Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define.
Inflorescence
उत्तर
A specialised axis or branch over which flowers are produced or borne in definite manner is known as inflorescence.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student was asked to observe and identify the various parts of an embryo of a red kidney bean seed. He identified the parts and listed them as under:
I. Tegmen
II. Testa
III. Cotyledon
IV. Radicle
V. Plumule
The correctly identified parts among these are
(A) I, II and III
(B) II, III and IV
(C) III, IV and V
(D) I, III, IV and V
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
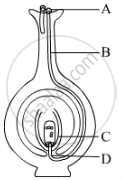
Name the parts labelled as A, B, C and D in the diagram given below:
"The chromosomal number of the sexually producing parents and their offspring is the same." Justify this statement.
State the function of flowers in the flowering plants.
The fusion of male and female gametes is termed as ______.
The reproductive part of a plant is the ______.
Mature ovary forms the ______.
Where are the pollen grains produced?
Explain the terms 'cross-pollination'?
How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
What type of plants reproduce by sexual reproduction method?
What changes take place in the flower after fertilisation which lead to the formation of seeds and fruit?
Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) pollination, fertilisation, seed, embryo
(b) seed, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seed
(d) embryo, seed, pollination, fertilisation
Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual.
(ii) They contain sexual reproductive organs.
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants.
(iv) after fertilization they give rise to fruits.
The correct sequence of reproductive stages occurring in flowering plants is ______
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Stamens make egg cells.
Mention the function of Flower.
Give one example each of unisexual and bisexual flowers. Differentiate between the two types of pollination that occur in flowers. What happens when a pollen lands on a suitable stigma? Write about the events that occur till the seed formation in the ovary.
Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following:
Pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary.
Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
Identify the odd. Stigma, Style, Pollen, Ovary.
Find an odd one out.
Find an odd one out.
Write the functions of sepals
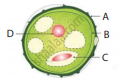
Identify the parts A, B, C, and D?
The anther wall consists of four wall layers where ______
The flower of the Hibiscus plant is ______
Variations occur as a result of ______
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
- They possess both stamen and pistil
- They possess either stamen or pistil
- They exhibit cross pollination
- Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gamete producing organs in the flower.
Trace the path a male gamete takes to fertilise a female gamete after being released from the penis.
Double fertilization means ______.
Triple fusion involves ______.
Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located? Explain the structure of its male reproductive part.
Explain the post fertilization changes that occur in the ovary of a flower.
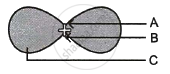
Given below is a diagram of a germinating seed. Label the parts that:
- gives rise to future shoot.
- gives rise to future root system.
- stores food.
- Assertion: Primary endosperm nucleus is diploid.
- Reason: It is the product of double fertilisation.
