Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a real magnified image by a convex lens. (In your sketch the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus of lens should be shown clearly).
उत्तर

A convex lens forms a real and magnified image when an object is placed between F and 2F.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If an object is at a considerable distance (or infinity) in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
A burning candle whose flame is 1.5 cm tall is placed at a certain distance in front of a convex lens. An image of candle flame is received on a white screen kept behind the lens. The image of flame also measures 1.5 cm. If f is the focal length of convex lens, the candle is placed:
(a) at f
(b) between f and 2f
(c) at 2f
(d) beyond 2f
Calculate the focal length of a convex lens which produces a virtual image at a distance of 50 cm of an object placed 20 cm in front of it.
A convex lens of focal length 6 cm is held 4 cm from a newspaper which has print 0.5 cm high. By calculation, determine the size and nature of the image produced.
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.50 m
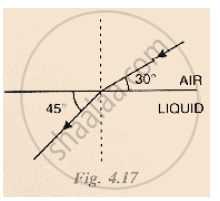
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from sir to a liquid.
(a) write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
(b) use snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
For finding the focal length of a convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object, one should use as the object.
(1) a well lit distant tree
(2) window grill in the class room
(3) any distant tree
(4) a lighted candle kept at the other end of the table.
Draw a diagram to show the convergent action of a convex lens by treating it as a combination of glass block and two triangular glass prisms, with the aid of two parallel incident rays.
An object is placed in front of a convex lens such that the image formed has the same size as that of the object. Draw a ray diagram to illustrate this.
