Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define ligancy and critical radius ratio. Calculate critical radius radio for ligancy 6.
उत्तर
LIGANCY:-
In an ionic solid the cation and anion are positioned at alternate lattice points. Generally cations are smaller than anions in size. In a given crystal the number of anions surrounding a cation is called the ligancy i.e., the coordination number of an ionic crystal.
RADIUS RATIO:-
If the surrounding anions touch each other as well as touch the central cations the condition is called critical. In this case the cation-anion radius ratio is called the critical radius ratio rC /rA . Here rC and rA are the cation and anion radii respectively.
OCTAHEDRAL CONFIGURATION:
The octahedral configuration of neighbouring anions is found in NaCl structure. Here four anions A, B ,C and D are arranged at the corners of a square with the cation O at the centre of the square. Two more anions are situated in front and at the back of the cation. The centres of all six anions form an octahedron.
Here in ∆ BOC , < BOC = 90°, BC = 2rA , OB = rC + rA and <BCO =45°,
Hence, `( BO)/(BC)` = cos45°
`Or, ( r_C +r _A)/(2r_A) = 1/(√2)`
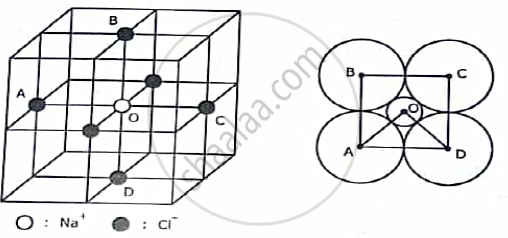 The critical radius ratio here is,
The critical radius ratio here is,
`(r_C)/(r_A)=0.414`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw and explain the unit cell of sodium chloride (NaCl) crystal determine effective number of NaCl molecule per unit cell and co-ordination number.
Calculate the critical radius ratio of an ionic crystal in ligancy-6 . what is the maximum size of cation in ligancy 6 configuration when size of anion is 2.02A°?
Draw the unit cell of HCP structure and work out the no. of atoms per unit cell.
What is the principle of solar cell? Write its advantages and disadvantages
Find the following parameter for DC(Diamond Cubic) structure:-
⦁ No. of atoms per unit cell.
⦁ Co-ordination number.
⦁ Nearest atomic distance.
⦁ Atomic radius.
⦁ APF.
A quartz crystal of thickness 1.5 mm vibrating with resonance. Calculate it’s fundamental frequency if the Young’s modulus of quartz crystal is 7.9×1010N/m2 and density is 2650 kg/m3 .
With neat diagram of unit cell, explain the structure of NaCl crystal and calculate the no .of ions per unit cell, co ordination no. and lattice constant. Calculate the packing factor of NaCl crystal assuming the radius of Na+is 0.98 A° and radius of Cl is 1.81 A°.
Define ligancy and critical radius ratio. Calculate critical radius ratio for ligancy 8.
With neat diagram of unit cell , explain the structure of HCP crystal and calculate the no. of ions per unit cell, co ordination no., lattice constant and packing factor of the structure.
Explain with Diagram Hcp Unit Cell Based on Lattice Parameters.
A quartz crystal of thickness 1 mm is vibrating at resonance. Calculate its fundamental frequency. (Assume that for quartz, Y= 7.9x 1010 N/m2 and p = 2.650 gm/cc.
Define Ligancy. Find the value of critical radius ratio for Ligancy 3.
