Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider the given pairs of triangles and say whether each pair is that of congruent triangles. If the triangles are congruent, say ‘how’; if they are not congruent say ‘why’ and also say if a small modification would make them congruent: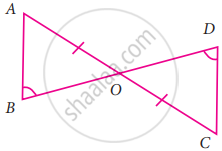
उत्तर
In the given figure BD bisect AC
In ΔAOB and ΔOCD
OA = OC ...(Given)
∠AOB = ∠DOC ...(vertically opposite angles)
∠B = ∠D ...(Given)
By ASA congruency
ΔAOB ≅ ΔOCD
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given below are measurements of some parts of two triangles. Examine whether the two triangles are congruent or not, by the ASA congruence rule. In the case of congruence, write it in symbolic form.
∆DEF, ∠D = 60º, ∠F = 80º, DF = 6 cm.
∆PQR, ∠Q = 60º, ∠R = 80º, QP = 6 cm.
In the given figure, AC ≡ AD and ∠CBD ≡ ∠DEC. Prove that ∆BCF ≡ ∆EDF.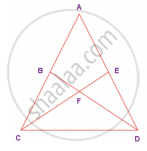
To conclude the congruency of triangles, mark the required information in the following figure with reference to the given congruency criterion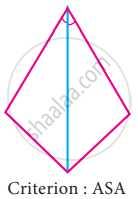
For the given pair of triangles state the criterion that can be used to determine the congruency?
In the given figure, AD = CD and AB = CB. Identify the other three pairs that are equal
In the given figure, Δ______ ≅ ΔPQR.
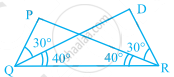
In the given figure, ∆ARO ≅ ∆______.
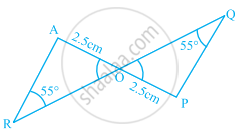
If hypotenuse and an acute angle of one right triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and an acute angle of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent.
In the given figure, AD ⊥ BC and AD is the bisector of angle BAC. Then, ∆ABD ≅ ∆ACD by RHS.
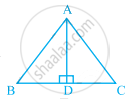
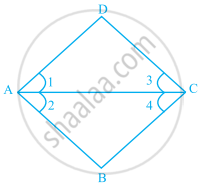
In the given figure, ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠3 = ∠4.
- Is ∆ADC ≅ ∆ABC? Why ?
- Show that AD = AB and CD = CB.