Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between open circulation and closed circulation.
उत्तर
| Open circulation | Closed circulation | ||
| 1. | In open circulation, blood is circulated through the body cavities (haemocoels). | 1. | In closed circulation, blood circulates the blood vessels and does not come in direct contact with cells and body tissues. |
| 2. | The blood flows with low pressure. | 2. | The blood flows with high pressure. |
| 3. | Exchange of material takes place directly between blood and cells or tissues of the body. | 3. | Exchange of material between blood and body tissues is through intermediate fluid called lymph. |
| 4. | It usually does not contain any respiratory pigment like haemoglobin so it does not transport respiratory gases | 4. | It contains respiratory pigments like haemoglobin for transportation of respiratory gases. |
| 5. | e.g. Arthropods and molluscs | 5. | e.g. All vertebrates, higher molluscs and annelids |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Normal range of breathing rate per minute in an average adult person at rest is ______.
How is the process of respiration different from breathing?
Short answer question.
Why is it advantageous to breathe through the nose than through the mouth?
Long answer question:
Smita was working in a garage with the doors closed and automobile's engine running. After some time she felt breathless and fainted. What would be the reason? How can she be treated?
The volume of air that remains in the lungs after maximum respiration is ______.
Differentiate between inhalation and exhalation.
Explain the mechanism of breathing.
Vital capacity is ______.
After a long deep breath, we do not respire for some seconds due to ______.
Make the correct pairs.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (P) IC | i. maximum volume of air breathe in after forced. |
| (Q) EC | ii. Volume of air present after expiration in lungs. |
| (R) VC | iii. Volume of air inhaled after expiration. |
| (S) FRC | iv. Volume of air present after expiration in lungs. |
Make the correct pairs.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (P) Tidal volume | i. 1000 to 1100 ml |
| (Q) Residual volume | ii. 500 ml |
| (R) Expiratory reserve volume | iii. 2500 to 3000 ml |
| (S) Inspiratory reserve volume | iv. 1100 to 1200 ml |
For which of the following reasons stepwise cellular respiration is useful?
Which of the following is CORRECT with reference to oxygen dissociation curve?
Identify the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration
The impulse for voluntary muscles for forced breathing starts in ____________.
Whenever we feel drowsy or sleepy, we start yawning. Does yawning help us in any way?
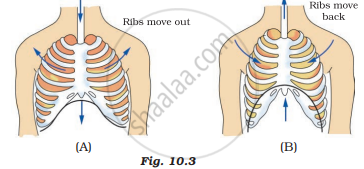
Observe the figures given in Figures 10.3 (A) and (B) and answer the following.
Which of the figures A or B indicates the process of inhalation and which is the process of exhalation?
The partial pressures (in mm Hg) of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) at alveoli (the site of diffusion) are ______
In breathing movements, air volume can be estimated by ______.
Explain the mechanism of breathing with neat labelled sketches.
In alveolar air, the partial pressure of CO2 is ______.
Describe the steps in breathing.
In HMP shunt, number of molecules of CO2 evolved are ______.
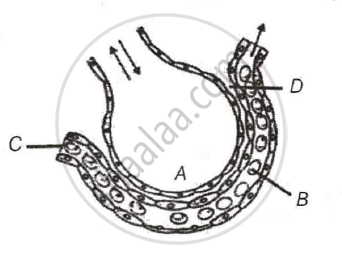
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gas takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function.
Listed below are four respiratory capacities (1 - 4) and four jumbled respiratory volumes of a normal human adult
| Respiratory Capacities | Respiratory Volumes |
| 1. Residual volume | 2500 mL |
| 2. Vital capacity | 5500 mL |
| 3. Inspiratory sore volume | 1200 mL |
| 4. Total Lung capacity | 4500 mL |
Which one of the following is the correct matching of two capacities and volumes?
Give function of carbonic anhydrase.
