Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Read the passage given below:
1. Every morning Ravi gives his brain an extra boost. We're not talking about drinking strong cups of coffee or playing one of those mind-training video games advertised all over Facebook. "I jump onto my stationary bike and cycle for 45 minutes to work," says Ravi. "When I get to my desk, my brain is at peak activity for a few hours." After his mental focus comes to a halt later in the day, he starts it with another short spell of cycling to be able to run errands.
2. Ride, work, ride, repeat. It's scientifically proven system that describes some unexpected benefits of cycling. In a recent study in the Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, scientists found that people scored higher on tests of memory, reasoning, and planning after 30 minutes of spinning on a stationary bike than they did before they rode the bike. They also completed the tests faster after pedalling.
3. Exercise is like fertilizer for your brain. All those hours spent on exercising your muscles, create rich capillary beds not only in leg and hip muscles, but also in your brain. More blood vessels in your brain and muscles mean more oxygen and nutrients to help them work. When you pedal, you also force more nerve cells to fire. The result: you double or triple the production of these cells – literally building your brain. You also release neurotransmitters (the messengers between your brain cells) so all those cells, new and old, can communicate with each other for better, faster functioning. 'That's a pretty profound benefit to cyclists.
4. This kind of growth is especially important with each passing birthday, because as we age, our brains shrink and those connections weaken. Exercise restores and protects the brain cells. Neuroscientists say, "Adults who exercise display sharper memory skills, higher concentration levels, more fluid thinking, and greater problem-solving ability than those who are sedentary."
5. Cycling also elevates your mood, relieves anxiety, increases stress resistance, and even banishes the blues. "Exercise works in the same way as psychotherapy and antidepressants in the treatment of depression, maybe better," says Dr. Manjari. A recent study analyzing 26 years of research finds that even some exercise – as little as 20 to 30 minutes a day – can prevent depression over the long term.
6. Remember: although it's healthy, exercise itself is a stress, especially when you're just getting started or getting back into riding. When you first begin to exert yourself, your body releases a particular hormone to raise your heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, says Meher Ahluwalia, PhD, a professor of integrative physiology. As you get fitter, it takes a longer, harder ride to trigger that same response.
On the basis of your understanding of the passage, complete the statements given below with the help of the options that follow:
(a) Ravi gets his brain to work at peak level by
(ii) playing games that need brain activity.
(iii) cycling on a stationary bike.
(iv) taking tablets to pump up his brain.
(b) When nerve cells work during exercise then
(ii) the brain is strengthened by multiplying them.
(iii) you start to lose your temper.
(iv) your stationary cycle starts to beep.
Answer the following questions briefly:
(c) How does exercise help the brain?
(d) Why does Ravi do a circuit of 'ride, work, ride'?
(e) What is the work of neurotransmitters?
(f) What benefits other than greater brain activity does one get from cycling?
(g) Why is exercise so important for adults?
(h) How is exercise itself a stress?
(ii) inactive (para 4)
उत्तर
(a) iii) cycling on a stationary bike.
(b) ii) the brain is strengthened by multiplying them.
(c) Exercise works as a fertilizer for our brain. It builds our brain by creating rich capillary beds in our brain.
(d) Ravi does a circuit of ‘ride, work , ride’ because it helps him sharpen his memory in reasoning and planning.
(e) Neurotransmitters work as a messengers between our brain cells.
(f) The benefits other than greater brain activity one gets from cycling is creation of rich capillary beds in leg and hip muscles.
(g) Exercise is important for adults as restores and protects the brain cells which shrink with their passing age.
(h) Exercise itself is a stress as it increases our heart rate, blood pressure and blood glucose level , when we begin to exert ourselves.
(i) i) fertilizer
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
 During the devastating July 2005 floods that hit Mumbai, Rajen Dutia received an urgent call from a relative, Lopa Vyas late in the evening. “A friend’s mother is stranded near your home, Rajen. Can you please take her home? Her name is Rashmi,” Vyas told him.
During the devastating July 2005 floods that hit Mumbai, Rajen Dutia received an urgent call from a relative, Lopa Vyas late in the evening. “A friend’s mother is stranded near your home, Rajen. Can you please take her home? Her name is Rashmi,” Vyas told him.
Mumbai had come to a halt and people were trapped everywhere. Despite power failure and raging rain, Dutia stepped out and made his way to the spot, where he found Rashmi as well as a dozen other people. They were stranded in the dark, shivering in the rain. They all lived far away and had no place to go for the night.
Rajen took all of them to his one-bedroom flat, where he served them dinner and invited them to spend the night.
"By doing so," says Rajen, "I was simply fulfilling my karma, paying the universe back for the good it had done for me."
"God is kind. My daughter had just started her new job that day, and had gone for her training. She was stranded too. While she was trying to get to our relatives, she almost drowned, but a young stranger saved her. He and his friends even dropped her to my relative's place and phoned me to say she was safe. One good turn deserves another."
A2. Order
Look at the following sentences from the passage and put them in the correct sequence: (2)
(a) He took them to his one-bedroom flat.
(b) Rajen found Rashmi as well as a dozen other people shivering in the rain.
(c) Mumbai had come to a halt and people were trapped everywhere.
(d) Rajen Dutia received an urgent call.
A3

During the devastating July 2005 floods that hit Mumbai, Rajen Dutia received an urgent call from a relative, Lopa Vyas late in the evening. “A friend’s mother is stranded near your home, Rajen. Can you please take her home? Her name is Rashmi,” Vyas told him.
Mumbai had come to a halt and people were trapped everywhere. Despite power failure and raging rain, Dutia stepped out and made his way to the spot, where he found Rashmi as well as a dozen other people. They were stranded in the dark, shivering in the rain. They all lived far away and had no place to go for the night.
Rajen took all of them to his one-bedroom flat, where he served them dinner and invited them to spend the night.
"By doing so," says Rajen, "I was simply fulfilling my karma, paying the universe back for the good it had done for me."
"God is kind. My daughter had just started her new job that day, and had gone for her training. She was stranded too. While she was trying to get to our relatives, she almost drowned, but a young stranger saved her. He and his friends even dropped her to my relative's place and phoned me to say she was safe. One good turn deserves another."
A2. Order
Look at the following sentences from the passage and put them in the correct sequence: (2)
(a) He took them to his one-bedroom flat.
(b) Rajen found Rashmi as well as a dozen other people shivering in the rain.
(c) Mumbai had come to a halt and people were trapped everywhere.
(d) Rajen Dutia received an urgent call.
A3(i). Fill in the blanks :
Select the words given in the passage (1)
(i) Thousands Of pilgrims were …………….. due to the cloud burst in Uttarakhand.
(ii) The tiger was ……………… by the hunter.
(ii). Antonyms:
Select the correct antonyms for the given words from the alternatives :
(1) Please :
(a) unplease (b) displease (c) misplease
(2) Safe: '
(a) insafe (b) safeless (c) unsafe
A4(i) Tags :
Select the correct tag for the alternatives given below :
One good turn deserves another.
(a) Doesn’t it? (b) don’t it (c) does it?
(ii). Guess:
Choose the correct answer : (1)
Rajen can you please take her home? ‘Can’ indicates :
(a) Obligation (b) ability (c) permission
A5. Personal Response :
‘ one good turn
Deserves another.’
Explain with an
example of your own.
The natural life span of a domesticated horse is about 25 – 30 years, 10 years down from what it was in the wild. You can tell a horse’s age from the number of teeth he has. They get all their teeth by the age of 5, after which those teeth just get longer. Horses have close to 360 degree all round vision. The only place they cannot see is directly behind or right in front of themselves, which is why it’s dangerous to stand behind a horse. If they later I it also means that they cannot see a jump once they are about four feet from it, and have to rely on memory as to its height and shape! Each of the horse’s two eyes work independently wherever a horse’s ear points is where the horse is looking. A horse is able to sleep standing up as he is able to lock his leg muscles so that he dosen’t fall asleep. Nor do all horses in the same field ever lie down at once – one animal always stands “on look out” duty.
1) What is the life span of a wild horse?
(2) Why do the horse owners cover their horse’s eyes with blinkers?
(3) What prevents a horse from falling while asleep?
(4)
(a) Falls /shorter/ the mane/ on the/ side/ legged.[Rearrange the words to make a meaningful sentence]
(b) Form antonyms by adding a prefix :
(i) able
(ii) direct
(5)
(a) They get all their teeth by the age of five. [Pick out the prepositions]
(b) If they feel something behind them they may kick. [Rewrite using ‘unless’]
(6) How have horses helped man through the ages?
He holds him with his skinny hand,
“There was a ship,” quoth he.
i. Who does ‘He’ refer to in the above extract?
ii. What do we know about the speaker’s feelings?
iii. Why is his hand called ‘skinny’?
Q1 Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow:
1. Too many parents these days can't say no, As a result, they find themselves raising 'children' who respond greedily to the advertisements aimed right at them. Even getting what they want doesn't satisfy some kids; they only want more. Now, a growing number of psychologists, educators, and parents think it's time to stop the madness and start teaching kids about what's really important: values like hard work, contentment, honesty, and compassion. The struggle to set limits has never been tougher ‒ and the stakes have never been higher. One recent study of adults who were overindulged as children paints a discouraging picture of their future: when given too much too soon, they grow up to be adults who have difficulty coping with life's disappointments. They also have a distorted sense of entitlement that gets in the way of success in the workplace and in relationships.
2. Psychologists say that parents who overindulge their kids set them up to be more vulnerable to future anxiety and depression. Today's parents themselves raised on values of thrift and self-sacrifice, grew up in a culture where no was a household word. Today's kids want much more, partly because there is so much more to want. The oldest members of this generation were born in the late 1980s, just as PCs and video games were making their assault on the family room. They think of MP3 players and flat-screen TV as essential utilities, and they have developed strategies to get them. One survey of teenagers found that when they crave something new, most expect to ask nine times before their parents give in. By every measure, parents are shelling out record amounts. In the heat of this buying blitz, even parents who desperately need to say no find themselves reaching for their credit cards.
3. Today's parents aren't equipped to deal with the problem. Many of them, raised in the 1960s and '70s, swore they'd act differently from their parents and have closer relationships with their own children. Many even wear the same designer clothes as their kids and listen to the same music. And they work more hours; at the end of a long week, it's tempting to buy peace with 'yes' and not mar precious family time with conflict. Anxiety about the future is another factor. How do well-intentioned parents say no to all the sports gear and arts and language lessons they believe will help their kids thrive in an increasingly competitive world? Experts agree: too much love won't spoil a child. Too few limits will.
4. What parents need to find, is a balance between the advantages of an affluent society and the critical life lessons that come from waiting, saving, and working hard to achieve goals. That search for balance has to start early. Children need limits on their behaviour because they feel better and more secure when they live within a secure structure. Older children learn self-control by watching how others, especially parents act. Learning how to overcome challenges is essential to becoming a successful adult. Few parents ask kids to do chores. They think their kids are already overburdened by social and academic pressures. Every individual can be of service to others, and life has meaning beyond one's own immediate happiness. That means parents eager to teach values have to take a long, hard look at their own.
(a) Answer the following:
- What values do parents and teachers want children to learn?
- What are the results of giving the children too much too soon?
- Why do today's children want more?
- What is the balance which the parents need to have in today's world?
- What is the necessity to set limits for children?
(b) Pick out words from the passage that mean the same as the following:
- a feeling of satisfaction (para 1)
- valuable (para 3)
- important (para 4)
One of the greatest advances in modern technology has been the invention of computers. They are widely used in industries and in universities. Now there is hardly any sphere of human life where computers have not been pressed into service of man. We are heading fast towards the day when a computer will be as much part of man's daily life as a telephone or a calculator.
Computers are capable of doing extremely complicated work in all branches of learning. They can solve the most complex mathematical problems or put thousands of unrelated facts in order. These machines can be put to varied uses. For instance, they can provide information on the best way to prevent traffic jams. This whole process by which machines can be used to work for us has been called 'automation'. In the future 'automation' may enable human beings to enjoy more leisure than they do today. The coming of automation is bound to have important social consequences.
Some years ago an expert on automation, Sir Leon Bagrit, pointed out that it was a mistake to believe that these machines could 'think'. There is no possibility that human beings will be "controlled by machines". Though computers are capable of learning from their mistakes and improving on their performance, they need detailed instructions from human beings to operate. They can never, as it were, lead independent lives or "rule the world" by making decisions of their own.
Sir Leon said that in future, computers would be developed which would be small enough to carry in the pocket. Ordinary people would then be able to use them to obtain valuable information. Computers could be plugged into a national network and be used like radios. For instance, people going on holiday could be informed about weather conditions. Car drivers can be given alternative routes when there are traffic jams. It will also be possible to make tiny translating machines. This will enable people who do not share a common language to talk to each other without any difficulty or to read foreign publications.
a) What is the greatest advancement in modern technology?
b) What complicated works are computers capable of doing?
c) Write one use of computers.
d) Explain automation.
e) Why can't computers lead independent lives or rule the world?
f) How would computers as translating machines help people?
g) What was the prediction of Sir Leon about computers in the future?
h) How can computers help people going on holiday?
Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
These meadows aren't worth much to me. They only come to five dessiatins, and are worth perhaps 300 roubles, but I can't stand unfairness. Say what you will, I can't stand unfairness.
(a) Who speaks the above lines and to whom?
(b) How much are the meadows worth?
(c) Find a word in the extract the means 'not based on what is just.'
Read the passage given below :
1. When you grow up in a place where it rains five months a year, wise elders help you to get acquainted with the rain early. They teach you that it is ignorant to think that it is the same rain falling every day. Oh no, the rain is always doing different things at different times. There is rain that is gentle, and there is also rain that falls too hard and damages the crops. Hence, the prayer for the sweet rain that helps the crops to grow.
2. The monsoon in the Naga hills goes by the native name, khuthotei (which means the rice-growing season). It lasts from May to early or mid-October. The local residents firmly believe that Durga Puja in October announces the end of rain. After that, one might expect a couple of short winter showers, and the spring showers in March and April. Finally, comes the "big rain" in May; proper rainstorms accompanied by heart-stopping lightning and ear-splitting thunder. I have stood out in storms looking at lightning are across dark skies, a light-and-sound show that can go on for hours.
3. This is the season when people use the word sezuo or süzu to refer to the week-long rains, when clothes don't dry and smell of mould, when fungus forms on the floor and when you can't see the moon or the stars because of the rainclouds. But you learn not to complain. Rain, after all, is the farmer's friend and brings food to the table. Rituals and festivals centre around the agricultural rhythm of life, which is the occupation of about 70 percent of the population.
4. The wise learn to understand its ways. I grew up hearing my grandfather say. "It's very windy this year. We'll get good rain." If the windy season was short and weak, he worried there might not be enough rain for the crops. I learned the interconnectedness of the seasons from childhood, and marvelled at how the wind could bring rain. Another evening, many rainy seasons ago, my paternal aunt observed the new moon and worried, "Its legs are in the air, we're in for some heavy rain." She was right. That week, a storm cut off power lines and brought down trees and bamboos.
5. Eskimos boast of having a hundred names for snow. Norwegians in the north can describe all kinds of snow by an equal amount of names : pudder, powder snow, wet snow, slaps, extra wet snow, tight snowfall, dry snow, and at least 95 more categories of snow. Likewise, in India we have names and names for rain. Some are common, some are passing into history.
6. The rains are also called after flowering plants and people believe that the blossoming of those plants draws out rain. Once the monsoons set in, field work is carried out in earnest and the work of uprooting and transplanting paddy in flooded terrace fields is done. The months of hard labour are June, July and August. In August, as the phrogü plant begins to bloom, a rain will fall. this August rain, also called phrogü, is a sign that the time for cultivation is over. If any new grain seeds are sown, they may not sprout; even if they do sprout, they are not likely to bear grain. The rain acts as a kind of farmer's almanac.
7. The urban population of school-goers and office-goers naturally dislikes the monsoon and its accompanying problems of landslides, muddy streets and periodic infections. For non-farmers, the month of September can be depressing, when the rainfall is incessant and the awareness persists that the monsoons will last out till October. One needs to have the heart of a farmer to remain grateful for the watery days, and be able to observe – from what seems to the inexperienced as a continuous downpour – the many kinds of rain. Some of the commonly known rain-weeks are named after the plants that alternately bloom in August and September. The native belief is that the flowers draw out the rain.
8. Each rain period has a job to fulfil : October rain helps garlic bulbs to form, while kümünyo rain helps the rice bear grain. Without it, the ears of rice cannot form properly. End October is the most beautiful month in the Naga hills, as the fields turn gold and wild sunflowers bloom over the slopes, all heralding the harvest. Prayers go up for protecting the fields from storms, and the rains to retreat because the grain needs to stand in the sun and ripen. The cycle nears completion a few weeks before the harvest, and the rain does retreat so thoroughly from the reaped furrows that the earth quickly turns hard. The months of rain become a distant memory until it starts all over again.
On the basis of your understanding of the above passage, complete the statements given below with the help of options that follow:
a) The rains are called after flowering plants because
(ii) flowers grow in the rainy season.
(iii) it is believed that the plants bring the rain.
(iv) flowers grow all the year round.
b) The rain is like a calendar for farmers because
(ii) it tells them the birthdays of their children.
(iii) each month has a time for plantation.
(iv) different kinds of rain tell different things.
c) People who live in cities don't like rain because
(ii) they are not bothered about the farmers.
(iii) they don't like the plants that grow during the rain.
(iv) going shopping becomes difficult.
d) People pray asking the rain the retreat because
(ii) children don't get a chance to play.
(iii) the crops need the sun and heat to ripen.
(iv) they like to pray.
Answer the following questions briefly:
e) Why do the elders want you to understand the rains in the Naga hills?
f) What does Durga Puja mean to the farmers of the Naga hills?
g) What kind of rain is called sezuo?
h) What is the occupation of more than half the population of the Naga hills?
i) How is the heart of the farmer different from that of the city person?
j) When does rain becomes a memory in the minds of the of the Naga hills?
k) Find words from the passage which mean the same as the following:
(ii) nonstop (para 7)
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
The most alarming of man’s assaults upon the environment is the contamination of air, earth, rivers, and sea with lethal materials. This pollution is for the most part irrevocable; the chain of evil it initiates is for the most part irreversible. In this contamination of the environment, chemicals are the sinister partners of radiation in changing the very nature of the world; radiation released through nuclear explosions into the air, comes to the earth in rain, lodges into the soil, enters the grass or corn, or wheat grown there and reaches the bones of a human being, there to remain until his death. Similarly, chemicals sprayed on crops lie long in soil, entering living organisms, passing from one to another in a chain of poisoning and death. Or they pass by underground streams until they emerge and combine into new forms that kill vegetation, sicken cattle, and harm those who drink from once pure wells.
It took hundreds of millions of years to produce the life that now inhabits the earth and reached a stage of adjustment and balance with its surroundings. The environment contained elements that were hostile as well as supporting. Even within the light of the sun, there were short wave radiations with power to injure. Given time, life has adjusted and a balance reached. For time is the essential ingredient, but in the modern world is no time.
The rapidity of change and the speed with which new situations are created follow the heedless pace of man rather than the deliberate pace of nature. Radiation is no longer the bombardment of cosmic rays; it is now the unnatural creation of man’s tampering with the atom. The chemicals to which life is asked to make adjustments are no longer merely calcium and silica and copper and all the rest of the minerals washed out of the rocks and carried in the rivers to the sea; they are the synthetic creations of man’s inventive mind, brewed in his laboratories, and having no counterparts in nature.
(a) On the basis of your understanding of the above passage make notes on it using headings and sub-headings. Use recognizable abbreviations (wherever necessary-minimum four) and a format you consider suitable. Also supply a title to it.
(b) Write a summary of the passage in about 80 words.
Read the passage given below :
1. To ensure its perpetuity, the ground is well held by the panther both in space and in time. It enjoys a much wider distribution over the globe than its bigger cousins and procreates sufficiently profusely to ensure its continuity for all time to come.
(ii) in the branches of the trees
(iii) behind the tree trunks
(iv) at its heels
(ii) trains its cubs
(iii) watches the progress of the mother
(iv) is impulsive and impatient
Answer the following questions briefly :
(ii) came down / fell (para 7)
Read the following extract and answer the questions given below:
The Jahangir Art Gallery, the State Bank of lndia building and the canteen close by which offered affordable fare, the amazing street fare, bhelpuri and vadapav. The joy of reading Bombay Times with its page 3 people one would never meet but who seemed like old friends. The Strand bookstore where one could browse for hours. And just when a book was longingly but firmly put down from nowhere, Mr Shanbagh would materialise magically at one's elbow with a special price. Not to forget the joys of trawling the booklined pavements at Fountain, where one could watch the world go by. And wherever I chose to go, there was always my friend, the sea, oh. I loved her, in all her moods, but especially in the monsoon when violent and enraged she splattered Worli seaface with walls of sea spray. My friends are lost, some passed away, some moved away, there were many whose names I never found out, though we took the train together, or met in the lift, every day.
Like every migrant, I promise myself, someday I will return. I may, perhaps, return sometime, but even so, I know, "that one cannot step into the same river twice." You seduced me steadily, o Mumbai, with your glamour and bright lights. City of dreams, tinsel town. I pay tribute to you. Today, I say good-bye with a heavy heart.
(1) What does this extract focus on?
(2) Which mood of the sea did the writer like the most?
(3) How would the writer spend her free time?
( 4) According to you, how can you make your locality clean and beautiful?
(5) Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed :
(i) She splattered Worli seaface with walls of sea spray.
(Rewrite it using the Simple Present tense.)
(ii) I never found out their names though we took the train together
(Make it a Compound Sentence.)
(iii) I promise myself, someday I will return.
(Rewrite it using the modal auxiliary 'must'.)
(6) Find out the words from the extract which mean -
(i) courageously
(ii) attracted
Read the following extract and answer the questions given below :
Early risers clearly have the edge in life. By the time most of us wake up, they've been through their morning rituals, enjoyed their walk, had their tea and read the daily news. They're also likely to have made long-distance calls before dawn to those similarly inclined. Thus, by the time the sun warms up they're likely to have discussed all varieties of 'men, matters, and affairs' with a dozen people.
The upshot of these varying tendencies is that such extreme contrasts often exist in the same household. Weeks pass before the younger lot (typically late risers) and the older lot (normally early birds) come face to face. It's almost as if they live in different time zones and different countries.
All over the country, things are likely to be pretty much the same in this respect, one would think. If the man of the house, any house, decides to take a day off from work, he'd probably find his son emerging from his room at about I0 a.m. and that too in a 'rubbing-eyes' mode. After fooling around for a while the lad would probably dash off to college in a rush whilst simultaneously zipping up his jeans and sending text messages on his phone. His father would undoubtedly be left shaking his head and burying himself deeper into his newspaper.
(1) What is the extract about?
(2) How do the early risers get a headstart in life?
(3) What kind of lifestyle of the young son is reflected in the extract?
(4) According to you, why do the youngsters rise up late?
(5) Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed:
(i) He goes for his morning walk at 1 p.m.
(Rewrite it in the Present Perfect Continuous Tense.)
(ii) They live in different time zones.
(Make it a complex sentence.)
(iii) The man decides to take a day off from work.
(Rewrite it using the noun form of the underlined word.)
(6) Find out the words from the extract which mean:
(i) have a slight advantage over
(ii) coming out
Read the following extract and answer the questions given below.
|
I grew up in India in which telephones were both rare and virtually useless. When I left India in 1975 to go to the US for graduate studies, we had perhaps, 600 million residents in the country and just two million landline telephones. Having a telephone was a rare privilege: if you weren’t an important government official, or a doctor, or a journalist, you might languish in a long waiting list and never receive a phone.
Telephone were such a rarity (after all, 90% of population had access to a telephone line) that elected members of Parliament had amongst their privileges the right to allocate 15 telephone connections to whomever they deemed worthy.
And if you did have a phone, it wasn’t necessarily a blessing. I spent my high school years in Calcutta, and I remember that if you picked up your phone, you had no guarantee you would reach the number you had dialled. Sometimes you were connected to someone else’s ongoing conversation, and they had no idea you were able to hear them; there was even a technical term for it, the ‘cross - connection’ (appropriately, since these were connections that made us very cross). If you wanted to call another city, say Delhi, you had to book a ‘trunk call’ in the morning and then sit by the telephone all day waiting for it to come through; or you could pay eight times the going rate for a ‘lightning call’ = but even lightning struck slowly in India those days, so it only took half an hour instead of the usual three or four or more to be connected.
|
Questions:
(1). Why were telephones a rarity before 1975? (1)
(2) What special rights did elected members of Parliament use to have? (2)
(3) How did the author differentiate between a ‘trunk call’ and a ‘lightning call’? (2)
(4) Do you think the cellphone has made us global? (2)
(5) Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed. . (3)
(i) You could pay eight times the going rate for a ‘lighting call’. (Rewrite it using modal auxiliary showing compulsion)
(ii) I spent my high school years in Calcutta. [Rewrite it using past perfect tense]
(iii) Telephones were a rarity. [Make it a rhetorical question]
(6) Match the words in column ‘A’ with their meanings in column ‘B’. (1)
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (i) | Privilege |
(i)
|
means to reach or get |
| (ii) | Access |
(ii)
|
remedy |
| (iii) | special right |
We were an argrarian people. And my main hobby in my early teens was to wander through paddy field to see the different kinds of birds and how they nest. On the outskirts of the paddy fields, there had been many coconut trees and black palm trees. Beautifully crafted nests of the weaver-birds thookkanaam kuruvikal-would be seen dangling from the ends of palm leaves. Hundreds of these little birds would land on the paddy to squeeze the milk from the tender rice. They would come to the fields when the young stalks come out of the rise-plants. At this stage of the paddy, my father would send me to our field with a tin drum to scare these birds away. But often I have enjoyed the sight of these little birds balancing on the tender stalks and squeezing the milk out of the green rice. When the paddy is ripe enough to harvest, flocks of parrots would land there and cut the ripe stalks with their sharp beaks and fly away with the stalks dangling in their beaks. I have always liked to see this sight also.
The nest of parrots were neatly crafted holes in the trunks of palm trees. I continued to wonder how they made chose holes on the hard trunks until I saw the patient work of the woodpeckers. They were the carpenters and their long, sharp and strong beaks, chisels. They make the holes (in search of worms inside the weak spots of the trunks) and the parrots occupy them. If I heard the sound tak, tak, tak. I knew it was a woodpeckers chiselling a had trunk. I would go after him. It seems that the woodpecker is the only bird which can walk perpendicularly on the tree trunks! How beautiful the sight was! Its strong legs, red crest, the dark red stripe on the face and black beak and the tak, tak, tak sound used to captivate me
A1. Complete the following table :Choose two sentence that appropriately mention the theme of the passage :
(i) The extract deals with the techniques to scare the birds away.
(ii) The extract depicts how parrots make holes on the tree trunks.
(iii) The extract depicts the writer’s love towards the birds.
(iv) The extract deals with the activities of different birds.
A2. Complete the flow-chart :

A3. Complete the following table :

A4. Vocabulary -
Match the pairs of the words in column ‘A’ with their meaning in column ‘B’ :
| Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
| (i) dangling | (a) connected with farming |
| (ii) squeezing | (b) attract the attention |
| (iii) agrarian | (c) hanging freely |
| (iv) captivate | (d) pressing firmly |
A5. Personal response -
Suggest two measures to increase the number of birds.
A6. Grammer -
Rewrite the following sentences in the way instructed
(i) The paddy is ripe enough to harvest
(Remove ‘enough’ and rewrite the sentence.)
(ii) How beautiful the sight was!
(Rewritte as an assertive sentence)
Read the following passage and do the given activities :
A1. Fill up the blanks with virtues of dogs : (2)
(1) __________
(2) __________
(3) __________
(4) __________
| Human and dogs are inseparable for thousands of years and they are dependent on each other for protection and survival. Relationship between humans and dogs is often characterized by strong emotional bonds which run both way. Dogs are very popular as pets and companions. Dog is the ‘Man’s Best Friend’ and a family member. The dog is one of the most loyal, faithful and devotee animal. In earlier days dogs were kept mainly for hunting and guarding; now they are kept for companionship, protection and showmanship. There are millions of people all over the world who are dog lovers Puppies need more attention at the, early age. As much as possible try many methods of socialization, such as playing with them, taking them for walk, expose them to crowds, make them to obey the orders etc. |
A2. Methods of socialization of puppies are : (2)
(1) …......................
(2) …......................
(3) …......................
(4) …......................
A3. Cross out the odd man : (2)
(i) Inseparable, dependent, protection, popular.
(ii) Hunting. guarding, playing, petting.
(iii) Earlier, human, relationship, family
(iv) Often, mainly, now, emotional
A4.
(1) There are millions of people all over the world. (1)
(Pick out the determiners and write them)
(2) Puppies need more attention. (1)
(Rewrite the sentence without changing its meaning beginning with : Puppies don’t ….....)
A5. Should we ban keeping pets ? Justify. (2)
Read the following extract and answer the questions given below :
Reuben arrived at the factory. The sack buyer was about to lock up.
"Mister! Please don't close up yet." The man turned and saw Reuben, dirty and sweat-stained.
"Come back tomorrow, boy."
"Please, Mister. I have to sell the sacks now-please." The man heard a tremor in Reuben's voice and could tell he was close to tears.
"Why do you need this money so badly?"
"It's a secret."
The man took the sacks, reached into his pocket and put four nickels into Reuben's hand. Reuben murmured a quiet thank-you and ran home.
Then, clutching the tin can, he headed for the store.
"I have the money" he solemnly told the owner, pouring his coins onto the counter.
The man went to the window and retrieved Reuben's treasure. He wiped the dust off and gently wrapped it in brown paper. Then he placed the parcel in Reuben's hands.
Racing home, Reuben burst through the front door. His mother was scrubbing the kitchen range. "Here Mum!Here!" Reuben exclaimed as he ran to her side. He placed a small box in her work-roughened hand.
She unwrapped it carefully, to save the paper. A blue-velvet jewel box appeared. Dora lifted the did, tears beginning to blur her vision.
In gold tettering on a small, almond-shaped brooch was the word 'Mother'
It was Mother's Day, 1946
Dora had never received such a gift; she had no finery except her wedding ring. Speechless, she smiled radiantly and gathered her son into her arms.
(1) Why did Reuben insist on the sack buyer to buy his sacks that day only?
(2) How did the mother react when Reuben gave her the gift?
(3) In what way was Reuben's gift special to his mother?
(4) What do you plan to do on Mother's Day?
(5) Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed :
(i) I have to sell the sacks.
(Rewrite it replacing the underlined part with the modal auxiliary showing 'compulsion'.)
(ii) She smiled radiantly and gathered her son into her arms. (Use 'As soon as'.)
(iii) She unwrapped it carefully.
(Rewrite the sentences using the noun form of the underlined word.)
(6) Find out the words/phrases from the extract which mean:
(i) showing joy (ii) got back
Read the first activity, read the extract and then do all the activities:
A1. Complete the following sentence choosing the correct alternatives:
He goes for a morning walk at 1 p.m., because -
(1) ______________________________________________
(2) ______________________________________________
(a) He arrives from work past midnight.
(b) He has to stay in bed for a longer time till late morning.
(c) He has a special plan for early morning.
(d) He does not like to join the early birds' club.
|
Some people can just never wake up early. They munch their breakfast on the way to work. They have excuses ready when they reach the office late. They miss trains on a regular basis. They have never seen a sunrise or met the milkman. Until a loved one turned over a new leaf recently, she was one such late riser. Try as she might, she couldn't help pressing the snooze button a hundred times before she finally got up. She felt terrible about this tendency but there was nothing she could do about it. Come morning, She would just not be able to shrug off the desire to sleep a while more. Only when divine intervention answered her prayers recently was she able to join the early bird's club. Another relative has no plans of joining this league through. She is rather unabashed about waking up past noon on a daily basis. To be fair, her husband is a media personality who typically arrives home from work past midnight. That does indeed give them sufficient justification to stay longer in slumberland each morning. This practice does lead to certain oddities through. He goes for his 'morning' walk at 1 pm, heatwaves, and appalled onlookers notwithstanding. They once returned from a night out only to meet the neighbour's son who was off on an early morning jog! Early risers clearly have the edge in life. By the time most of us wake up, they've been through their morning rituals, enjoyed their walk, had their tea and read the daily news. They're also likely to have made long-distance calls before dawn to those similarly inclined. Thus, by the time the sun warms up they're likely to have discussed all varieties of 'men, matters, and affairs' with a dozen people. |
A2. Web :
Complete the following web :

A3. Complete the following statement :
Early risers clearly have the edge in life, because -
(1)
(2)
A4. Vocabulary :
Match the words in column 'A' with their meanings in Column 'B'.
| Column 'A' | Column 'B' |
| (1) justification | (a) dismiss |
| (2) oddities | (b) sleep |
| (3) slumber | (c) strange things |
| (4) shrug off | (d) clarification |
A5. Personal Response:
State two things that you can do to join the early birds' club.
A6. Grammar:
Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed :
(1) She felt terrible about this tendency but there was nothing she could do about it. (Rewrite the sentence using 'although'.)
(2) They have never seen a sunrise or met the milkman. (Rewrite using 'neither ... nor'.)
Read the first activity, read the extract and then do all the activities:
A1. Correct the following statements with the help of the facts from the extract :
(1) Everybody in every part of the globe would have access to administration and social care services because he or she would not be able to afford them.
(2) We would avoid boom and bust cycles and be able to surmount natural disaster with great ease.
|
To me, a world without poverty means that every person would have the ability to take care of his or her own basic life needs. In such a world, nobody would die of hunger or suffer from malnutrition. This is a goal world leaders have been calling for decades, but have never set out any way of achieving it. Today 40,000 children die each day around the world from hunger-related diseases. In a poverty-free world, no children would die of such causes. Everybody in every part of the globe would have access to education and health-care services because he or she would be able to afford them. Unlike today, the state would not be required to provide free or subsidized health-care or schooling. All state organizations created to provide free or subsidized services for the poor would no longer be required and welfare agencies, or the national welfare department. No free schools, no free hospital care, no begging in the streets. State-run safety-net programmers would have no rationale for existence because no one would live on charity anymore. State-run social security programmers, income-support programmes would be unnecessary. Social structures in a poverty-free world would, of course, be quite different from those that exist in a poverty-ridden world. But nobody would be at the mercy of anyone else, and that is what would make all the difference between a world without poverty and one riddled with it. Finally, a poverty-free world would be economically much Stronger and far more stable than the world today. one-fifth of the world's inhabitants who today live a life of extreme poverty would become income earners and income spenders. They would generate extra demand in the market to make the world economy grow. They would bring their creativity and innovations into the market-place to increase the world's productive capacity. Since nobody would ever become poor, except on a temporary and limited basis, the economy would probably not go through extreme swings. We would avoid boom-and-bust cycles and be able to surmount man-made disasters with greater ease. |
A2.
Complete the following statement :
The situation in the world without poverty would be different, because -
(1) the state need not ___________
(2) nobody __________
A3. Find out :
Find and write in the blank boxes :
One-fifth of the world's inhabitants today live a life of extreme poverty. How would they economically Stand in a poverty-free world?
| They would be income earners and income spenders |
A4. Vocabulary :
Find out the words from the extract that mean the following :
(1) calamity (2) overcome
(3) bringing new ideas (4) financially
A5. Personal Response :
Suggest at least four solutions to overcome the problems of increasing poverty.
A6. Grammar :
Rewrite the following sentences in the ways instructed :
(1) Nobody would die of hunger or suffer from malnutrition.
(Remove the negative and rewrite.)
(2) Everybody in every part of the globe would have accessed education and health-care services.
(Rewrite the above sentences beginning with 'Education'.)
Read the passage given below.
Then all the windows of the grey wooden house (Miss Hilton used to live here. She expired last week.), were thrown open, a thing I had never seen before.
At the end of the day a sign was nailed on the mango tree: FOR SALE.
Nobody in the street knew Miss Hilton. While she lived, her front gate was always locked and no one ever saw her leave or saw anybody go in. So even if you wanted to, you couldn't feel sorry and say that you missed Miss Hilton.
When I think of her house I see just two colours. Grey and green. The green of the mango tree, the grey of the house, and the grey of the high iron fence that prevented you from getting at the mangoes.
If your cricket ball fell in Miss Hilton's courtyard you never got it back. It wasn't the mango season when Miss Hilton died. But we got back about ten or twelve of our cricket balls.
The house was sold and we were prepared to dislike the new owners ever before they came. I think we were a little worried. Already we had one resident of the street who kept on complaining about us to our parents. He complained that we played cricket on the pavment; and if we were not playing cricket he complained that we were making too much noise anyway.
One afternoon, when I came back from school Pal, said, "Is a man and a woman. She pretty pretty, but he ugly like hell". I didn't see much. The front gate was open, but the windows were shut again. I heard a dog barking in an angry way.
One thing was settled pretty quickly. Whoever these people were they would never be the sort of people to complain that we were making noise and disturbing their sleep.
A lot of noise came from the house that night. The radio was going at full volume until midnight when the radio station closed down. The dog was barking and the man was shouting. I didn't hear the woman.
On the basis of your understanding the above passage complete the following statements :
(a) Nobody went into Miss Hilton's house because her front __________.
(b) Her house had only two colours, (i) __________ and (ii) __________.
(c) High iron fence did not let the boys get __________.
(d) They never got it back if their __________ fell into her courtyard.
(e) The boys were ready to dislike the __________.
(f) One resident of the street always __________.
(g) New owners of Miss Hilton's house were (i) __________ and (ii) __________.
(h) A man was shouting, a dog was barking, only __________.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
| 1. | A fisherman, enfeebled with age, could no longer go out to sea so he began fishing in the river. Every morning he would go down to the river and sit there fishing the whole day long. In the evening he would sell whatever he had caught, buy food for himself and go home. It was a hard life for an old man. One hot afternoon while he was trying to keep awake and bemoaning his fate, a large bird with silvery feathers alighted on a rock near him. It was Kaha, the heavenly bird. “Have you no one to care for you, grandpa?” asked the bird. “Not a soul.” “You should not be doing such work at your age,” said the bird. “From now on I will bring you a big fish every evening. You can sell it and live in comfort.” True to her word, the bird began to drop a large fish at his doorstep every evening. All that the fisherman had to do was take it to the market and sell it. As big fish were in great demand, he was soon rolling in money. He bought a cottage near the sea, with a garden around it and engaged a servant to cook for him. His wife had died some years earlier. He had decided to marry again and began to look for a suitable woman. |
| 2. | One day he heard the royal courtier make an announcement. Our king has news of a great bird called Kaha,” said the courtier. “Whoever can give information about this bird and help catch it, will be rewarded with half the gold in the royal treasury and half the kingdom!” The fisherman was sorely tempted by the reward. Half the kingdom would make him a prince! |
| 3. | “Why does the king want the bird,” he asked. “He has lost his sight,” explained the courtier. “A wise man has advised him to bathe his eyes with the blood of Kaha. Do you know where she can be found?” “No…I mean …no, no…” Torn between greed and his sense of gratitude to the bird, the fisherman could not give a coherent reply. The courtier, sensing that he knew something about the bird, informed the king. The king had him brought to the palace. |
| 4. | “If you have information about the bird, tell me”, urged the king. “I will reward you handsomely and if you help catch her, I will personally crown you king of half my domain.” “I will get the bird for you,” cried the fisherman, suddenly making up his mind. “But Kaha is strong. I will need help. The king sent a dozen soldiers with him. That evening when the bird came with the fish, the fisherman called out to her to wait. “You drop the fish and go and I never get a chance to thank you for all that you‘ve done for me," he said. “Today I have laid out a feast for you inside. Please alight and come in. Kaha was reluctant to accept the invitation but the fisherman pleaded so earnestly that she finally gave in, and alighted. The moment she was on the ground, the fisherman grabbed one of her legs and shouted to the soldiers hiding in his house to come out. They rushed to his aid but their combined effort could not keep Kaha down. |
| 5. | She rose into the air with the fisherman still clinging to her leg. By the time he realised he was being carried away, the fisherman was too high in the air to let go. He hung on grimly, and neither he nor Kaha was ever seen again. |
Based on your understanding of the above passage, answer the questions.
- Why did the fisherman start fishing in the river?
- How did the fisherman spend the day before he met Kaha?
- How did the fisherman betray Kaha?
- Why was the fisherman doubtful about revealing information about Kaha to the courtier?
Read the passage given below.
|
5 |
Technology is making advancements at a rapid rate but at the cost of a valued tradition - the crafts industry. The traditional crafts industry is losing a lot of its trained and skilled craftsmen. With that, the art of embellishing brass and copper utensils with fine engravings is also disappearing. The government has identified around 35 crafts as a languishing craft. |
|
10 |
The speciality of handcrafted items is their design, an association with long traditions belonging to a specific region. The word ‘handcrafted’ does not imply the involvement of dexterous human fingers or an agile mind with a moving spirit anymore. Lessening drudgery, increasing production and promoting efficiency have taken precedence. The labour-saving devices are taking the place of handcrafted tools and this has jeopardized the skills of these artisans. |
|
15 |
Mechanisation has made its way into everything - cutting, polishing, edging, designing etc. Ideally, the use of machinery should be negligible and the handicrafts should be made purely by hand with a distinguishable artistic appeal. However, with the exception of small-scale industries, the export units are mostly operated by machines. The heavily computerised designs contribute to faster production at lower costs. |
|
20 |
Although mechanization of crafts poses a challenge to safeguarding traditional crafts, the artisans are lured with incentives in order to impart handicrafts training. Some makers do see machines as a time-saving blessing since they are now able to accomplish difficult and demanding tasks with relative ease. These machines might give a better 25finesse to these products but they don’t stand out as handcrafted. The quantity has overtaken quality in this industry. |
|
30 |
A need to highlight the importance of the handmade aspect is required by both the government and private sectors, in order to amplify awareness and also support the culture of making handicrafts. A few artisans are still trying their best to rejuvenate and revive their culture and heritage but it’s an uphill task competing with the machine-made goods. A multitude of artisans have changed their professions and are encouraging their progeny to follow suit. There are others who have stayed their ground but are clearly inclined towards buying machines. |
|
35 |
Nearly two decades ago, there were around 65 lakh artisans in the country. Three years ago, when the government started the process of granting a unique number to the artisans based on the Aadhaar card, 25 lakhs were identified. Loss of traditional crafts is clearly a worrying issue, but it stands to reason that forcing any artisan to follow old ways when concerns of livelihood overrule other considerations, is unfair. |
Based on your understanding of the passage, answer the questions given below.
- What does the writer mean by calling handicrafts a ‘valued tradition’?
- Rewrite the following sentence by replacing the underlined phrase with a word that means the same from lines 5-15.
If it continues, the workcation (work + vacation) trend will be a powerful boost to domestic tourism operators failing to make progress in the economic slump caused due to the pandemic. - State any two reasons why artisans are choosing to work via machines rather than handcrafted tools.
- Why do the artisans need to be ‘lured with incentives’ to impart handicrafts training?
- List one likely impact of the support of government and private sectors towards the culture of making handicrafts.
- How does the writer justify an artist’s act of abandoning her/his traditional craft for a more lucrative option?
Read the following passage and do the activities.
A1. Complete the following sentences.
- Vegetarianism has not spread as desired because ______.
- Vegetarians are of various types ______.
|
Vegetarianism promotes a natural way of life. But despite its implicit message of universal love and nonviolence, it has not spread as it should have. This may be because it usually is an inward looking habit and is best cultivated in the mind. Leading a vegetarian way of life helps the animal kingdom to coexist with man. The animals supply milk, manure and energy. This has been central to Indian culture for thousands of years. A vegetarian lifestyle is natural, multifaceted and helps preservation in a healthy way. Food and health are closely related. Vegetarians are of various types. There are lacto-vegetarians who consume dairy products; Lacto-ovo-vegetarians include eggs in addition to dairy products. Vegans are pure vegetarians who do not consume any food derived from animals. The Western science of food considers food as something to sustain only the human body, whereas Indian science considers food as something which sustains not only the body, but also maintains the purity of heart, mind and soul. Thus, an item of food which is injurious to the mind is not considered to be fit for consumption, even if it is otherwise beneficial to the body or satisfies the taste. Indian food science does not give so much importance to protein or even to a balanced diet but it gives importance to food that increases the strength of the body and its vitality. Vegetarian foods provide an infinite variety of flavours whereas non-vegetarian foods have hardly any taste of their own. In fact, non-vegetarian foods have to be seasoned with ingredients from the vegetable kingdom to make them palatable. |
A2. What is the importance of eating vegetarian food?
A3.
- Pick out two adjectives from the given passage.
- Find words in the passage which mean the following:
- Indirect
- Tasty
A4. Convert the following sentence to negative without changing the meaning.
Leading a vegetarian way of life helps the animal kingdom to coexist with man.
A5. Why do you think vegetarianism is being promoted on a global level? Justify with your response.
Read the passage given below:
| (1) | Ratan, a global brand in Dairy products, works on a business model popularly known as, 'The Ratan Model'. This model aims to provide value for money to the customers and protect the interests of farmers simultaneously. | ||||||||||
| (2) | The Ratan model is a three-tiered structure that is implemented in its Dairy production: Firstly, Ratan acts as a direct link between milk producers and consumers that removes the middlemen. Secondly, farmers (milk producers) control procurement, processing and marketing. Thirdly, it is a professionally managed organization. | ||||||||||
| (3) | One can understand the Ratan Model better by taking cognizance of 'Ratan's Target Audience', where it has targeted the mass market of India with no premium offerings and works on providing the best quality products at affordable prices. | ||||||||||
| (4) | So Ratan formulates its pricing policy on the low cost price strategy which has attracted a lot of customers in the past and it continues to do so. | ||||||||||
| (5) | Another stance used by Ratan's Target Audience is based on customer-wise targeting and industry wise targeting. This strategy divides the target audience on the following two bases : | ||||||||||
| (6) |
The above table showcases how Ratan has a diversified customer base. |
||||||||||
| (7) | Industry Based Target Audience: Ratan has segmented milk for various industries such as ice-cream manufacturers, restaurants, coffee shops, and many similar industries. Further, it has segmented butter, ghee and cheese for bakeries, snack retailers, confectioneries, and many more. | ||||||||||
| (8) | The target audience study tells us that Ratan has a strong presence in both Business to Business and Businessto-Customers. | ||||||||||
| (9) | Ratan's marketing campaigns and strategies are implemented in a very attractive way. For example, the story of the 'Ratan Girl' is a popular 'ad' icon. It is a hand drawn cartoon of a young girl. | ||||||||||
Based on your understanding of the passage answer any Six out of the Seven questions given below:
- What does 'The Ratan Model' aim at?
- In dairy production how many tiers are there?
- Ratan acts as a direct link...? Explain.
- "Ratan Target audience is described as a diversified market. Explain with reference to the given table.
- Name the two basis on which Ratan divides the target audience.
- In which two spheres does Ratan have a strong presence?
- Which is the most loved ad icon of Ratan?
Read the following table displaying the details of five House Captains.
| Name | Motto | Participation in activities | Achievements | Awards | Personal Qualities | Drawbacks | Other notable things |
| Rohit | "Together we can achieve greatness" | Debate club, Quiz club | 1st prize in Science Olympiad | Best Student | Diligent, confident, empathetic | Sometimes tends to be overly competitive | Volunteer at a local NGO |
| Sanya | "Service before self" | Social service club, Drama club | 1st prize in Debate competition | Best Orator | Compassionate, organized, responsible | Can be overly self critical at times | Participated in a Model United Nations conference |
| Rajat | "Never give up, always rise up" | Sports club, Music club | 2nd position in Chess competition | Best Sportsperson | Perseverant, team player, adaptable | Can sometimes be indecisive | Plays in a local band |
| Aryan | "Success through hard work" | Photography club, Science club | 1st prize in a Photography competition | Budding Innovator | Creative, curious, detail oriented | Can sometimes procrastinate | Built a working model of a wind turbine for a science fair |
| Ananya | "Strive for excellence" | "Dance club, Art club | 1st prize in Art competition | Creative Mind | Confident, hardworking, imaginative | Tends to overthink things | Published her own poetry collection |
Answer the following questions, based on the table above.
(i) Identify the person who is likely to ask many "why" questions, and support your choice with one reason. (2)
(ii) Which house captain is most likely to struggle the most with handling stress during the school's annual inter-house sports tournament? (1)
- Rohit
- Sanya
- Rajat
- Ananya
(iii) Give two justifications for Sanya being the best fit to lead a school-wide initiative to promote mental health and well-being among students. (2)
(iv) Select the correct option to fill the blank and complete the analogy. (1)
______ : paint brush :: Rajat : tabla
- Rohit
- Sanya
- Aryan
- Ananya
(v) Based on the personal qualities of the House Captains, why is Rajat the most likely to be a collaborative worker? (1)
(vi) Complete the given sentence with the appropriate reason, with reference to the information in the table. (1)
We can infer that Aryan’s overall performance may be negatively impacted by his weakness in time management because ______.
(vii) Explain briefly why situation (b), from the three situations given below, showcases Ananya's motto, "Lead by example"? (1)
- During a group project, Ananya assigns each team member specific tasks and sets a high standard for the project's quality. She tells them to actively participate in the project and take it to fruition.
- During a house debate competition, Ananya notices that a few of her house members are struggling to articulate their arguments effectively. Ananya takes the time to listen to their concerns and provides constructive feedback and support.
- During a fundraising event, Ananya volunteers to be in charge of organizing and coordinating the event but she frequently delegates tasks to others and attends to her school assignment while her team completes the task successfully.
(viii) Select the option that correctly matches the House Captains (a) -(c), to the trophies (i)-(v). (1)
| House Captains | (a) Rajat | (b) Ananya | (c) Aryan |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (v) |
- (a) - (ii) , (b) - (i) , (c) - (iii)
- (a) - (i) , (b) - (v) , (c) - (iv)
- (a) - (v) , (b) - (iii) , (c) - (ii)
- (a) - (iii) , (b) - (iv) , (c) - (i)
Read the following text.
| (1) | In recent years, there has been a surge in both group and solo travel among young adults in India. A survey conducted among young adults aged 18-25 aimed to explore the reasons behind their travel preferences and recorded the percentage variation for 10 common points that influence travel choices. |
| (2) | Among those who prefer solo travel, the most common reason cited was the desire for independence and freedom (58%), followed closely by the opportunity for introspection and self-discovery (52%). Additionally, solo travellers appreciated the ability to customize their itinerary to their preferences (44%) and the chance to meet new people on their own terms (36%). |
| (3) | On the other hand, those who prefer group travel often cited the desire for socializing and making new friends (61%) as their primary reason. Group travel also provided a sense of security and safety in unfamiliar places (52%) and allowed for shared experiences and memories with others (48%). Additionally, group travellers enjoyed the convenience of having pre-planned itineraries and organized transportation (38%). |
| (4) | Interestingly, both groups had similar levels of interest in exploring new cultures and trying new experiences (40% for solo travellers, 36% for group travellers). Similarly, both groups valued the opportunity to relax and escape from the stresses of everyday life (36% for solo travellers, 32% for group travellers). |
| (5) | However, there were also some notable differences between the two groups. For example, solo travellers placed a higher priority on budget-friendly travel options (38%) compared to group travellers (24%). Conversely, group travellers were more likely to prioritize luxury and comfort during their travels (28%) compared to solo travellers (12%). |
| (6) | Overall, the survey results suggest that both group and solo travel have their own unique advantages and appeal to different individuals, based on their preferences and priorities. |
Answer the following questions, based on given passage.
- Infer two possible ways that the survey, mentioned in paragraph (1) could be beneficial. Answer in about 40 words. (2)
- Which travel choice point of the survey would influence tour operators to incorporate group dinners, social events, and shared accommodations in their itinerary? (1)
- Freedom to customise itinerary
- Luxury and comfort
- Security and safety
- Desire for making new friends
- What do the top choices in the survey, for travelling solo and in a group suggest about young adults? (1)
- Identify the solo traveller from the following three travellers: (1)
- Reshma- I don’t want to keep hunting for rickshaws or taxis. A pre-booked vehicle is perfect.
- Nawaz-I’m happy sharing a room in a hostel. I don’t need hotel accommodation.
- Deepak-I’m not worried about my well-being, even while exploring remote areas.
- Which of the following is an example of an opportunity for self-discovery, as mentioned in paragraph 2? (1)
- Trying new cuisine
- Hiring a tour guide
- Purchasing local artifacts
- Advance booking travel tickets
- How might the differences in budget priorities between solo and group travellers impact the types of accommodations and activities offered by the travel industry in India? (2)
- Complete the sentence appropriately. The similarities in the percentage of both solo and group travellers who are interested in exploring new cultures and trying new experiences may be due to ______. (1)
- State TRUE or FALSE. (1)
The title, "Wanderlust: The Solo Travel Trend Among Young Adults in India", is appropriate for this passage.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
| 1. | The man with the white face entered the carriage at Rugby. He moved slowly in spite of the urgency of his porter, and even while he was still on the platform I noted how ill he seemed. He dropped into the corner over against me with a sigh, made an incomplete attempt to arrange his travelling shawl and became motionless, with his eyes staring vacantly. Presently he was moved by a sense of my observation, looked up at me, and put out a spiritless hand for his newspaper. Then he glanced again in my direction. I feigned to read. I feared I had unwittingly embarrassed him, and in a moment I was surprised to find him speaking. |
| 2. | "I beg your pardon?" said I. "That book," he repeated, pointing a lean finger, "is about dreams." "Obviously," I answered, for it was Fortnum Roscoe's Dream States, and the title was on the cover. He hung silent for a space as if he sought words. "Yes," he said at last, "but they tell you nothing." I did not catch his meaning for a second. "They don't know," he added. I looked a little more attentively at his face. "There are dreams," he said, "and dreams." That sort of proposition I never dispute. "I suppose--" he hesitated. "Do you ever dream? I mean vividly." "I dream very little," I answered. "I doubt if I have three vivid dreams in a year." "Ah!" he said and seemed for a moment to collect his thoughts. "Your dreams don't mix with your memories?" he asked abruptly. "You don't find yourself in doubt; did this happen or did it not?" "Hardly ever. Except just for a momentary hesitation now and then. I suppose few people do." "Does he say--?" He indicated the book. "Says it happens at times and gives the usual explanation about intensity of impression and the like to account for its not happening as a rule. I suppose you know something of these theories--" "Very little--except that they are wrong." |
| 3. | His emaciated hand played with the strap of the window for a time. I prepared to resume reading, and that seemed to precipitate his next remark. He leant forward almost as though he would touch me. "Isn't there something called consecutive dreaming--that goes on night after night?" "I believe there is. There are cases given in most books on mental trouble." "Mental trouble! Yes. I daresay there are. It's the right place for them. But what I mean--" He looked at his bony knuckles. "Is that sort of thing always dreaming? Is it dreaming? Or is it something else? Mightn't it be something else?" |
| 4. | I should have snubbed his persistent conversation but for the drawn anxiety of his face. I remember now the look of his faded eyes and the lids red stained--perhaps you know that look. "I'm not just arguing about a matter of opinion," he said. "The thing's killing me." "Dreams?" "If you call them dreams. Night after night. Vivid!—so vivid . . . this--" (he indicated the landscape that went streaming by the window) "seems unreal in comparison! I can scarcely remember who I am, what business I am on . . . ."He paused. "Even now--" "The dream is always the same--do you mean?" I asked. "It's over." "You mean?" "I died." "Died?" |
| 5. | "Smashed and killed, and now, so much of me as that dream was, is dead. Dead forever. I dreamt I was another man, you know, living in a different part of the world and in a different time. I dreamt that night after night. Night after night I woke into that other life. Fresh scenes and fresh happenings--until I came upon the last--" "When you died?" "When I died." "And since then--" "No," he said. "Thank God! That was the end of the dream.. . " |
| 6. | It was clear I was in for this dream. And after all, I had an hour before me, the light was fading fast, and Fortnum Roscoe has a dreary way with him. "Living in a different time," I said: "do you mean in some different age?" "Yes." "Past?" "No, to come--to come." "The year three thousand, for example?" "I don't know what year it was. I did when I was asleep, when I was dreaming, that is, but not now--not now that I am awake. There's a lot of things I have forgotten since I woke out of these dreams, though I knew them at the time when I was--I suppose it was dreaming. They called the year differently from our way of calling the year . . . What did they call it?" He put his hand to his forehead. "No," said he, "I forget." He sat smiling weakly. For a moment I feared he did not mean to tell me his dream. As a rule, I hate people who tell their dreams, but this struck me differently. I proffered assistance even. "It began--" I suggested. |
| 7. | "It was vivid from the first. I seemed to wake up in it suddenly. And it's curious that in these dreams I am speaking of I never remembered this life I am living now. It seemed as if the dream life was enough while it lasted. Perhaps--But I will tell you how I find myself when I do my best to recall it all. I don't remember anything clearly until I found myself sitting in a sort of loggia looking out over the sea. I had been dozing, and suddenly I woke up--fresh and vivid--not a bit dreamlike—because the girl had stopped fanning me." |
On the basis of your reading of the above excerpt, choose the correct option to answer the following questions:
- How did the man with the white face behave as he entered the carriage? (1)
- Excited and enthusiastic
- Scared
- Excited and nervous
- showed no enthusiasm
- What was the name of the book which the narrator was reading? (1)
- Fortnum Roscoe's Dream States
- Dream States
- Dreams of the States
- State of the Dream
- What was the man’s opinion about the theory of dreams given in the narrator’s book? (1)
- He felt that it was all correct.
- He felt the book painted a wrong picture.
- He felt that the book explained nothing.
- He felt that the book was confusing.
- Statement 1: The narrator couldn’t snub the man’s conversation.
Statement 2: The man with the white face looked anxious. (1)
- Both 1 & 2 are correct and 2 is the reason for 1.
- Both 1 & 2 are correct and 2 is not the reason for 1.
- 1 is correct and 2 is incorrect.
- Both 1 & 2 are incorrect.
- What is NOT the reason for narrator being interested in listening to the man’s description of his last dream? (1)
- The man’s dream was about an alien.
- It was getting dark.
- The narrator had still an hour’s journey left.
- His book was getting boring.
- What did the man NOT say about the last dream which he had? (1)
- It was a dream which wasn’t clear.
- He was sitting in the loggia.
- His last dream was very clear.
- He would wake up in these dreams suddenly.
- Which of the following is NOT true for the Man with the white face? (1)
- He moved around slowly.
- He looked sickly.
- He didn’t want to talk about his dream.
- He didn’t believe in theories of Fortnum Roscoe's Dream States.
- "I dream very little," I answered. "I doubt if I have three vivid dreams in a year. This line highlights that the narrator did not – (1)
- Have normal dreams.
- Good sleep pattern.
- Give much importance to the science behind dreams.
- like talking to the man with the white face.
- How does the use of vivid and descriptive language in the passage enhance the reader's understanding of the man's experience? (1)
- Complete the sentence appropriately. (1)
It is fair to say that the man's experience of consecutive dreaming is similar with being lost in a maze because ______. - Choose the right answer which explains the phrase: (1)
He hung silent for a space as if he sought words.
- he was at a loss of words.
- he was indecisive.
- he was left hanging because of his indecisiveness.
- he stayed silent for some time as if he searched for words.
- State whether the following opinion is TRUE or FALSE. (1)
The author implies that memory and consciousness are not objective, but rather are shaped by our subjective experiences and perceptions. - What does the man with the white face, most likely mean by "there are dreams, and dreams"? (Reference - paragraph 2) (1)
- What do the man's "vacant" stare and "spiritless" hand suggest about his condition? (1)
- In paragraph 2, the narrator says, “I did not catch his meaning for a second.”
Which of the following expressions correctly display the usage of “catch”? (1)- catch a glimpse
- catch a hunger
- catch an anger
- catch a skill
Read the passage given below.
|
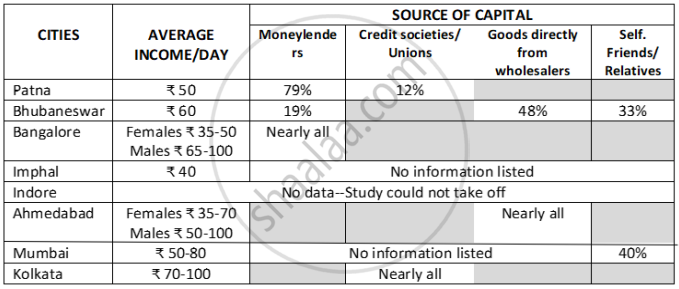
Most cities, may not be prohibit hawking as a profession, but do place restrictions on the use of urban space. Therefore, a comprehensive study was conducted in 1998-99 on street vending, to provide concrete data for furthering the cause of the hawkers. Eight cities were selected - Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, Imphal, Patna, Bhubaneswar and Bangalore. Three points were important while selecting respondents –hawkers were from different parts of a city; sold a variety of goods and adequate numbers of women were covered. The questionnaire was included questions on personal details, details regarding the work and the hazards faced. Table: Results of the survey
It is fair to say that hawkers cannot be removed, because apart from their own livelihood, their services benefit the common urban dweller. |
Based on your understanding of the passage, answer the given questions.
- Fill in the blank by selecting the appropriate option. 1
The study aims to ______ the practice of street vending in urban spaces.
- support
- discourage
- understand
- prove
- Jagan goes door to door with his basket of goods to sell bananas in the city. What action from his end would lead to a prohibition on hawking? 1
- State TRUE or FALSE. 1
The following question could have been a part of the study survey.
What are the challenges presented by the security guards? - Complete the sentence appropriately. 1
The most preferred form of source of capital, according to the survey table, exposes the hawkers to exploitation because ______. - State a point in support for the given opinion: 1
Street vending must be legalised as a profession.
Read the passage given below:
| (1) | Seagulls, as you know, never falter, never stall. To stall in the air is for them a disgrace and a dishonour. But Jonathan Livingston Seagull, unashamed, stretching his wings again in that trembling hard curve – slowing, slowing, and stalling once more –was no ordinary bird. Most gulls don't bother to learn more than the simplest facts of flight – how to get from shore to food and back again. For most gulls, it is not flying that matters, but eating. For this gull, though, it was not eating that mattered, but flight. More than anything else, Jonathan Livingston Seagull loved to fly. |
| (2) | This kind of thinking, he found, is not the way to make oneself popular with other birds. Even his parents were dismayed as Jonathan spent the whole day alone, making hundreds of low-level gliders, experimenting. "Why, Jon, why?" his mother asked. "Why is it so hard to be like the rest of the flock, Jon? Why can't you leave low flying to the pelicans, the albatross? Why don't you eat? Son, you're bone and feathers!" "I don't mind being bone and feathers, Mom. I just want to know what I can do in the air and what I can't, that's all. I just want to know." "See here Jonathan," said his father, not unkindly. "Winter isn't far away. Boats will be few, and the surface fish will be swimming deep. If you must study, then study food, and how to get it. This flying business is all very well, but you can't eat a glide, you know. Don't you forget that the reason you fly is to eat?" |
| (3) | Jonathan nodded obediently. For the next few days, he tried to behave like the other gulls; he really tried, screeching and fighting with the flock around the piers and fishing boats, diving on scraps of fish and bread. But he couldn't make it work. It wasn't long before Jonathan Gull was off by himself again, far out at sea, hungry, happy, learning. The subject was speed and in a week's practice he learned more about speed than the fastest gull alive. Time after time it happened. Careful as he was, working at the very peak of his ability, he lost control at a high speed. The key, he thought at last, dripping wet, must be to hold the wings still at high speeds – to flap up to fifty and then hold the wings still. |
| (4) | From two thousand feet he tried again, rolling into his dive, beak straight down, wings full out and stable from the moment he passed fifty miles per hour. It took tremendous strength, but it worked. In ten seconds he had blurred ninety miles per hour. Jonathan had set a world speed record for seagulls! But victory was short-lived. The instant he began his pullout, the instant he changed the angle of his wings, he snapped into the same uncontrollable disaster, and at ninety miles per hour, it hit him like dynamite. Jonathan Seagull exploded in midair and smashed down into a brick-hard sea. As he sank low in the water, a strange hollow voice sounded within him. There's no way around it. I am a seagull. I am limited by my nature. If I were meant to learn so much about flying, I'd have charts for brains. If I were meant to fly at speed, I'd have a falcon's short wings. Short wings. A falcon's short wings! That's the answer! What a fool I've been! All I need is a tiny little wing, all I need is to fold most of my wings and just fly on the tips along. Short wings! |
Based on your understanding of the passage, answer the questions given below:
- Complete the sentence by choosing an appropriate option: (1)
Majority of seagulls fly only short distances as ______.- they are more interested in food than flight
- they don't have energy
- they are not meant to fly low
- food is not available at high speed
- Why were Jonathan Livingston's parents' dismayed? (1)
- Give two reasons for Jonathan's unconventional behaviour. (1)
(Clue: think about Jonathan's point of view.) - Select the option that conveys the opposite of 'glory' from the words used in paragraph 1. (1)
- disgrace
- dishonour
- learning
- unashamed
- The writer would not agree with the given statements based on paragraph 2, EXCEPT (1)
- Jonathan could not fly but only glide.
- Jonathan wanted to be popular with other birds.
- Jonathan realised that even the albatross flew at high altitudes.
- The reason seagulls flew was to find food.
- Jonathan was different, from other seagulls. Based on your understanding of paragraph 2, list what Jonathan wanted to know. (1)
- What was the mother's concern about Jonathan? (1)
- Complete the given sentence with an appropriate inference with respect to the following: (1)
Father reminds Jonathan that he 'can't eat a glide' in order to ______. - It, wasn't long before Jonathan Gull was off by himself again, far out at sea. Which trait of Jonathan does this statement reveal? (1)
- practical bird
- persistent learner
- lonely and sad
- carefree and irresponsible
- Was it fair to fly like a falcon when he was just a seagull? Why does he say so? (1)