Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the T.S. of human testis
Describe the histology of ‘human testis’.
उत्तर १
Externally, each testis is covered by three layers. These are:
a. Tunica vaginalis:
It is the outermost incomplete peritoneal covering made up of connective tissue and
epithelium.
b. Tunica albuginea:
It is the middle layer formed by fibrous connective tissue.
c. Tunica vasculosa:
It is the innermost layer formed of delicate connective tissue, supporting a network of blood capillaries.

ii. Each testis contains about 200-300 tubules called seminiferous tubules.
iii. These are lined by a single layer of cuboidal germinal epithelium which undergo
spermatogenesis.
iv. In the germinal epithelium, various stages of spermatogenesis such as spermatogonia,
primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes, spermatids and sperms are seen.
v. Between these cells, few large and pyramidal cells called nurse cells or sertoli cells are
present.
vi. Bundles of sperms are seen attached to Sertoli cells.
vii. These cells provide nourishment to the sperms till maturation.
viii. In between seminiferous tubules, connective tissue containing blood vessels, nerves, lymph vessels
and groups of interstitial cells (Cells of leydig) is present.
ix. Interstitial cells produce male hormone testosterone.
उत्तर २

Histology of Testis : -
The testis is externally covered by fibrous connective tissue called Tunica albuginea. It is covered internally by Tunica vasculos which is formed by capillaries. Externally it is covered by the incomplete peritoneal covering called as Tunica vaginalis.
1) The Transverse section shows the presence of seminiferous tubules lined by cuboidal germinal epithelial cells. The germ cell undergoes the process of spermatogenesis
2) The transverse section also reveals different stages of spermatogenesis like spermatogonia, primary and secondary spermatocyte, spermatids and sperm.
3) Few large pyramidal cells present between germinal cells are known as Sertoli cells or Nurse cells. The function of Sertoli cells is to provide Nourishment of the sperm till maturation.
4) Between the seminiferous tubules, are the present cluster of polygonal cells known as Interstitial cells or Leydig cells. The Leydig cells secrete male sex hormone Testosterone or Androgen
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the location and function of the Sertoli cells in humans.
The diagram shown below is the lateral section of the testis of man. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow:

(i) Label the part I to 4 of the diagram.
(ii) State the functions of the parts labeled 1 and 2.
In humans, sperm production occurs in the organ ______.
Select the MISMATCHED pair.
Spot the odd one out from the following structures with reference to the male reproductive system.
Mark the odd one.
A pair of ducts arising from testis, which carries sperms are ______
Given below is a certain situation. Analyze and describe its possible impact on a person:
Testes of a male boy are not able to descend into the scrotum during his embryonic development.
The packing tissues between the coils of the seminiferous tubules are called as ______.
The figure given ahead is an organ system of humans. Study the same and answer the following questions.
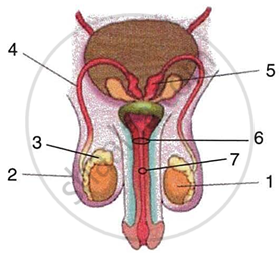 |
- Identify the organ system.
- Label the guidelines 1 to 7.
- Write one important role of parts 3 and 6.
- Name the cells of part 1 that produce testosterone.
- What is the significance of the part 1 being located in a separate sac suspended outside the body?
