Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the digestive role of chymotrypsin. What two other digestive enzymes of the same category are secreted by its source gland?
उत्तर १
The enzyme trypsin (present in the pancreatic juice) activates the inactive enzyme chymotrypsinogen into chymotrypsin.
Chymotrypsinogen  Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin
(Inactive) (Active)
The activated chymotrypsin plays an important role in the further breakdown of the partially-hydrolysed proteins.
Proteins  Peptides
Peptides
The other digestive enzymes of the same category are trypsinogen and carboxypeptidase. These are secreted by the same source-gland, pancreas.
Trypsinogen is present in an inactive form in the pancreatic juice. The enzyme enterokinase – secreted by the intestinal mucosa – activates trypsinogen into trypsin.
Trypsinogen  Trypsin + Inactive peptide
Trypsin + Inactive peptide
The activated trypsin then further hydrolyses the remaining trypsinogen and activates other pancreatic enzymes such as chymotrypsinogen and carboxypeptidase. Trypsin also helps in breaking down proteins into peptides.
Proteins  Peptides
Peptides
Carboxypeptidases act on the carboxyl end of the peptide chain and help in releasing the last amino acids.
Peptides 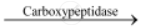 Small peptide chain + Amino acids
Small peptide chain + Amino acids
उत्तर २
Chymotrypsin is a proteolytic enzyme of pancreatic juice secreted by exocrine part of pancreas. It helps in digestion of proteins. It converts proteins, peptones and proteoses into oligopeptides and dipeptides. Two other proteolytic enzymes present in pancreatic juice are trypsinogen and procarboxypeptidase.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct answer among the following:
Gastric juice contains
(i) pepsin, lipase and rennin
(ii) trypsin lipase and rennin
(iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase
(iv) trypsin, pepsin and renin
Choose the correct answer among the following:
Succus entericus is the name given to
(i) a junction between ileum and large intestine
(ii) intestinal juice
(iii) swelling in the gut
(iv) appendix
Match column I with column II
| Column I | Column II | ||
| a | Bilirubin and biliverdin | 1 | Parotid |
| b | Hydrolysis of starch | 2 | Bile |
| c | Digestion of fat | 3 | Lipases |
| d | Salivary gland | 4 | Amylases |
How does pepsinogen change into its active form?
Answer briefly:
How does bile help in the digestion of fats?
Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
How does butter in your food gets digested and absorbed in the body?
Name different types of teeth and their number in an adult human.
Trypsinogen is an inactive enzyme of pancreatic juice. An enzyme, enterokinase, activates it. Which tissue/ cells secrete this enzyme?/ How is it activated?
Name the enzymes involved in the breakdown of nucleotides into sugars and bases?
Define digestion in one sentence.
Correct the following statement by deleting one of entries (given in bold).
Saliva contains enzymes that digest starch/protein.
Name the part of the alimentary canal where major absorption of digested food takes place. What are the absorbed forms of different kinds of food materials?
Correct the statement given below by the right option shown in the bracket against them.
Rennin is a proteolytic enzyme found in gastric juice in (infants/adults).
Correct the statement given below by the right option shown in the bracket against them.
Dipeptides, disaccharides and glycerides are broken down into simple substances in region of small intestine. (jejunum/duodenum)
How is the intestinal mucosa protected from the acidic food entering from stomach?
A person had roti and dal for his lunch. Trace the changes in those during its passage through the alimentary canal.
