than 1,
- equal to 1, and
- less than 1?
Both a pair of scissors and a pair of pliers belong to the same class of levers. Name the class of lever. Which one has the mechanical advantage less than 1?
Match the following:
| 1. | Class I lever | a. | Wheelbarrow |
| 2. | Class II lever | b. | Seesaw |
| 3. | Class III lever | c. | Axe |
| 4. | Wedge | d. | Hockey sick |
Differentiate Class I lever and Class II lever.
