Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Essential difference between electrostatic shielding by a conducting shell and magnetostatic shielding is due to ______.
- electrostatic field lines can end on charges and conductors have free charges.
- lines of B can also end but conductors cannot end them.
- lines of B cannot end on any material and perfect shielding is not possible.
- shells of high permeability materials can be used to divert lines of B from the interior region.
पर्याय
a, b and c
a, c and d
b, c and d
c and d
उत्तर
a, c and d
Explanation:
Electrostatic shielding is the phenomenon to block the effects of an electric field. The conducting shell can block the effects of an external field on its internal content or the effect of an internal field on the outside environment. For protecting sensitive equipment from the external magnetic field it should be placed inside an iron cane (magnetic shielding). Magnetostatic shielding is done using an enclosure made of a high permeability magnetic material to prevent a static magnetic field outside the enclosure from reaching objects inside it or to confine a magnetic field within the enclosure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following substances are para-magnetic?
Bi, Al, Cu, Ca, Pb, Ni
A tangent galvanometer shows a deflection of 45° when 10 mA of current is passed through it. If the horizontal component of the earth's magnetic field is `B_H = 3.6 xx 10^-5 "T"` and radius of the coil is 10 cm, find the number of turns in the coil.
Choose the correct option:
A rectangular magnet suspended freely has a period of oscillation equal to T. Now it is broken into two equal halves (each having half of the original length) and one piece is made to oscillate freely. Its period of oscillation is T′, the ratio of T′/T is ______.
Above the curie temperature the susceptibility of ferromagnetic substance varies ____________.
A short bar magnet has a magnetic moment of 0.48 J T−1. Give the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field produced by the magnet at a distance of 10 cm from the centre of the magnet on
- the axis,
- the equatorial lines (normal bisector) of the magnet.
Why does a paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetising field) when cooled?
A certain region of space is to be shielded from magnetic fields. Suggest a method.
Assertion: A paramagnetic sample display greater magnetisation (for the same magnetic field) when cooled.
Reason: The magnetisation does not depend on temperature.
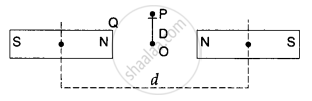
Two identical bar magnets are fixed with their centres at a distance d apart. A stationary charge Q is placed at P in between the gap of the two magnets at a distance D from the centre O as shown in the figure. The force on the charge Q is ______.
A hydrogen atom is paramagnetic. A hydrogen molecule is
