Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a current carrying wire (current I) in the shape of a circle. Note that as the current progresses along the wire, the direction of j (current density) changes in an exact manner, while the current I remain unaffected. The agent that is essentially responsible for is ______.
पर्याय
source of emf.
electric field produced by charges accumulated on the surface of wire.
the charges just behind a given segment of wire which push them just the right way by repulsion.
the charges ahead.
उत्तर
Consider a current carrying wire (current I) in the shape of a circle. Note that as the current progresses along the wire, the direction of j (current density) changes in an exact manner, while the current I remain unaffected. The agent that is essentially responsible for is electric field produced by charges accumulated on the surface of wire.
Explanation:
Current per unit area (taken normal to the current), I/A, is called current density and is denoted by `vecJ`.
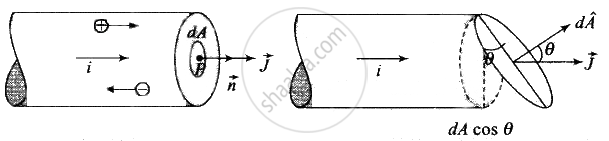
The SI unit of the current density ate A/m2. The current density is also directed along E and which is also a vector quantity and the relationship is given by
`vecJ = σvecE = vecE/ρ`
Where σ = conductivity and ρ = resistivity or specific resistance of the substance.
The `vecJ` changes due to the electric field produced by changes accumulated on the surface of wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the SI unit of resistivity
Keeping the p.d. constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved. The current will become:
(a) one-fourth
(b) four time
(c) half
(d) double
In a conductor 6.25 × `10^16` electrons flow from its end A to B in 2 s. Find the current flowing through the conductor (e = 1.6 × `10^-19` C)
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
A wire of resistance 9 ohm having length 30 cm is tripled on itself. What is its new resistance?
What length of copper wire of resistivity 1.7 × 10-8 Ω m and radius 1 mm is required so that its resistance is 2Ω?
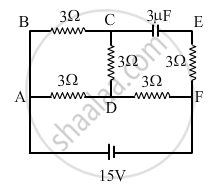
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm AD.
What is the resistance of a conductor through which a current of 0.5 A flows when a potential difference of 2V is applied across its ends?
The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. If other parameters of the electrical circuit remain unaltered, the amount of heat produced in the resistor will become ______.
