Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
| Real image | Virtual image | |
| 1. | When the rays of light diverging from a point after reflection or refraction actually converge at some point, then that point is the real image of the object. | When the rays of light diverging from a point after reflection or refraction appear to diverge from some other point. |
| 2. | A real image is always inverted and can be taken on the screen. | A virtual image is always erect and cannot be taken on the screen. |
| 3. | A real image is formed by eye, photographic camera, convex lens except when the object is very close to a concave mirror. |
A virtual image is formed by a plane mirror, a convex mirror and a concave lens. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe an experiment to show that a light ray bends when it passes from one transparent medium into another transparent medium.
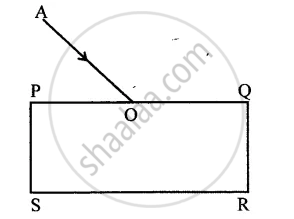
The diagram in figure shows a ray of light AO falling on a rectangular glass slab PQRS. Complete the diagram till the ray of light emerges out of the slab. Label on the diagram the incident ray, the refracted ray and the emergent ray.
What is mirage? Give a reason for its formation?
Name the mirror which always forms an erect and virtual image. What is the size of the image as compared to that of the object?
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image when the object is brought from infinity up to the convex lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams.
You can see your image in polished floors, but not in wooden table because ______.
Say TRUE or FALSE
The image formed in a pinhole camera is always the same size as the object
Figure shows a pencil placed above a mirror
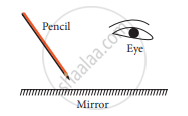
- Draw its image formed by the mirror
- Show how light rays from the object are reflected at the mirror to form the image for the eye.
We can create enlarged, virtual images with ______.
If magnification is +1.5. The image is ______.
