Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the gamma decay process with an example.
उत्तर
In α and β decay, the daughter nucleus is in the excited state most of the time. The typical life time of excited state is approximately 10-11 s. So this excited state nucleus immediately returns to the ground state or lower energy state by emitting highly energetic photons called γ rays. In fact, when the atom is in the excited state, it returns to the ground state by emitting photons of energy in the order of a few eV. But when the excited state nucleus returns to its ground state, it emits a highly energetic photon (γ rays) of energy in the order of MeV. The gamma decay is given by
\[\ce{^A_ZX^* -> ^A_ZX + gamma (γ) rays}\]
Gamma emission
Here the asterisk (*) means excited state nucleus. In gamma decay, there is no change in the mass number or an atomic number of the nucleus.
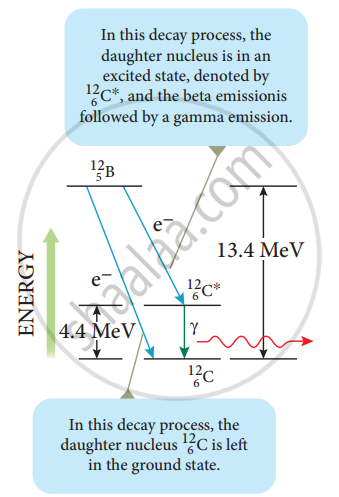
Boron \[\ce{^12_5B}\] has two beta decay modes:
-
It undergoes beta decay directly into ground state carbon by emitting an electron of a maximum of energy 13.4 MeV.
- it undergoes beta decay to an excited state of carbon \[\ce{^12_6C^*}\] by emitting an electron of maximum energy 9.0 MeV followed by gamma decay to ground state by emitting a photon of energy 4.4 MeV.
It is represented by
\[\ce{^12_5B -> ^12_6C + e- + \bar{v}}\]
\[\ce{^12_6C^* -> ^12_6C + \gamma}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the symbolic representation of alpha decay, beta decay and gamma emission.
What is half-life of nucleus? Give the expression.
What is meant by activity or decay rate? Give its unit.
Define curie.
Discuss the alpha decay process with example.
Obtain the law of radioactivity.
Explain the idea of carbon dating.
Calculate the time required for 60% of a sample of radon to undergo decay. Given T1/2 of radon = 3.8 days.
Mean life (τ) of a radioactive substance is x times of its half-life (t). Here x is:
What percentage of original radioactive substance is left after 5 half-life time.
