Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Bring out the relationship between AR and MR curves under various price conditions.
उत्तर
If a firm is able to sell additional units at the same price then AR and MR will be constant. If the firm sells its additional units only by reducing the price then both AR and MR will fall and be different.
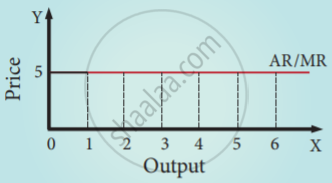
Constant AR and MR: (at fixed price)
If the price remains constant, MR also remains constant and coincides with AR. Under perfect competition as the price is constant, AR is equal to MR and their shape will be straight line horizontal to X-axis.
TR – AR – MR – Constant price
| Quantity Sold (Q) | Price (P) ₹ | Total Revenue (TR) ₹ | Average Revenue (AR) ₹ | Marginal Revenue (MR) ₹ |
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| 3 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 5 |
| 4 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 5 |
| 5 | 5 | 25 | 5 | 5 |
| 6 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 5 |
Declining AR and MR: (at declining price)
When a firm sells large quantities at lower prices both AR and MR will fall. But the fall in MR will be steeper than the fall in the AR and MR lies below AR.
The MR curve divides the distance between the AR curve and Y-axis into two equal parts. The decline in AR need not be a straight line or linear. If the prices are declining with the increase in quantity sold, the AR can be non-linear may be concave or convex to the origin
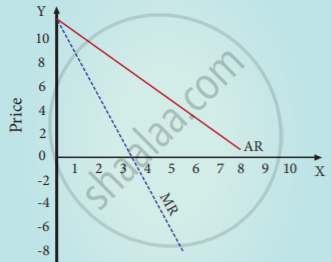
AR, TR, MR declining price
| Quantity Sold (Q) | Price (P)/ Average Revenue (AR) ₹ | Total Revenue (TR) ₹ | Marginal Revenue (MR) ₹ |
| 1 | 10 | 10 | - |
| 2 | 9 | 18 | 8 |
| 3 | 8 | 24 | 6 |
| 4 | 7 | 28 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 | 30 | 2 |
| 6 | 5 | 30 | 0 |
| 7 | 4 | 28 | -2 |
| 8 | 3 | 24 | -4 |
| 9 | 2 | 18 | -6 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | -8 |
