Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain about domestic electric circuits. (circuit diagram not required)
उत्तर
In our homes, electricity is distributed through the domestic electric circuits wired by the electricians. The first stage of the domestic circuit is to bring the power supply to the main box from a distribution panel, such as a transformer. The important components of the main box are: (i) a fuse box and (ii) a meter. The meter is used to record the consumption of electrical energy. The fuse box contains either a fuse wire or a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB). The function of the fuse wire or an MCB is to protect the household electrical appliances from overloading due to excess current.
An MCB is a switching device, which can be activated automatically as well as manually. It has a spring attached to the switch, which is attracted by an electromagnet when an excess current passes through the circuit. Hence, the circuit is broken and the protection of the appliance is ensured.
The electricity is brought to houses by one wire that has red insulation and is called the ‘live wire’. The other wire has black insulation and is called the ‘neutral wire’. The electricity supplied to your house is actually an alternating current having an electric potential of 220 V. Both, the live wire and the neutral wire enter into a box where the main fuse is connected with the live wire. After the electricity meter, these wires enter into the main switch, which is used to discontinue the electricity supply whenever required. After the main switch, these wires are connected to live wires of two separate circuits.
Out of these two circuits, one circuit is of a 5 A rating, which is used to run the electric appliances with a lower power rating, such as tube lights, bulbs, and fans. The other circuit is of a 15 A rating, which is used for two insulated wires. Out of these two wires, run electric appliances with a high power rating, such as air-conditioners, refrigerators, electric iron, and heaters. It should be noted that all the circuits in a house are connected in parallel so that the disconnection of one circuit does not affect the other circuit. One more advantage of the parallel connection of circuits is that each electric appliance gets an equal voltage.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw circuit symbols for
a cell
Draw circuit symbols for
a battery of three cells
Resistances R1, R2, R3 and R4 are connected as shown in the figure. S1 and S2 are two keys. Discuss the current flowing in the circuit in the following cases.
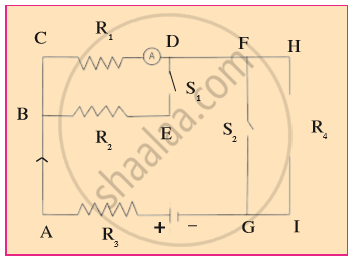
- Both S1 and S2 are closed.
- Both S1 and S2 are open.
- S1 is closed but S2 is open.
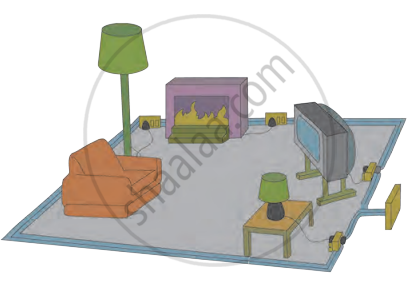
The accompanying figure shows some electrical appliances connected in a circuit in a house. Answer the following questions.
- By which method are the appliances connected?
- What must be the potential difference across individual appliances?
- Will the current passing through each appliance be the same? Justify your answer.
- Why are the domestic appliances connected in this way?
- If the T.V. stops working, will the other appliances also stop working? Explain your answer.
In an electric circuit, electron flow a from of point of ______ potential to the point of ______ potential.
A battery is to be formed by joining 3 dry cells with connecting wires. Show how will you connect the wires by drawing a diagram.
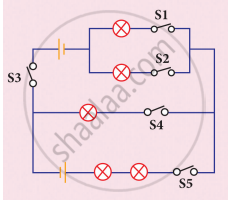
Study the electric circuit below. Which of the following switches should be closed so that only two bulbs will light up
What is electric circuit?
What are the types of electric circuits?
A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to become hot. As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire
