Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe with the aid of a diagram some form of a fuse which is used in the electric lighting circuit of a house. Give two reasons why a fuse must not be replaced by an ordinary copper wire.
उत्तर
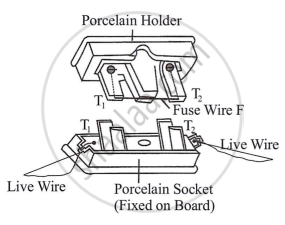
The figure above shows the most common fuse arrangement in which the fuse wire is stretched between the two metallic terminals T1 and T2 in a porcelain holder. This holder fits into a porcelain socket having two metallic terminals, to each of which the live wire of the circuit is connected. A fuse must not be replaced with a copper wire because copper has very low resistivity and a high melting point.
Ordinary wire has low resistance and high M.P. and when High current passes into the appliance and gets damaged even then fuse will not melt and will not disconnect the appliance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For a fuse, higher the current rating ________ is the fuse wire.
A fuse wire is made of an alloy of ______ and ______. If the current in a circuit exceeds the current rating of the fuse wire, it ______.
‘A fuse is rated 8 A’. can it be used with an electrical appliance of rating 5kW, 200V?
An electric kettle is rated 3 kW, 250 V. Give reason whether this kettle can be used in a circuit which contains a fuse of current rating 13 A.
How does the thickness of a fuse wire depend on its current rating?
Why fuse wire must always be connected in ‘live’ wire? Explain.
What is an ‘electric fuse’? State its two characteristics of electric fuse.
Explain the significance of kWh meter, main switch and main fuse in house-circuiting.
(a) Name the electrical appliance shown in the diagram below.

(b) Name the material of the wire used in this device.
(c) Name two important characteristics of this wire.
How does the length of a fuse wire depend on its current rating?
