Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe five types of leucocytes, with the help of diagrams. Add a note on their functions.
उत्तर
Leucocytes are colourless, nucleated, amoeboid and phagocytic cells.
Leucocytes are of two types: Granulocytes and Agranulocytes.
i. Granulocytes: They are produced in red bone marrow and contain large sized granules in the cytoplasm.
Granulocytes are of three types:
- Neutrophils (neutro = neutral, philic = affinity)
They constitute about 70% of total WBCs.
Nucleus is multilobed containing 3 to 5 lobes.
The granules in cytoplasm of these cells take up neutral stain.
Functions: These are chief phagocytic cells.
They protect the body against invasion of bacteria.
Dead neutrophils along with damaged tissue are removed from the body in the form of pus.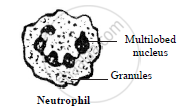
- Eosinophils (acidophils):
They constitute about 3% of total WBCs.
The nucleus is bilobed.
The granules in the cytoplasm of these cells take up acidic stain.
Functions:
They are non-phagocytic and their number increases during allergic reactions. They show anti-histamine property.
- Basophils:
They are the smallest white blood cells which constitute about 0.5% of the total WBCs.
They show twisted nucleus (‘S’ or comma shaped).
The granules in the cytoplasm of these cells take up basic stain.
Functions:
They are non-phagocytic.
They secrete heparin, histamine, thus play an important role in local anticoagulation and formation of ground substance.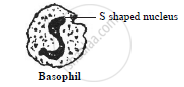
ii. Agranulocytes: They are produced in spleen and do not contain granules in the cytoplasm.
Agranulocytes are of two types:
- Lymphocytes: They form 30% of total WBCs.
Nucleus is large, spherical and surrounded by thin layer of cytoplasm.
Functions: They produce antibodies and opsonins to neutralize the harmful effects of foreign matter and their toxins.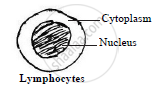
- Monocytes: They are the largest leucocytes and constitute 1 to 3% of total WBC. They have large amount of cytoplasm and kidney shaped nucleus.
Functions: They are phagocytic in action. They engulf foreign particles. e.g. bacteria.
They also remove the damaged and dead cells, hence are referred to as scavengers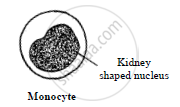
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Human blood clotting factor VIII is used to treat __________.
(A) pituitary dwarfism
(B) diabetes mellitus
(C) haemophilliacs
(D) cystic fibrosis
Select the odd one from the following:
Formation of a to b is carried out in the presence of Ca++ions during clotting.
Select the CORRECT option for a and b
What is the mineral element essential to form a blood clot?
Thrombocytes are essential for coagulation of blood. Comment.
Explain the process of blood clotting.
Name the following:
A genetic disorder in which the blood does not clot.
1 gram of solid sodium chloride was taken in a clean and dry test tube and concentrated sulphuric acid was added to it.
- Name the gas evolved in the reaction.
- What will be observed when this gas is tested with (1) dry and (II) wet blue litmus paper?
Write your conclusion about the nature (acidic/basic) of this gas.
Give reasons/explain:
Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
State whether the following statement is true or false and correct the false statement.
The solid fibrin and thrombin are one and the same thing.
